Scales
advertisement

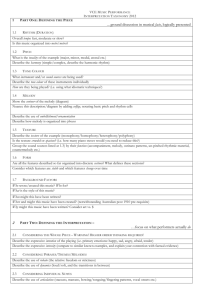
Chapter 2: Rhythm, Melody, and Harmony Rhythm • Rhythm: the organization of time in music – Gives shape or profile to the melody – Provides vitality and definition to a melody – Divides long spans of time into smaller, more easily comprehendible units • Rhythm is the most fundamental element of music Elements of Rhythm • Beat: a regularly recurring sound that divides the passing to time into equal units; the basic pulse of music • Tempo: speed at which the beat sounds – Allegro, Presto; Lento, Grave – Accelerando: speeding up – Ritardando (Ritard): slowing down • Meter: organizing beats into groups – Measure: each group of beats – Downbeat: first beat in each unit – Accent: emphasis or stress places on a beat Rhythmic Notation • Music notation began in 13th-century Paris Meter/Time Signatures • Duple (2/4) meter: two beats per measure Meter/Time Signatures • Duple (3/4) meter: two beats per measure Syncopation • Syncopation: when the accent is on the weak beat or between beats – Creates a feeling of being “off beat” – Often heard in jazz, Latin music, and hip-hop Listening Exercise: Rhythm • Pg. 17 Melody • Melody: a series of notes arranged in order to form a distinctive, recognizable musical unit; the “tune” • Pitch: the relative position (high or low) of a musical sound • Octave: Span between the first note and the eighth note of a scale • Interval: the distance between any two pitches Listening to Melodies • Listen for the melodic contour Melodic Notation • Musical notation began around the year 1000 CE • Staff: Gridwork of line and spaces where music is written • Noteheads and flags show different durations and rhythms • A clef indicates the range of pitches • Grand Staff: Scales, Mode, Tonality, and Key • Scale: – A sequential arrangement of pitches – Ascend and descend in an unvarying pattern – Mode: term describing a general type of scale: major, minor, etc. • Major and minor scales used in almost all Western melodies • Chromatic Scale: Uses all twelve pitches equally divided within the octave Scales • Major • A seven-note scale • Order of whole and half steps: 1-1-1/2-1-1-1-1/2 • Usually associated with joy, confidence, tranquility, etc. • Minor • A seven-note scale • Order of whole and half steps: 1-1/2-1-1-1/2-1-1 • Usually associated with fear, anxiety, sorrow, despair, etc. Major/ Minor Listening Quiz • E-book p. 24 Tonality • Tonality(or Key): The organization of music around a central pitch (the tonic) – Modulation: a musical move to a different tonal center • Planets rotate around and are pulled towards the sun, just as outlying pitches are pulled toward the tonic pitch Hearing Melodies and Phrases • Melodies are composed on smaller segments called phrases – We usually follow along with the phrases when we listen to music Harmony • Harmony: sounds that provide the support and enrichment - an accompaniment – for melody – Built on chords: a group of two or more pitches that sound at the same time – Triad: the basic chord in Western music • Tonic: first note of the scale • Dominant: fifth note of the scale • Chord Progression: a succession of chords moving forward in a purposeful fashion – Cadence: the end of a chord progression Harmony Illustration • E-book p. 26 (Oh What a Beautiful Morning) • E-book p. 29 (Duke of Earl) Consonance and Dissonance • Consonance: pitches sounding agreeable and stable – Creates a sense of calm • Dissonance: pitches sounding momentarily disagreeable unstable – Creates a sense of tension and anxiety • Consonance and Dissonance allows music to convey a wide range of emotion