Position
advertisement

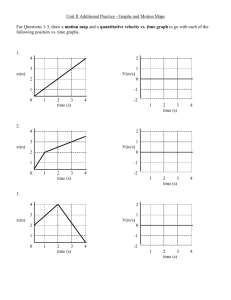
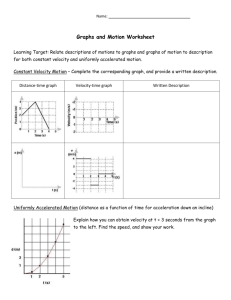
Motion and Forces Lesson 1: Position and Motion Position Position describes the location of an object. A reference point is a location to which you compare other locations. When you describe a position by comparing it to the location of another object or place, you are using a reference point. Location Describe Waldo's position? Location Describe Waldo's position in reference to the sailboat. Motion Motion is a change in position relative to a reference point. Position, Motion, Reference Imagine you are flying in an airplane.... Position, Motion, Reference Describe the position of the pilot relative to where you are sitting? Position, Motion, Reference Describe the position of the pilot relative to where you are sitting? In front of me 15 rows ahead of me In the front of the aircraft Others..... Position, Motion, Reference Is the pilot in motion relative to where you are sitting? Position, Motion, Reference Is the pilot in motion relative to where you are sitting? No, the pilot's position is not changing relative to where I am sitting (always in the same spot). Position, Motion, Reference If I throw a ball to the pilot, is the ball in motion relative to where you are sitting? Position, Motion, Reference If I throw a ball to the pilot, is the ball in motion relative to where you are sitting? Yes, the ball is moving from my position to the pilots position. Position, Motion, Reference Is the pilot, the ball, or yourself in motion relative to someone on the ground? Position, Motion, Reference Is the pilot, the ball, or yourself in motion relative to someone on the ground? All three are in motion relative to someone on the ground. Speed The speed of an object is a measure of how far something moves in a given amount of time (how quickly something changes position). EXAMPLE: Two cars traveling at different speeds..... - Would travel the same distance when both go from Dunlap to Chicago, but the faster car would arrive sooner. - Would travel different distances if they both drove for one hour. Average Speed Average speed is a way to calculate the speed of an object that may not always be moving at a constant speed. When traveling to Chicago, the speed limit may change, therefore the cars speed will change..... Cars Speed Average Speed Time Distance Time Graphs • How is average speed calculated? – Speed can be calculated by dividing the distance an object travels by the time it takes to cover that distance – Speed = Distance / Time • Standard unit for speed is meters per second (m/s) Distance Time Graphs • Used to plot the distance an object travels over time • The distance of an object away from a reference point is plotted on the y axis. Time is plotted on the x-axis. Distance Time Distance Time Graphs • Imagine two friends racing their bikes against each other. Each start from a stop and race 100 meters down the track. Friend 1 wins the race in a time of 8 seconds while Friend 2 had a time of 11 seconds. • Create a distance time graph for each Friend in the race (on the same plot) Distance Time Graphs Starting Line Finish Line Friend 1 Distance = 0 meters Time = 0 seconds Distance = 100 meters Time = 8 seconds Friend 2 Distance = 0 meters Time = 0 seconds Distance = 100 meters Time = 11 seconds 100 Distance (m) 50 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Time (s) 9 10 11 12 13 Distance Time Graphs Starting Line Friend 1 Distance = 0 meters Time = 0 seconds Distance = 100 meters Time = 8 seconds Friend 2 Distance = 0 meters Time = 0 seconds Distance = 100 meters Time = 11 seconds 100 Distance (m) Finish Line 50 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Time (s) 9 10 11 12 13 Distance Time Graphs 100 Distance (m) Friend 1 Friend 2 50 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Time (s) • Just from looking at the graph alone, who won the race? How can you tell? Distance Time Graphs 100 Distance (m) Friend 1 Friend 2 50 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Time (s) • Just from looking at the graph alone, who won the race? How can you tell? – Friend 1 won the race. The line for Friend 1 is steeper (slope is bigger). Distance Time Graphs • The slope, or steepness, of the line is equal to the average speed of the object - The faster the object the steeper the line (Friend 1 steeper than Friend 2) • Average speed can be calculated from the graph by dividing the change in distance by the change in time for that interval • Average Speed (Slope) = change in y / change in x Distance Time Graphs 100 Distance (m) Friend 1 Friend 2 50 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Time (s) Length of y Length of y Friend 1 Length of x 100 meters / 8 seconds = 12.5 m/s Friend 2 Length of x 100 meters / 11 seconds = 9.09 m/s Velocity Question: Is there a difference between velocity and speed? Yes! Velocity is a vector. • A vector is a quantity that has both size and direction. • Velocity is a speed in a specific direction. Examples: 7 m/s south, 5 m/s forward, 2 m/s downward, etc. Question: Is it possible for two objects to have the same speed but different velocity's? Why? Velocity Question: Is it possible for two objects to have the same speed but different velocity's? Why? – Could both be traveling the same speed but in opposite directions. – Imagine two bicycles going towards each other on the sidewalk. Both could be speeding along at 7 m/s (speed) but they are traveling the opposite direction (velocity). Velocity Imagine riding a elevator to the top floor of a building and back down. Assume the ride took 5 seconds in each direction and top floor of the building was 10 meters above the ground. Draw a distance time graph showing the average speed and another graph showing the average velocity. Remember, velocity includes direction! Velocity Imagine riding a elevator to the top floor of a building and back down. Assume the ride took 5 seconds in each direction and top floor of the building was 10 meters above the ground. Draw a distance time graph showing the speed and another graph showing the average velocity. Remember, velocity includes direction! Speed 20 20 Total distance traveled, regardless of direction 10 Velocity 0 10 Total distance traveled, including direction. Traveling up is positive, traveling down is negative 0 0 5 Average speed: 10 meters / 5 s = 2 m/s 10 0 5 10