Medical terminology
advertisement

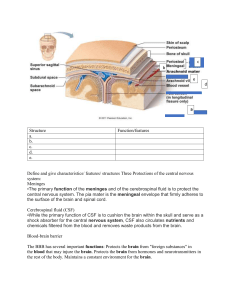
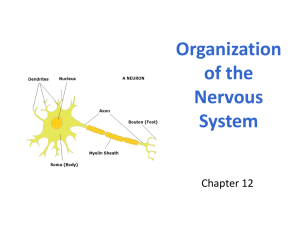
Nervous System Dr.Hannah The nervous system is a very complex system in the body. The nervous system is the body's information gatherer, storage center and control system. and is often likened to the central computer within a vast, complicated communication network Its divided into two parts Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) CNS: consists of the brain and the spinal cord PNS: includes the nerves that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord COMBINING FORM MEANING Cerebell/o Cerebellum Cerebr/o Cerebrum Encephal/o Brain COMBINING FORM MEANING Medulla oblongata Medull/o Myel/o Spinal cord Neur/o nerve Alzheimer disease: deterioration of mental capacity-which can lead to dementia. Cerebrovascular accident: damage of the blood vessels supplying brain-stroke Concussion: Blunt injury to the brain which causes loss of consciousness Epilepsy: chronic brain disorder characterized by recurrent seizure activity Glioblastoma: brain tumour from glial cells Hemiplegia: plegia-paralysis, hemione half. Usually result of stroke Meningitis: Inflammation of the meninges Multiple sclerosis: destruction of myelin sheath on nerve cells in central nervous system Paraplegia: paralysis affecting lower part of the body. Plegia-paralysis, para-one side Syncope: fainting; inadequate blood supply to the brain. (NOT the loss of the blood supply like in a stroke) Cerebral angiography: X-Ray of the brain + contrast in the artery. Computed Tomography (CT) scan: cross sectional X-Ray. Good for detecting of haemorrhage in a brain cavity Lab and Diagnostic procedures •Electroencephalography: recording of electrical activity within the brain Lumbar Puncture (LP): spinal tap procedure by which CSF is removed. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis: blood cells, glucose, cultures, Gram stain, chemical composition. Obtained through Lumbar Puncture (LP) Magnetic resonance imagine (MRI): magnetic waves and radiofrequency are used to create images Positron emission tomography (PET) scan: uptake of radiographic material into the brain shows how the brain uses glucose and gives info on how the brain functions o o o o o o o o AD CNS CSF CVA EEG LP MS TIA Alzheimer disease Central nervous system Cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrovascular accident Electroencephalography Lumbar puncture Multiple sclerosis Transient ischemic attack