CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics
advertisement

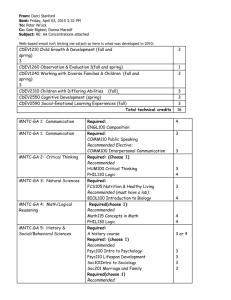
CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics Inverse Kinematics 1 CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics Forward/Direct Kinematics: CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics X Given x a unique q CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics Workspace CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics • Reachable Workspace • Dexterous Workspace CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics X CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics 𝛾 𝛾 Given X Find q=(1, 2, 3) Algebraic Solution CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics The kinematics of the example seen before are: c123 s123 0 l1c1 l2 c12 s 123 B 0 T T W 3 0 0 c123 0 0 0 l1s1 l2 s12 1 0 0 1 Assume goal point is specified by 3 numbers: 𝑐𝛾 𝑠𝛾 𝐵 𝑊𝑇 = 0 0 −𝑠𝛾 𝑐𝛾 0 0 0 𝑥 0 𝑦 1 0 0 1 Algebraic Solution (cont.) By comparison, we get the four equations: c c123 s s123 CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics x l1c1 l2 c12 y l1s1 l2 s12 Summing the square of the last 2 equations: x 2 y 2 l 2 l 2 2l l c 1 2 1 2 2 From here we get an expression for c2 x y l l c2 2l1l2 2 2 2 1 2 2 Algebraic Solution (III) CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics • When does a solution exist? • What is the physical meaning if no solution exists? • Two solutions for 2 are possible. Why? Using c12=c1c2-s1s2 and s12= c1s2-c2s1: x k1c1 k 2 s1 y k1s1 k 2 c1 where k1=l1+l2c2 and k2=l2s2. To solve these eqs, set 𝑟 = 𝑘12 + 𝑘22 and φ= 𝐴𝑇𝐴𝑁2(𝑘2 , 𝑘1 ) Algebraic Solution (IV) k1 CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics φ l2 2 k2 l1 Then: k1=r cos φ , k2=r sin φ , and we can write: x/r= cos φ cos 1 - sin φ sin 1 y/r= cos φ cos 1 - sin φ sin 1 or: cos(φ +1) = x/r, sin(φ +1) =y/r CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics Algebraic Solution (IV) Therefore: φ+1 = Atan2(y/r,x/r) = Atan2(y,x) and so: 1 = Atan2(y,x) - Atan2(k2,k1) Finally, 3 can be solved from: 1+ 2+ 3 = γ Geometric Solution IDEA: Decompose spatial geometry into several plane geometry problems CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics y L2 L1 x Applying the “law of cosines.” CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics CSCE 452 Intro to Robotics