McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2009 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES (LO)
AFTER READING CHAPTER 15, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
LO1
LO2
Explain what is meant by a marketing
channel of distribution and why
intermediaries are needed.
Distinguish among traditional
marketing channels, electronic
marketing channels, and different
types of vertical marketing systems.
15-2
LEARNING OBJECTIVES (LO)
AFTER READING CHAPTER 15, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
LO3
LO4
Describe the factors and
considerations that affect a company’s
choice and management of a
marketing channel.
Recognize how conflict, cooperation,
and legal considerations affect
marketing channel relationships.
15-3
FIGURE 15-1 The variety of terms used
for marketing intermediaries that vary in
specificity and use in consumer and
business markets
15-4
FIGURE 15-2 Intermediaries minimize
transactions and the cost of distribution for
producers and customers
15-5
LO1
NATURE AND IMPORTANCE OF
MARKETING CHANNELS
THE VALUE CREATED BY INTERMEDIARIES
Marketing Channel
Functions Performed by Intermediaries
• Transactional Function
• Logistical Function
• Facilitating Function
Utilities Received by Consumers
15-6
FIGURE 15-3 Marketing channel
intermediaries perform three functions, each
consisting of different activities
15-7
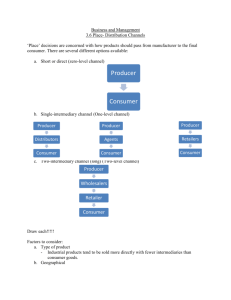
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
LO2
MARKETING CHANNELS FOR
CONSUMER GOODS AND SERVICES
Direct Channel
Indirect Channel
• Retailers
• WholesalersRetailers
• AgentsWholesalersRetailers
15-8
FIGURE 15-4 Common marketing channels
for consumer offerings by the kind and
number of intermediaries
15-9
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
LO2
MARKETING CHANNELS FOR
BUSINESS GOODS AND SERVICES
Direct Channel
Indirect Channel
• Industrial Distributor
• Agents
• AgentsIndustrial Distributors
15-10
FIGURE 15-5 Common marketing channels
for business offerings by the kind and
number of intermediaries
15-11
FIGURE 15-6 Consumer electronic
marketing channels are similar to those for
consumer and business offerings
15-12
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
LO2
DUAL DISTRIBUTION &
STRATEGIC CHANNEL ALLIANCES
Dual Distribution
Strategic Channel Alliances
15-13
FIGURE 15-7 Functions performed by
independent wholesaler types
15-14
LO2
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
CHANNEL INTERMEDIARIES
Merchant Wholesalers
• Full-Service Wholesalers
General Merchandise
(Full-Line) Wholesalers
Specialty Merchandise
(Limited-Line) Wholesalers
15-15
LO2
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
CHANNEL INTERMEDIARIES
Merchant Wholesalers
• Limited-Service Wholesalers
Rack Jobbers
Cash and Carry Wholesalers
Drop Shippers/Desk Jobbers
15-16
LO2
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
CHANNEL INTERMEDIARIES
Agents and Brokers
• Manufacturer’s Agents
• Selling Agents
• Brokers
Manufacturers
• Branch Offices
• Sales Offices
15-17
LO2
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
VERICAL MARKETING SYSTEMS
Vertical Marketing Systems
Corporate Systems
• Forward Integration
• Backward Integration
Contractual Systems
• Wholesaler-Sponsored Voluntary Chains
• Retailer-Sponsored Cooperatives
15-18
LO2
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
VERICAL MARKETING SYSTEMS
Contractual Systems
• Franchising
Manufacturer-Sponsored Retail Franchise
Systems
Manufacturer-Sponsored Wholesale Systems
Service-Sponsored Retail Franchise Systems
Service-Sponsored Franchise Systems
15-19
LO2
CHANNEL STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION
VERICAL MARKETING SYSTEMS
Administered Systems
Channel Partnership
15-20
FIGURE 15-8 Three types of vertical
marketing systems: corporate, contractual
(most popular), and administered
15-21
LO3
CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL CHOICE CONSIDERATIONS
Target Market Coverage
• Intensive Distribution
• Exclusive Distribution
• Selective Distribution
15-22
●Intensive
Retail Store Distribution
-many outlets as possible
-Convenience Goods
• Selective
-Preferred group of
outlets in an area
-Shopping Goods
• Exclusive
-One retail outlet per area
-Specialty Goods
LO4
CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL RELATIONSHIPS
Channel Captain
Channel Influence
• Economic
• Identification
• Expertise
• Legitimate Right
15-24
FIGURE 15-9 The Clayton Act and Sherman
Act place legal restrictions on specific
marketing channel strategies and practices
15-25
Marketing Channel
A marketing channel consists
of Individuals and firms involved
in the process of making a
product or service available for
use or consumption by consumers
or industrial users.
