ch 2 b jeopardy
advertisement
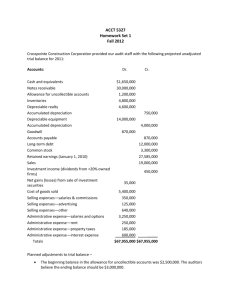
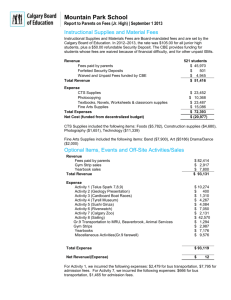
Terminology Financial Statements GAAP Transactions Other $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 BUSINESS TRANSACTION A financial event that affects assets, liabilities or owners equity An asset representing amounts due from customers ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE Costs incurred by a business in earning revenue EXPENSES Owner withdrawing money for personal use DRAWINGS The fees a business charges for buying or selling goods (ex: real estate, for clients) COMMISSIONS The two financial statements are called… INCOME STATEMENT & BALANCE SHEET The financial statement that is completed first INCOME STATEMENT Advertising Expense can be found on the .. INCOME STATEMENT What 3 questions does the heading of an Income Statement ask WHO? WHAT? WHEN? What does the income statement tell the reader? HOW MUCH THE BUSINESS MADE OR LOST OVER A REPORTED PERIOD OF TIME Revenue should be recognized at the time of sale and/or rendering services GAAP REVENUE PRINCIPLE Expenses must be recognized and recorded when they are incurred GAAP EXPENSES PRINCIPLE Revenues & expenses must be correlated to report net income/net loss for an accounting period GAAP MATCHING PRINCIPLE One aspect of accounting theory that views the business as being separate, distinct, and apart from its owners GAAP ENTITY CONCEPT DAILY DOUBLE DAILY DOUBLE Taylor’s Catering Co. Advertised on the local radio station, Country 100. They received the radio station’s monthly invoice on March 29, 2009. The invoice indicated that payment was due by the 15th of the following month. 1. What GAAP underlies this transaction? 2. What is the key date in this transaction? Why is this date regarded as key? 3. Record the elements that are affected, whether they increase or decrease the accounting equation and explain why? 1. Expense Principle 2. March 29, 2009 – b/c the expense is recognized when the expense is incurred, not when the cash is paid out. 3. The elements affected are liabilities (increase) and owner’s equity (decrease – new expense). Two accounts – accounts payable and advertising expense Salaries, Heat, Phone, Cell Phone, Adverstising EXPENSES Received $280 on account from a client -What accounts are affected? -Increase or decrease? ACC. REC. decreases by 280 CASH increases by 280 Paid $1500 on account Accounts? Increase or Decrease? Acc. Pay. Decreases by $1500 Cash Decreases by $1500 When a computer is purchased for cash, what side of the account is affected? LEFT SIDE ASSETS The new info added to the OE section of the balance sheet in this chapter ... - REVENUE AND EXPENSES (NET INCOME OR NET LOSS) - DRAWINGS Create the OE section of the balance sheet based on the following information: Drawings $1200 Capital $10 000 Net Income $ 8 000 Owner’s Equity Lapointe, Capital $10 000 Add: Net Income 8 000 18 000 Less: Drawings 1 200 Total Owner’s Equity $16 800 What is the difference between sales and fees earned? SALES – SELLING GOODS FEES EARNED – SERVICE BASED BUSINESS When an asset is bought on credit, liabilities... INCREASE Sold services to a customer on credit. A = L + OE Accounts? Increase? Decrease? Fees Earned – Increase Acc. Rec. - Increase Paid cash for rent expense. Accounts? Increase? Decrease? CASH – DECREASES RENT EXPENSE – IS SUBTRACTED FROM REVENUE As a team create an income statement and balance sheet based on the information on the next slide. You must create it as a group and submit one copy of each sheet. The same person cannot write both. Lapointe’s Teaching Service (Aug. 31, 2009) Fees Earned: 10 000, Rent Expense: 2000, Advertising Expense: 1000, Telephone Expense: 500- IS – for the month Cash: 10 000, Car: 7000, Equipment: 2000, Bank Loan Pay: 6000, Acc.Pay. Joe: 200, Acc.Pay. John: 800, Drawings: 1000, Capital 6500 - Income Statement - Balance Sheet Return back to your original seat Hand out study guide Ch. Problems and Questions due the day of exam Practice Test and Quizzes Due