Earth's Surface
advertisement

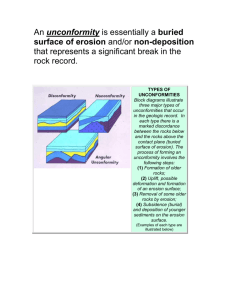
Earth’s Surface Erosion Vocabulary Erosion- the process that wears down and carries away rocks and soil Erosion Gravity acts as a force of erosion by causing a mass movement • Mass movement- a process that moves sediment down a hill Mass Movement Landslide- a rapid movement of large amounts of rock and soil Mass Movement Mudflow- a rapid downhill movement of a mixture of water, rock and soil Mass Movement Slump- mass of rock and soil suddenly slips down a slope • This is different from a landslide because it comes down in one large mass Mass Movement Creep- a very slow movement of rock and soil • Usually creeps cause objects to sit at unusual angles Water Erosion Stream- a channel along which water continually flows River- a large stream usually forming from several streams flowing together Features of Streams Flood Plain- a flat area along a stream that is entirely covered only during times of floods Meander- the winding and bending of a stream as it erodes the land • Only older streams do this Oxbow Lake- when sediment builds up, cutting off the meander from the rest of the river, causing a separate, curved lake Water Erosion Fast moving rivers that are straight and narrow cut steep slopes and create a Vshaped valley • ExampleGrand Canyon Grand Canyon Water Erosion Waterfall- a river cuts through soft rock faster than hard rock • Example- Niagara Falls Niagara Falls Groundwater Erosion A form of chemical erosion Makes caves and sinkholes • CAVE- limestone erodes away, leaving behind a dry narrow passage • SINKHOLE- weakened limestone where the entire portion of the ground suddenly collapses Glacial Erosion Glaciers erode land in 2 ways • Plucking- as a glacier flows over land it picks up rocks • Abrasion- gauges and scratches in rocks as a glacier drags across land Causes large, bowl shaped valleys called cirques Cuts U-shaped valleys in landforms May leave behind large, cold glacial lakes Wind Erosion Deflation- wind picks up and carries away small particles • The faster the wind, the larger the particles it can carry Example- Sand dunes