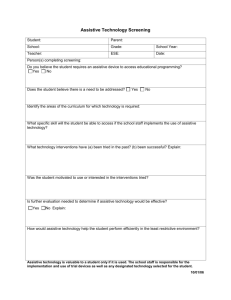
The use of assistive technology in accessing the curriculum
advertisement

Assistive Technology Chris McKenzie Crystal Drury Assistive Technology Advisers The CORRECT Assistive Technology can enable students to : • be involved learning activities which would otherwise be inaccessible, • demonstrate competence and achieve results based on ability not limited by disability. Students’ use of assistive technology should be reviewed to ensure that the provisions effectively meet the changing demands of their course. DO-IT Technology Video Hardware Braille display alternative keyboards, keyguards magnification units: CCTVs Software Screenreader: JAWS Magnification: ZoomText Scan reader: Kurzweil3000 Prediction software Voice recognition Onscreen keyboard Video available online at: www.washington.edu/doit/Video Role of Technology Team – needs assessment – application for Disabled Students Allowance (DSA) – purchasing, setup and installation – training in assistive software – research and development • laptop and equipment loan pool • on-campus Assistive Technology (AT) • advice to departments - Disability Resource Development Fund (DRDF) Development of AT Service • • • • • • • • • • • • 1998 - Assistive Technology Adviser Appointed 1999 - Initial funding for AT Loan Pool 2002 - Assistant AT Adviser Appointed 2002 - SSIS notification system introduced (PEGASUS) 2002 - Assistive Technology Resource Room 2004 - Purchasing database introduced 2005 - Site Licensed software in labs 2005 - ATANET founded 2006 - ↑ AT Manager, 1 AT Adviser 2007 - Second AT Adviser Appointed 2007 - Central Scanning Service introduced 2008 - AT Support Assistant Appointed Assistive Software Available for all On Campus at Strathclyde University MindGenius Organisation and planning tool based on the concept of Mind-mapping TextHelp Read & Write GOLD Text-to-speech software to assist with reading text on a computer also with proofreading own work Assistive Software Available for User Groups Kurzweil 3000 Scan and Read tool Kurzweil 1000 Scan and Read tool for visually impaired users ZoomText Magnification and screen reading tool for VI users JAWS Dedicated screen reader for blind users Assistive Hardware Available for all On Campus at Strathclyde University Braille Emboser The Braille Embosser can be used to create Braille copies of your work, handouts or research. CCTV CCTVs allow you to magnify the object or book you wish to look at on a larger screen. Scanners A scanner will allow you to convert printed text into images that can be edited and/or read aloud. Assistive Technology in use • A student with the use of one-hand only for typing uses a compact keyboard and voice recognition software when completing written assignments. • A social work student with dyslexia uses a scanner and text-to-speech software to accurately read his course notes. The visually and auditory feedback aids his comprehension of the content and reduces the need to re-read several times. • A student with Aspergers syndrome describes hyper-sensitivity to noise. They use noise-cancelling headphones within noisy environments to allow them to dull the background noise and focus on a speaker. Assistive Technology in use A pharmacy student with a visual impairment has a microscope fitted with a magnification camera which is in turn connected to a TV screen on which it displays the magnified view of the slide. An architecture student with a visual impairment uses a desktop magnification system when drawing and accessing images or text. Current Research & Developments • Live Remote Captioning • Teaching Room Technologies • • • • Visual Display Equipment Audio Equipment Automated Video Capture (‘web lectures’) Video Streaming & Captioning LRC What is LRC • Service for deaf and hard of hearing students • Live speech converted into text How it works • Audio transmitted to captioning studio via mobile • Captioner uses voice recognition software to re-speak • Text returns to students laptop within seconds Technology Why was it introduced • To explore an alternative to the current services i.e. electronic notetaking, speedtext and manual notetakers • Aim is to improve reliability, flexibility and scalability of services for students - Mobile technology - Accessible for numerous students simultaneously - No travel required - Remote institutions LRC video clips Trial Still ongoing - Rolled out September 2009 - 2 students, 2 departments, 2 campuses - Accuracy of transcription excellent - Positive student feedback - Initial technical issues overcome - Ongoing improvements Teaching Room Technologies • • • • Visual Display Equipment Audio Equipment Automated Video Capture (‘web lectures’) Video Streaming & Captioning Visual Display Equipment • Initial Position • No clear consensus among teaching staff • Need to develop an agreed