4bonetypes
advertisement

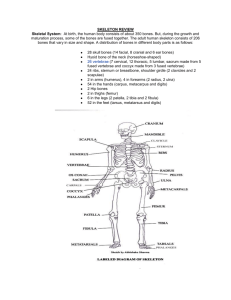
4 Types of Bones & Skeletal Organization ACOS OBJ 6.4)identifying the four bone types. 6) Identify bones that compose the skeletal system. 6.2) identifying subdivisions of the skeleton as axial & appendicular skeletons. 4 Types of Bones • 1. Long Bones: Hard dense bones that consist of a shaft & two ends. Composed mostly of compact bone. – EX: Femur, Humerus, Tibia 2. Short Bones: length and width are the close to the same. Composed mostly of spongy bone. (cube-shaped) -EX: Carpals(wrist bones), and tarsals(ankle bones) 3. Flat Bones: relatively thin and FLAT. -EX: sternum, ribs, scapula, and Cranial bones 4. Irregular Bones: Odd shaped bones -EX: Facial Skeleton, Vertebrae, and Sacrum • Examples of Long Bones Examples of Short Bones Examples of Flat Bones Examples of Irregular Bones Skeletal Organization • There are 2 major portions of the skeletal system. – 1. Axial Skeleton (Ax-?): Bony & cartilaginous parts that support & protect organs of the head neck and trunk. – 2. Appendicular Skeleton: Bones of the upper & lower limbs –Bones that anchor limbs to the axial skeleton Axial Skeleton • 1. Skull – Composed of the cranium & facial bones. 2. Hyoid Bone- located in the neck between the lower jaw & larynx. - Supports the tongue & is an attachment for certain muscles that help move the tongue during swallowing. 3. Vertebral Column ( Backbone) – Many vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. -Distal end several vertebrae fuse together to form the SACRUM - Coccyx: Located at the end of the sacrum. Axial Skeleton Continued • 4. Thoracic Cage: Protects organs of thoracic cavity & the upper abdominal cavity. – 12 Pairs of Ribs ( Articulate posteriorly w/ thoracic vertebrae & anteriorly w/ the sternum. Axial Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton • 1. Pectoral Girdle – Composed of the SCAPULA & CLAVICLE - connects the bones of upper limbs to the axial skeleton Appendicular Skeleton Continued • 2. Upper Limbs – Consist of: • 1 humerus • 2 forearm bones ( Radius & Ulna) • A Wrist ( 8 carpals) • A Hand ( 14 Phalanges) • 5 Metacarpals in the palm -Radius - Ulna - Humerus→ Articulate w/ each other at - The elbow joint Distal Upper Limb • 3. Pelvic Girdle – 2 Coxae ( hipbones) • Connects bones of lower limbs to the axial skeleton - Sacrum - Coccyx • 4. Lower Limbs – Femur ( Thighbone) – 2 leg bones ( Large TIBIA & slender FIBULA ) – Ankle ( 7 Tarsals) Distil end of Tibia & Fibula – 5 Metatarsals – 14 phalanges Lower Limbs Pg.137 Table 7.2