IPCC Adv. Accounting Test
advertisement
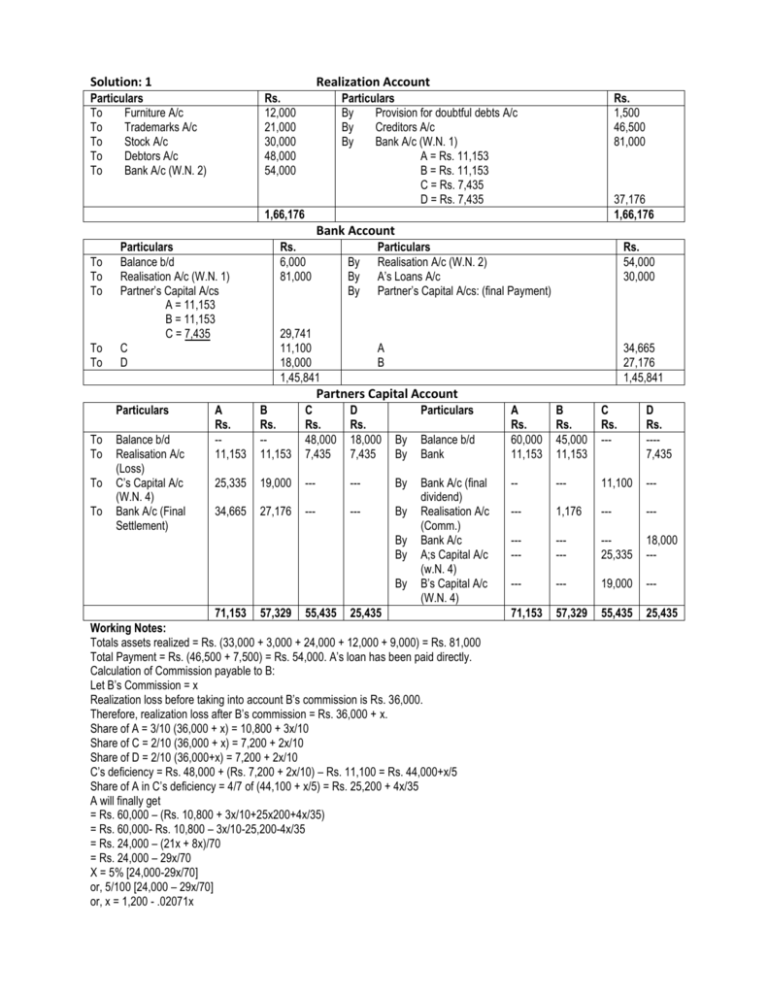
Solution: 1 Realization Account Particulars To Furniture A/c To Trademarks A/c To Stock A/c To Debtors A/c To Bank A/c (W.N. 2) Rs. 12,000 21,000 30,000 48,000 54,000 Particulars By Provision for doubtful debts A/c By Creditors A/c By Bank A/c (W.N. 1) A = Rs. 11,153 B = Rs. 11,153 C = Rs. 7,435 D = Rs. 7,435 Rs. 1,500 46,500 81,000 37,176 1,66,176 1,66,176 Bank Account To To To To To Particulars Balance b/d Realisation A/c (W.N. 1) Partner’s Capital A/cs A = 11,153 B = 11,153 C = 7,435 C D Rs. 6,000 81,000 By By By 29,741 11,100 18,000 1,45,841 Particulars Realisation A/c (W.N. 2) A’s Loans A/c Partner’s Capital A/cs: (final Payment) Rs. 54,000 30,000 A B 34,665 27,176 1,45,841 Partners Capital Account Particulars To To To To Balance b/d Realisation A/c (Loss) C’s Capital A/c (W.N. 4) Bank A/c (Final Settlement) A Rs. -11,153 B Rs. -11,153 C Rs. 48,000 7,435 D Rs. 18,000 7,435 Particulars By By Balance b/d Bank 25,335 19,000 --- --- By 34,665 27,176 --- --- By Bank A/c (final dividend) Realisation A/c (Comm.) Bank A/c A;s Capital A/c (w.N. 4) B’s Capital A/c (W.N. 4) By By By 71,153 57,329 55,435 25,435 Working Notes: Totals assets realized = Rs. (33,000 + 3,000 + 24,000 + 12,000 + 9,000) = Rs. 81,000 Total Payment = Rs. (46,500 + 7,500) = Rs. 54,000. A’s loan has been paid directly. Calculation of Commission payable to B: Let B’s Commission = x Realization loss before taking into account B’s commission is Rs. 36,000. Therefore, realization loss after B’s commission = Rs. 36,000 + x. Share of A = 3/10 (36,000 + x) = 10,800 + 3x/10 Share of C = 2/10 (36,000 + x) = 7,200 + 2x/10 Share of D = 2/10 (36,000+x) = 7,200 + 2x/10 C’s deficiency = Rs. 48,000 + (Rs. 7,200 + 2x/10) – Rs. 11,100 = Rs. 44,000+x/5 Share of A in C’s deficiency = 4/7 of (44,100 + x/5) = Rs. 25,200 + 4x/35 A will finally get = Rs. 60,000 – (Rs. 10,800 + 3x/10+25x200+4x/35) = Rs. 60,000- Rs. 10,800 – 3x/10-25,200-4x/35 = Rs. 24,000 – (21x + 8x)/70 = Rs. 24,000 – 29x/70 X = 5% [24,000-29x/70] or, 5/100 [24,000 – 29x/70] or, x = 1,200 - .02071x A Rs. 60,000 11,153 B Rs. 45,000 11,153 C Rs. --- D Rs. ---7,435 -- --- 11,100 --- --- 1,176 --- --- ----- ----- --25,335 18,000 --- --- --- 19,000 --- 71,153 57,329 55,435 25,435 or, x+.02071x = 1,200 or, x = 1,200/1.02071 or, x = 1175.64 = 1,176 (approx.) C’s Deficiency of Rs. 44,335 is to be share by A and B in their Capital ratio of 60,000:45,000 or 4:3. D will not bear any deficiency loss because his capital account has debit balance. SOLUTION: 2 (a) (i) In the books of Cyber Ltd. i.e. Old company's books Realisation Account Rs. To Goodwill 5,000 By 8% Debentures To Fixed Assets 2,57,000 By Interest accrued on debentures To inventories 50,000 By Trade payables To Trade receivables 60,000 By P Ltd. (Purchase consideration) To Bank 1,000 By Equity shareholders To Preference share holders A/c (Bal. fig.) (W.N.3) 6,000 (ii) To Profit & loss A/c To Equity shares in Mahal Ltd. To Realisation A/c (b) (i) To Business Purchase