Date Printed: 2-19-12 Weekly Lesson Plan View (by Calendar Layer
advertisement

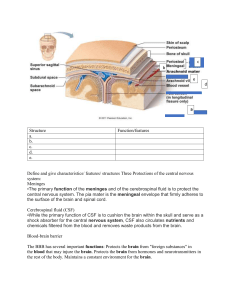
Date Printed: 2-19-12 Weekly Lesson Plan View (by Calendar Layer) - February 19, 2012 - February 25, 2012 Printed By: Lisa Cornwall CCSD - MS/HS Holidays and PD 2-20-12 Presidents' Day Observed (No School) 2-21-12 Staff Development Day Anatomy & Physiology H 2-22-12 Introduction 6.1-6.2, 6.11 IN: Sketch and label the structure of a typical neuron and describe the functions of each component.(Page 239-240 in the book) Lesson Format: PowerPoint; take notes. View Schoolhouse rock-telegraph line9nervous system); Assignment: Complete concept map on Nervous system overview. OUT: Explain the breakdown of the Peripheral Nervous System. Afferent division= Somatic sensory receptors(monitor the outside world and our position in it). Visceral sensory receptors (monitor internal conditions and the status of other organ systems). Efferent division= Somatic nervous system(skeletal muscle). Autonomic Nervous System= Parasympathetic division + Sypathetic division(smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, adipose tissue) commonly have opposite effects on one another. 2-23-12 6.1, 6.2, 6.11, 6.12 IN: Draw and explain the 3 types of neurons. (Page 2400. Lesson Format: Continue PowerPoint; Assignment: Complete concept check questions 1-3 page 244 OUT: Name and desribe the 4 types of neuroglial cells(page 242). 1. Astrocytes: are the largest and most numerous; secrete chemicals vital to the maintanence of the blood-brain barrier. 2. Oligodendrocytes: have fewer processes than astrocytes. Many are needed to coat an entire axon with myelin. Myelinated axons appear glossy white and are referred to as the white matter of the CNS. 3. Microglia: smallest and rarest. They are phagocytic cells derived from white cells that moved into the CNS as the nervous system was being formed. They perform protective functions. 4. Ependymal cells: line both the central canal of the spinal cord and the chambers of the brain, which are cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid(CSF). 2-24-12 Create sectional view of spinal cord 6.8, 6.4, IN: Draw the layers of the brain and the layers(meninges)of the spinal cord and label them. Lesson Format: Explain the layer/meninges of the brain and spinal cord; turn to page 253 and read with students. Explain activity of creating a a sectional view of the spinal cord Assignment: Create a sectional view of the spinal cord, show and explain parts to the teacher. OUT: Damage to which root of the spinal nerve would interfere with motor funtion? Ventral roots which contain the axons of the CNS motor neurons that control muscle and glands. Things needed: marshmellows(30), licorce strings, fruit snacks