WEEK 6
advertisement

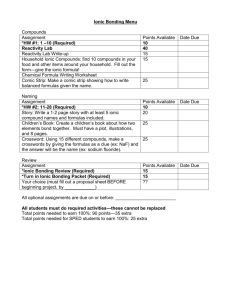
Honors Chemistry Week-At-A-Glance WEEK 6 Goal: SC4 Periodicity (Summative Assessment 9/17/12) https://sites.google.com/site/harrisonhighchemistrytarvin/ Monday, 9/17 Tuesday, 9/18 Wednesday, 9/19 Thursday, 9/20 Friday, 9/21 Essential Question: How is the periodic table organized? Essential Question: How can a compound made up of ions be neutral? Essential Question: How can a compound made up of ions be neutral? Essential Question: How can a compound made up of ions be neutral? Essential Question: How can a compound made up of ions be neutral? Standard: SC4b: Compare and contrast the trends in the chemical and physical properties of elements and their placement on the Periodic Table. SC4a: Use the Periodic Table to predict periodic trends including atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization energy, and electronegativity of various elements. Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas Objectives: Identify the locations and properties of assigned families of elements Investigate properties of ionization energy, electronegativity, and atomic radius Apply concepts from last unit to periodic table Objectives: Review how cations and anions are formed in reference to stability Criss-cross ion charges to write formulas for stable, neutral ionic compounds Objectives: Continue to criss-cross ion charges to write formulas for ionic compounds Begin to name ionic compounds Objectives: Continue to criss-cross ion charges to write formulas for ionic compounds Continue to name ionic compounds Focus naming practice on compounds containing transition metals which require Roman numerals Objectives: Continue to criss-cross ion charges to write formulas for ionic compounds Continue to name ionic compounds Focus naming practice on compounds containing transition metals which require Roman numerals Summative Assessment: Unit Three Periodicity test Opening Activity: Periodicity Test results Collaborative Activity: Small group brainstorm sessions about the formation of an assigned ion Visual/Auditory Activity: Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds Homework: Practice Problem Packet “More Binary & Ternary Compounds” Opening Activity: Cumulative Quiz Visual/Auditory Activity: Naming Ionic Compounds and Writing Formulas from Names Visual/Auditory Activity: Using Roman Numerals when Naming Ionic Compounds Collaborative Homework: Practice Problem Packet “Compound Names and Formulas” Opening Activity: Selfmonitoring progress on formula-writing homework Kinesthetic Activity: Ionic Compound Lab Homework: Use flashcards to prepare for the Polyatomic Ion Quiz Collaborative Activity: Practice writing names and formulas using no ion sheet assistance Exit Questions: Ionic compounds and names Homework: Additional periodic trends practice Make flashcards for polyatomic ions Honors Chemistry Week-At-A-Glance WEEK 7 Goal: SC1 Bonding Monday, 9/24 (Summative Assessment 10/3/12) https://sites.google.com/site/harrisonhighchemistrytarvin/ Tuesday, 9/25 Wednesday, 9/26 Thursday, 9/27 Friday, 9/28 Essential Question: How are compounds formed from only nonmetals? Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas SC3e Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds Objectives: Evaluate mistakes on ionic compound quiz Assess knowledge of polyatomic ions Introduce formulas and naming of covalent compounds Essential Question: How are compounds formed from only nonmetals? Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas SC3e Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds Objectives: Writing formulas and naming of covalent compounds Writing formulas and naming acids Introduce basic Lewis structures Essential Question: How are compounds formed from only nonmetals? Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas SC3e Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds Objectives: Review basic Lewis structures Draw advanced Lewis structures Apply electronegativity concepts to Lewis structures to predict polarity Use polarity to predict type of intermolecular forces Formative Assessment: Polyatomic Ion Quiz DUE: Forming Ionic Compounds Lab Report Formative Assessment: Ionic Naming and FormulaWriting Quiz Visual/Auditory Activity: Introduce Covalent Compound Formulas and Names Visual/Auditory Activity: Drawing Lewis Structures Formative Assessment: Ionic Naming and FormulaWriting Quiz Guided Practice Activity: Writing formulas and names for acids Visual/Auditory Activity: Drawing advanced Lewis structures and predicting the polarity of the compound Guided Practice: Practice problems packet Visual/Auditory Activity: VSEPR Bonding Theory Visual/Auditory Activity: Predicting the Intermolecular Forces within samples of the compound HW: Practice Problems Packet HW: Practice problems packet HW: Chemical Formulawriting and Nomenclature; Lewis Structure Worksheet Essential Question: How are compounds formed from only nonmetals? Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas SC3e Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds Objectives: Assess basic Lewis structures Apply electronegativity concepts to Lewis structures to predict polarity Use polarity to predict type of intermolecular forces Build models of covalent compounds to predict VSEPR geometry Formative Assessment: Covalent & Acid Naming and Formula-Writing Quiz Visual/Auditory Activity: VSEPR Bonding Theory Kinesthetic Activity: Ball & Stick Model kits HW: 8-1 Practice Problems Essential Question: How are compounds formed from only nonmetals? Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas SC3e Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds Objectives: Assess basic Lewis structures Apply electronegativity concepts to Lewis structures to predict polarity Use polarity to predict type of intermolecular forces Build models of covalent compounds to predict VSEPR geometry Formative Assessment: Combined Ionic, Covalent, and Acid Quiz Kinesthetic Activity: Comparing Properties of Ionic and Covalent Solids Lab Critical Thinking Activity: Higher Order Thinking Stations for Ionic and Covalent Compounds HW: Practice Problems Packet Honors Chemistry Week-At-A-Glance WEEK 8 Goal: Reactions (Summative Assessment 10/3/12) https://sites.google.com/site/harrisonhighchemistrytarvin/ Monday, 10/1 Tuesday, 10/2 Wednesday, 10/3 Thursday, 10/4 Friday, 10/5 Essential Question: What are the physical and chemical properties of ionic compounds? Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas SC3e Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds Objectives: Analyze formulas to discover rare ion charges and use them to write formulas Continue to name ionic compounds Experimentally observe the formation and properties of ionic compounds Formative Assessment: Combined Ionic, Covalent, Acid Quiz Critical Thinking Activity: Critical Thinking Partner Stations HW: Practice Problem Packet Essential Question: What are the physical and chemical properties of ionic compounds? Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas SC3e Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds Objectives: Analyze formulas to discover rare ion charges and use them to write formulas Continue to name ionic compounds Experimentally observe the formation and properties of ionic compounds Critical Thinking Activity: Unit Four Review Webquest Essential Question: What is the difference between ionic and covalent compounds? Essential Question: How are compounds formed from only nonmetals? Essential Question: How are chemical reactions represented? Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas SC3e Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds Objectives: Apply ionic and covalent compound objectives Analyze difficult compounds Compare and contrast ionic and covalent compounds Standard: SC1c: Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds based on balance of charges. SC1d: Use IUPAC nomenclature for both chemical names and formulas SC3e Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds Objectives: Writing formulas and naming of covalent compounds Writing formulas and naming acids Introduce basic Lewis structures Standard: SC2a: Identify and balance synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, and combustion equations. Unit Four Bonding Review Stations Summative Assessment: Unit Four Bonding Test HW: Practice Problem Packet Cumulative Quiz #3 Results of Unit Four Bonding Test Visual/Auditory Activity: Writing and balancing chemical equations from word equations notes Collaborative Practice: Writing and balancing equations with a partner (Writing Equations from Word Equations handout) Visual/Auditory Activity: Evidence of a chemical reaction notes HW: 9-2 Practice Problems (odd) Objectives: Writing chemical equations Balancing chemical equations Identifying types of chemical equations