Resonance and Damping Complete
advertisement
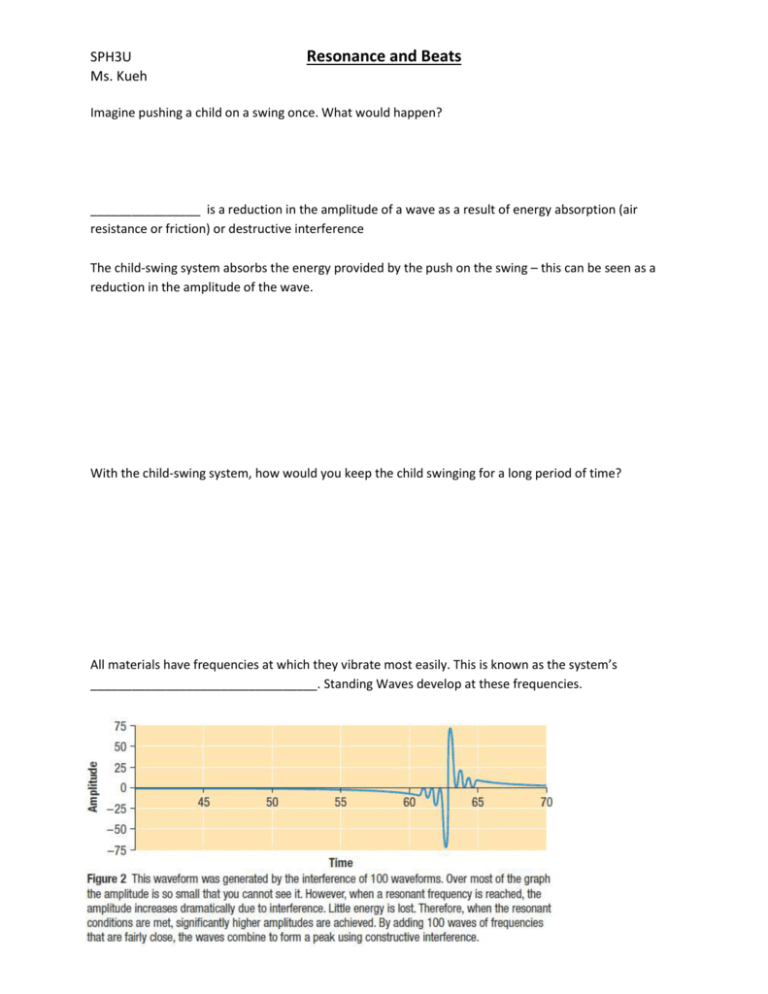
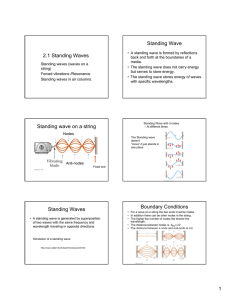
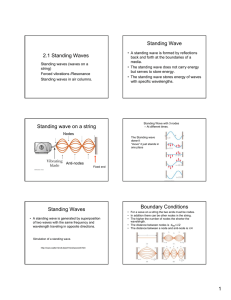
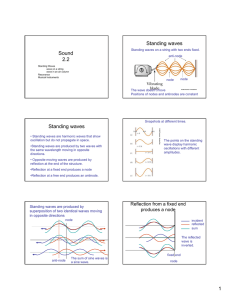
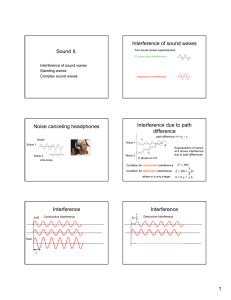
SPH3U Ms. Kueh Resonance and Beats Imagine pushing a child on a swing once. What would happen? ________________ is a reduction in the amplitude of a wave as a result of energy absorption (air resistance or friction) or destructive interference The child-swing system absorbs the energy provided by the push on the swing – this can be seen as a reduction in the amplitude of the wave. With the child-swing system, how would you keep the child swinging for a long period of time? All materials have frequencies at which they vibrate most easily. This is known as the system’s _________________________________. Standing Waves develop at these frequencies. Resonance and Standing Waves: For a standing wave to occur, the wavelength (and frequency) of a wave must be a multiple of one of the harmonics. If the frequency of the wave is not a multiple of one of the harmonics, a pattern will appear that no longer has nodes, and the visible “standing” effect is lost. The loss of the “standing” effect comes from losing the nodes, so that the string begins to vibrates in different locations making it difficult to see. In short, standing waves are a result of an interference pattern of a series of reflected waves. Standing waves occur at one of a medium’s harmonics and since the resonant frequency is one of the medium’s harmonics, standing waves are an example of resonance. When is resonance not ideal? When do you want to reduce the effects of a vibration? sound proofing In buildings, each component has its own resonant frequency and harmonics an external force such as the wind can vibrates the structure at a frequency close to the structure’s resonant frequency the amplitude of the vibration in the system increases significantly, to the point that it could cause damage structures could even collapse In cars, shock absorbers are designed to quickly dampen any up and down motion and keep the tires from lifting off the road As the shocks are compressed, energy is absorbed and thermal energy is generated in the compressed air and fluid inside them. This thermal energy can be released as exhaust. “The Sweet Spot“ Many sports equipment (like a baseball bat, or a golf club) have sweet spots areas where there is little vibration after a hit this is the location of a node Side by Side Speakers What happens when two speakers emit the same sound? Beats - two sound waves with nearly identical frequencies overlap and produce a sound with changing intensity Why do beats happen? The 2 waves are in phase for a short time, but one has a different frequency and will then be out of phase. This cycle repeats. Think of two cars with their left turn signal on. Sometimes they look like they are in phase, and sometimes they look as if they are out of phase. Beat Frequency – how many times per second you hear beats. 𝑓𝐵 = |𝑓2 − 𝑓1 | Example 1 A tuning fork emits a sound of 1024 𝐻𝑧. When placed next to a guitar string, beats with a frequency of 3 𝐻𝑧 is heard. What frequency is the guitar string emitting? Answers Homework: Read Section 14.8 pg. 507 #1 pg. 511 #5, 37 - 39