15-26
Industrial Distributor
An industrial distributor is an
intermediary that performs a
variety of marketing channel
functions, including selling,
stocking, delivering a full product
assortment, and financing.
15-27
Electronic Marketing Channels
Electronic marketing channels
employ the Internet to make
goods and services available for
consumption or use by consumers
or business buyers.
15-28
Direct Marketing Channels
Direct marketing channels
allow consumers to buy products
by interacting with various
advertising media without a
face-to-face meeting with a
salesperson.
15-29
Multichannel Marketing
Multichannel marketing involves
the blending of different
communication and delivery channels
that are mutually reinforcing in
attracting, retaining, and building
relationships with consumers who
shop and buy in traditional
intermediaries and online.
15-30
Dual Distribution
Dual distribution involves an
arrangement whereby a firm
reaches different buyers by
employing two or more different
types of channels for the same
basic product.
15-31
Strategic Channel Alliances
Strategic channel alliances is a
practice whereby one firm’s
marketing channel is used to sell
another firm’s products.
15-32
Merchant Wholesalers
Merchant wholesalers are
independently owned firms that
take title to the merchandise
they handle.
15-33
Manufacturer’s Agents
Manufacturer’s agents are
agents who work for several
producers and carry
noncompetitive, complementary
merchandise in an exclusive
territory. Also called
manufacturer’s representatives.
15-34
Selling Agents
Selling agents are agents who
represent a single producer and
are responsible for the entire
marketing function of that
producer.
15-35
Brokers
Brokers are independent firms
or individuals whose principal
function is to bring buyers and
sellers together to make sales.
15-36
Vertical Marketing Systems
Vertical marketing systems
are professionally managed and
centrally coordinated marketing
channels designed to achieve
channel economies and
maximum marketing impact.
15-37
Franchising
Franchising involves a contractual
arrangement between a parent
company (a franchisor) and an
individual or firm (a franchisee) that
allows the franchisee to operate a
certain type of business under an
established name and according to
specific rules.
15-38
Channel Partnership
A channel partnership consists
of agreements and procedures
among channel members for
ordering and physically distributing
a producer’s products through the
channel to the ultimate consumer.
15-39
Intensive Distribution
Intensive distribution is a level
of distribution density whereby a
firm tries to place its products and
services in as many outlets as
possible.
15-40
Exclusive Distribution
Exclusive distribution is a level
of distribution density whereby
only one retail outlet in a specific
geographical area carries the
firm’s products.
15-41
Selective Distribution
Selective distribution is a level
of distribution density whereby a
firm selects a few retail outlets in a
specific geographical area to carry
its products.
15-42
Channel Conflict
Channel conflict arises when
one channel member believes
another channel member is
engaged in behavior that
prevents it from achieving its
goals.
15-43
Disintermediation
Disintermediation involves
channel conflict that arises when
a channel member bypasses
another member and sells or
buys products direct.
15-44
Channel Captain
A channel captain is a channel
member (producer, wholesaler,
or retailer) that coordinates,
directs, and supports other
channel members.
15-45