4_5th Grade Physical Science Lessons 1-5
advertisement

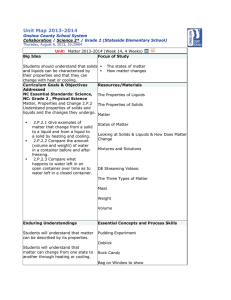
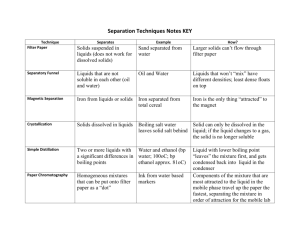
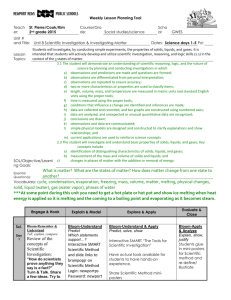
WHAT IS MATTER? Physical Science Chapter 1 Lesson 1 Mr. Etheridge Lesson 1 What is Matter? • All living and non living things are made of matter. • Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. • Mass is the amount of material that an object has it it and the amount of space the object takes up because of its mass is called volume. Matter, Mass, and Volume Physical Properties of Matter • http://www.brainpop.com/science/matterandchemistry/mat terchangingstates/ • Think about something you received for Christmas. What physical characteristics would you use to describe this gift to a friend? • A property is something about matter that can be observed and tells you what the matter is like. Physical Properties and States of Matter • Color, shape, size, and mass are some physical properties of matter. • One important property of matter is the state, or form the matter has. What are the three states of matter? Shapes of Solids, Liquids, and Gas • A solid has a shape and a volume of its own. Your desks and books are solids. • A liquid has a certain volume, but it has no shape of its own. It will take the shape of the container it is in. • A gas, like a liquid does not have a shape of its own. Unlike a liquid, gas does not have a volume of its own. Solids, Liquids, and Gas Mixtures and Solids • Matter can be mixed in very different ways. • Think about following directions in a cook book, the different ingredients you mix together are all forms of matter. • Mixture – two or more substances that are mixed together but can easily be separated. • Solution – is a mixture in which one substance spreads evenly throughout another substance. Example of Solution and Mixture Lesson 1 Review • What is matter and what are some ways you could describe matter? • What are the three states of matter? • How do the shapes and volumes of solids, liquids, and gases differ? Lesson 2 Measuring Length and Volume • Length is one property of matter • Length is used using the metric system • Centimeters = cm 1/100 of a meter • Millimeters = mm 1/1000 of a meter • Kilometers = km 1,000 meters • Volume is another property of matter that measures how much space an object takes up • Measured in cubic meters, so how many cubes fill the object • To measure the volume of a liquid you would measure in liters Volume of Solids and Liquids Continued The formula for finding volume is: Length x Width x Height = Volume A Graduated Cylinder is a tool used to measure the volume of liquids Lesson 2 Review • What is one unit used for measuring the volume of a solid? • What is the basic unit for measuring the volume of a liquid? • What measuring tool is used to measure the volume of a liquid? Lesson 3 Mass and Density • Just like length and volume, mass is a property of matter than can be measured. Mass is basically how heavy an object is. • Grams, Milligrams, and Kilograms are used to measure mass. Density • Density is another property of matter. Its how much mass is in a certain volume of matter. • If matter is more Dense it has more matter. If it is less Dense it will have less matter. The 100 mL of vinegar has a greater mass than the 100 mL of oil. Therefore the oil floats on the top and the vinegar sinks. Lesson Review • What metric units are used to measure mass? • How is density different than mass? Lesson 4 Physical Changes • Matter goes through certain changes. Sometimes those changes are fast and sometimes they are slow. • Changes in the shape, size, color are examples of a physical change. • Freezing, boiling, and melting • Physical change does not change matter into a different type of matter. So, no new substance is created. Physical Change Continued… • Crushing a can • Breaking Glass • Shredding Paper • Chopping Wood • Melting ice All of these are examples Of physical change Heating and Cooling Matter • Another way to change matter is by heating or cooling it. Heating or cooling matter to certain temperatures causes matter to change. • Melting Point – the temperature at which matter changes from a solid to a liquid. • Boiling Point – the temperature at which matter changes from liquid to a gas. • Freezing Point – the temperature at which matter changes from a liquid to a solid. Lesson 4 Review • Name 3 physical changes that can happen to material? • How does heating and cooling cause changes in matter? Lesson 5 Chemical Changes • Unlike physical change, a chemical change produces a completely different kind of matter. • Example: When we cook pancakes, a chemical change is taking place. Turn and talk to your shoulder partner to discuss this chemical change. Chemical Changes • To make pancakes we first have to mix all of the ingredients together as liquid batter. • As we pour the batter onto the griddle, it begins to cook and a gas is formed by the ingredients in the batter. • As the gas bubbles rise to the top and escape, they create tiny air pockets and the pancake begins to turn brown and solid. Rusting, Tarnishing, and Burning • Other examples of chemical changes taking place are rusting, tarnishing, and burning. Rust forms when oxygen from The air joins with iron on the surface Of this car When oxygen from the air Mixes with certain metals It can make them look dull Or discolored Oxygen and hydrogen Combine to create an Explosion shooting this Spaceship in the air Lesson 5 Review • Explain the difference between a physical and chemical change. • http://www.brainpop.com/science/matterandchemistry/propertychan ges/ • Name three examples of chemical change other than cooking.