To Equity shares application & allotment A/c (W.N.4) Rs. 1,00,000 8,000 1,00,000 1,36,000 35,000 3,79,000 3,79,000 Equity Shareholders Account Rs. 1,25,000 By Equity shares capital 80,000 35,000 2,40,000 In the books of Mahal Ltd. (New company) Bank Account Rs. 1,000 By Goodwill (for expenses on absorption) 56,000 By Trade Payables 1,00,000 × 16 100 By Balance c/d (Bal. fig.) 57,000 Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2012 Note No. (ii) Particulars 1. Equity and Liabilities (1) Shareholders Funds Share Capital (2) Non-current liabilities Long term borrowings Rs. 2,40,000 2,40,000 Rs. 8,000 16,000 33,000 57,000 Rs. 1 3,00,000 2 1,00,000 4,00,000 Total II. Assets (1) Non-current assets Fixed assets (a) Tangible assets **(W.N.2) (b) Intangible assets (2) Current assets (a) Inventories (b) Trade receivables (c) Cash and cash equivalents 2,52,000 8,000 3 47,000 60,000 33,000 4,00,000 Total Notes to Accounts Rs. 1 Share Capital Authorised share capital 30,000 equity shares of Rs. 10 each 3,00,000 issued and Subscribed 30,000 shares of Rs. 10 each fully paid up (out of the above, 24,400 (W.N.4) shares have been issued for consideration other than cash) 2 Long term Borrowings Secured 8% Debentures 3 Intangible assets Goodwill Working Notes: 1- Calculation of Purchase consideration 2- 3. 1,00,000 8,000 Rs. Payment to preference shareholders 5,000 equity shares@ Rs. 10 50,000 For arrears of dividend: (Rs. 12,000 x 5 shares / Rs. 100 @ Rs. 10) 6,000 Payment to equity shareholders (24,000 shares x 1/3) @ Rs. 10 80,000 Total purchase consideration 1,36,000 Calculation of fair value at which fixed assets have been acquired by Mahal Ltd. Since the question states that balance of purchase consideration is being attributed to fixed assets", it is implied that the amount of purchase consideration is equal to the fair value at which the net assets have been acquired. Therefore, the difference of fair value of net assets (excluding fixed assets) and the purchase consideration is the fair value at which the fixed assets have been acquired. Rs. Purchase consideration / Net assets 1,36,000 Add: Liabilities: 8% Debentures 1,08,000 1,00,000 1,00,000 1,16,000 Trade Payables ( × 16) × ( × 10 × 10) 100 100 3,60,000 Less: Inventory Rs. (50,000-3,000) Debtors Bank Fair value at which fixed assets has been acquired Preference shareholders’ Account 47,000 60,000 1,000 Rs. 56,000 To Equity Shares in Mahal Ltd. 4. 3,00,000 (1,08,000) 2,52,000 Rs 50,000 6,000 56,000 By Preference Share Capital By Realisation (Bal.fig.) 56,000 Calculation of number of Equity Shares issued to public Authorised Equity Shares Less: Equity shares issued for Interest accrued on debentures Trade Payables of Cyber Ltd. 1,00,000 ( × 10 𝑠ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑠) 100 Preference shareholders of Cyber Ltd. 12000 Arrears of preference dividend ( × 5) 100 24,000 Equity shareholders of Cyber Ltd. ( 3 ) Number of equity shares issued to public at par for Cash Number of Shares 30,000 800 10,000 5,000 600 8,000 (24,400) 5,600