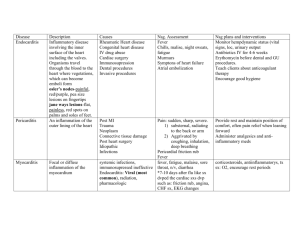
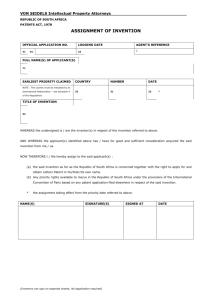
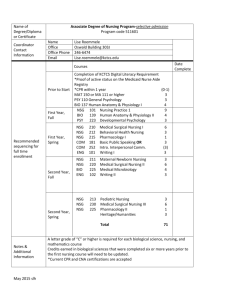
How to operationalize the disclosure requirement at
advertisement

How to operationalize the disclosure requirement at the national level in a manner supportive to the TRIPS Agreement and the CBD? Dr. N.S. Gopalakrishnan, Centre for IPR Studies, School of Legal Studies, Cochin University of Science & Technology, Cochin, Kerala, India nsg Over view • • • • Disclosure in IP Laws Details to be disclosed on source and origin Disclosure of evidence of PIC & ABS Implications for non-disclosure or wrong disclosure • Indian Experience nsg Disclosure in the IP Laws • Patent and Plant Varieties Protection laws – – – – – Obligation to disclose Details of the country of source and origin Evidence of PIC and ABS Nature of the obligation – mandatory Implications for non-disclosure and wrong disclosure nsg Obligation to Disclose • Obligation to disclose in the patent application – Use of genetic material and tk in the invention – directly or indirectly – Directly • Part of the claims in the invention – Indirectly • Used during the process of developing the claimed invention; • Used as a necessary prerequisite for the development of the invention; • Used to facilitate the development of the invention; and • Used as necessary background material for the development of the invention. nsg Disclosure of Source • Source of genetic materials – Complete details of the place or person from whom the material was obtained by the applicant • Individual, collection centers like gene bank or botanical garden, research institutions, open market etc. – Details of the disclosure • Name of the person or institution etc, details of the nature of the genetic material, knowledge about the genetic material and the source of the information nsg Disclosure of Origin • Country of origin of the genetic material in its original state - without any modification – – – – Name of the country Name of the place with in the country Details of the nature of the genetic material Details of the knowledge about the genetic material – Details of the source of the information nsg Evidence of PIC & ABS • Document issued by the authority recognized by the national law of country of origin – Declaration in the application – Attach the certificate issued by the competent authority showing PIC and ABS • National/regional authority • Agency recognized by local or indigenous community – Declare in the application that no legal mechanism in the country of origin • No arrangement with in the local or indigenous community nsg Nature of obligation • What is the nature of obligation? – With reference to source • Full responsibility to give correct information – With reference to country of origin • Information collected after making reasonable effort – With reference to PIC and ABS • Full responsibility to produce original documents issued by the competent authority nsg Implications • Consequences of non-disclosure or wrong disclosure in the patent application – Before grant of patent • With hold the examination of patent • Provide sufficient time for disclosure • If not disclosed application deemed to have withdrawn the application – After grant of patent • Revocation • Transfer of rights • Modification of claims nsg Biodiversity Law • Special Legislation on PIC and ABS – Obligation to take PIC and ABS – Identification of the persons/authorities authorized to issue certificate of PIC and ABS – Form of the certificate showing details – Time bound procedure for the issue of certificates Indian Experience • Patent (Amendment) Act 2002 • TK is not an invention – “an invention which in effect, is traditional knowledge or which is an aggregation or duplication of known properties of traditionally known component or components” – are not inventions for grant of patents (Section 3 (p)). nsg Indian Experience – Obligation to disclose – Disclose the source and geographical origin of the biological material in the complete specification, when used in an invention (Section 10(4)(D) • Prior art – Anticipation – oral knowledge – That the invention so far as claimed in any claim of the complete specification is anticipated having regard to the knowledge, oral or otherwise, available within any local or indigenous community in India or elsewhere nsg Indian Experience • Grounds of opposition and revocation – that the complete specification does not disclose or wrongly mentions the source or geographical origin of biological material used for the invention – Anticipated by oral or documentary knowledge (Sections 25(1)(j) & (k) and 64(1)(p) & (q)) nsg Indian Experience • The Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers' Rights Act 2001 – Disclosure in the application full details of the prior art of TK including location (section 18(e) – Evidence of prior informed consent (section 18(h) – Take prior informed consent in case of use of essentially derived varieties - Section 43 nsg Indian Experience • The Biological Diversity Act, 2002 – Prior informed consent for use of TK associated with genetic resources from the National Biodiversity Authority by the foreigners – Prior informed consent from the NBA before grant of patent protection for the invention based on genetic resources of India – Sharing of benefits with the community nsg Challenges – Create new institutional arrangements in patent offices of the countries rich with genetic resources for prior art search and examination • Creation of traditional knowledge documentation • Pool of experts in traditional knowledge including TK holders to assist examination of the patent application • Patent offices of foreign countries to seek assistance from these institutions for prior art search and examination in case of patent applications based on genetic resources and associated TK of that country. • Recognize these institutions as international searching and examination authorities for PCT applications nsg
![Introduction [max 1 pg]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007168054_1-d63441680c3a2b0b41ae7f89ed2aefb8-300x300.png)