standard: • Enhance Teaching & Learning experience • Improved Technical Support • Efficiency gains • Disabled Students and Staff Visual Display Equipment • No clear consensus among teaching staff... Visual Display Equipment • Room Control Systems Touch Screen Wall Mounted Buttons • Need for support in infrastructure essential Visual Display Equipment • Conclusions • Flexibility is important • High quality electronic visual display is most accessible Data projector Plasma/LCD screen • Availability of electronic copy crucial Audio Equipment •Room Specification •Based on room size •Installed microphones •Radio microphones •Sound Reinforcement •Loop systems • Teaching Room Audio Survey •Intended to compliment Visual Display Equipment Assessment Audio Equipment • Student Survey • Delivered online to all current students • Option to remain anonymous • ‘User-centric’ focus on user experience Audio Equipment • Strong agreement that speakers could be heard during class • However, results showed that almost 1/3 of student had to sit in specific areas to hear clearly • Over 70% felt that the teaching experience could be improved by better use of audio technology • 87.5% reported that speakers did not always use the available systems Automated Video Capture (web lectures) • • Introduction • Introduced in 2005/06 • Initially a pilot project within Faculty of Education Background • Managed by Learning Services • Around 140 recordings per annum • Fixed installations 2007 • Installed systems less obtrusive • Faster turnaround of video onto server Automated Video Capture (web lectures) • Technical specifications • Installed system • Portable systems • Windows Media Format • Process • Integrated with Virtual Learning Environment • Transcriptions & Captions Automated Video Capture (web lectures) • Feedback • Initial concern about attendance • No significant drop in attendance demonstrated • Could students film classes themselves? • Fixed systems only work perfectly if they are installed everywhere. Only as good as infrastructure that supports it. Video Streaming & Captioning • 24/7 access to video resources • Access on and off campus • Flexible approach to learning • Searchable Database (eStream) • Large volume of data, with user control • meta data (including deletion date) • Intellectual Property/Ownership/Copyright • Transcriptions & Captions • Outsourced • Expensive! • On Demand/Track Disabled students? • Moving past technology? Conclusions Accessible Teaching Room Technologies Low Cost No Cost • Accessibility of a standard PC - Windows Ease of Access Centre • MS Office • Freeware • Stylesheets Windows Ease of Access Centre Built-in features: • Display settings i.e. high contrast • Keyboard & mouse settings • Textual & Visual Alternatives • Narrator • Magnifier • Voice-recognition • On-Screen keyboard Display Options The Display option within Windows Accessibility allows you to switch to a high contrast scheme directly by using a keyboard shortcut. high contrast black and high contrast white are amongst the available schemes. This facility allows standard computers in open access labs to be readily switched to high contrast scheme by users who need or prefer such a display. WORD There are lots of ways that you can make MS Word easier to use. You can: change the background colours and font to suit your own preferences make the spell check tool work harder for you. Stylesheet A style sheet will allow you to view most web pages in the most accessible background colour and text size for you. To create a style sheet: Go to www.oneformat.com Select your preferred background colour and text size Download your style sheet Save to your computer then install Freeware EduApps http://www.rsc-nescotland.ac.uk/eduapps/ Over 60 pieces of open source software available to support reading, writing, planning as well as sensory, cognitive and physical difficulties Importance of liaising with Academic Departments • Student Records System • SSIS • PEGASUS Impact of Disability, Reasonable Adjustments & Exam Arrangements • Awareness Training Sessions • Assistive Technology • MS Office • Accessible Teaching materials The Use of Assistive Technology in promoting accessibility The availability of accessible course materials is key to most disabled student’s success. Students use of assistive technology can make accessing accessible materials possible – but often the process continues to demand more time than the same activities for their nondisabled peers. Non-Medical Personal Helpers and Reasonable Adjustments are also required. Accessible Resources Academic Support Reasonable Assistive Adjustments Technology Importance of liaising with other departments • • • • • • IT Training Team Systems Developers Teaching Room Support Library Services IT Helpdesk Learning Technology Enhancement Team Any Questions? www.strath.ac.uk/disabilityservice