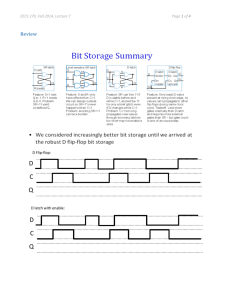
PowerPoint 演示文稿 PowerPoint 演示文稿 PowerPoint 演示文稿
advertisement

School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia UStore: A Low Cost Cold and Archival Data Storage System for Data Centers Quanlu Zhang†, Yafei Dai†, Fengqian Li#, Lintao Zhang∗ † Peking University # Shanghai Jiao Tong University * Microsoft Research Asia School of EECS, Peking University A BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO CLOUD STORAGE Microsoft Research Asia School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia “Cold Storage Is Hot Again” -- IDC Technology Assessment School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Hotmail: 5~22 GB per account, OneDrive: 7~25 GB per account User generated data: video feeds, sensor inputs, operational logs Long term archiving for financial and medical data System backups …… School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Managing storage growth Managing storage growth Designing, managing Designing,deploying, deploying, andand managing Backup, Recovery,and and Archive solutions Backup, Recovery, Archive solutions 79% 77% 43% 45% Making informed strategic/big-picture decisions 39% 36% Designing, deploying, and managing disaster recovery solutions Designing, deploying, and managing storage in a virtualized server environment 38% 39% 31% 29% 27% Lack of skilled storage professionals Designing, deploying, and managing storage in cloud computing environment 18% 16% 15% 15% Lack of skilled cloud technology professionals 11% 10% Convincing higher management to adopt cloud 10% 7% Infrastructure for Big Data analytics Managing external cloud service providers 4% 0% Source: Managing Storage: Trends, Challenges, and options (2013-2014). 37% 8% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% Percentage of Respondents 2013-14 2012-13 70% 80% 90% School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Much of the Data are Cold or Archiving Facebook Photo Access Patterns Source: Facebook, 2013 • Hot data: very low latency, high bandwidth • Cold data: low bandwidth, (relatively) low latency • Archival data: predictable workload, can tolerate long latency School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia What Characteristics Does An Ideal Cold and Archival Storage Possess? • Cheap – Low capital expense – Low operational expense • Incrementally deployable – No need to over-provision too much • Good Performance – Reasonable throughput – Relatively low access latency • Reliable and Available School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Which Storage Media? Tape Optical Disk Magnetic Disk School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Magnetic Disk is Promising for Cold and Archival Storage • The average cost per gigabyte fell from $437,500 in 1980 to $0.05 in 2013 • Shingled Magnetic Recording – High capacity • Helium-filled hard drives – Low power – High capacity School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia How to Connect and Manage Large Numbers of Disks to Provide Storage Service? School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Interconnection Technologies • SATA – 6.0 Gb/s transfer speed – SATA multiplier • support only 15 devices, not support cascade • SAS – 6 Gb/s transfer speed – SAS expander • Fibre Channel – High bandwidth, also high expense • Ethernet – ARM attaches and exposes disk – dedicated ARMs and network infrastructure School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia USB based Storage for Data Center Disk Array Box USB Hub Existing Server • USB 3.0 – 5.0Gb/s transfer speed (up to 10Gb/s for USB 3.1), 300~400MB/s realistic throughput – Tree structured hubs to address up to 127 devices – Supported by most new chipsets, very (very) cheap School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia The Problems of the Naïve Design • Limited performance – An enclosure of ~100 disks with only 400MB/s throughput • Single point of failure – Failure of the root hub or the server cause total data loss Desired Design Traditional wisdom: multi-path attached storage is expensive School of EECS, Peking University Two Primitives Hub Switch Control Microsoft Research Asia School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia The Data Plane (Simple Tree) School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia The Data Plane (2-Way Redundancy) Server 1 Server 2 School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia The Data Plane (4 Output Ports) School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia The Data Plane (4 Output Ports) School of EECS, Peking University The Control Plane • What can be controlled? – Switches and Power to each disk Control Plane Microsoft Research Asia School of EECS, Peking University SOFTWARE DESIGN Microsoft Research Asia School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Software Design • Serve the storage allocation and access • Detect failures and implement quick failover • Provide an appropriate interface for upper layer services and applications School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Software Architecture UStore ClientLib iSCSI Initiator UStore EndPoint UStore EndPoint UStore EndPoint UStore EndPoint UStore EndPoint iSCSI Target iSCSI Target iSCSI Target iSCSI Target iSCSI Target USB Monitor USB Monitor USB Monitor USB Monitor USB Monitor Host Interconnect Fabric …… School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Software Architecture Paxos UStore Master Control Commands UStore ClientLib Heartbeat Messages iSCSI Initiator UStore EndPoint UStore EndPoint UStore EndPoint UStore EndPoint iSCSI Target iSCSI Target iSCSI Target iSCSI Target USB Monitor USB Monitor USB Monitor USB Monitor Primary Controller Backup Controller Control Hubs, Switches, Disks Interconnect Fabric …… School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Configuring Interconnect Fabric UStore Master S1 : D1,D4 S2 : D7,D8 S3 : D2,D3 S4 : D5,D6,D7 S1 S2 S3 S4 Connect D1 to S3 and D4 to S2 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Configuring Interconnect Fabric UStore Master S1 : Crash S2 : D7,D8, D4 S3 : D2,D3, D1 S4 : D5,D6,D7 S1 S2 S3 S4 Connect D1 to S3 and D4 to S2 Reconfiguration Completion D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 School of EECS, Peking University UStore Prototype Microsoft Research Asia School of EECS, Peking University COST COMPARISON Microsoft Research Asia School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Cost Comparison • Capital Expense System Media Capital Expense Without Disks DELL PowerVault MD3260i Near-line SAS $3,340,000 $1,525,000 Sun StorageTek SL150 LTO6 Tape $1,748,000 - Pergamum SATA HD $756,000 $415,000 BACKBLAZE SATA HD $598,000 $257,000 UStore SATA HD $456,000 $115,000 • Operational Expense – – – – Low power consumption Low cooling cost Low space occupation Low operational cost School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia PERFORMANCE EVALUATION School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Throughput • SATA to USB bridge, USB hub, and USB switch have little impact on disk performance 4MB Sequence 4KB Sequence 200 IO/s MB/s 150 100 50 0 100% 50% 0% 16000 14000 12000 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 100% USB Hub&Switch 0% Read Percentage Read Percentage SATA 50% SATA USB Hub&Switch School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Total Throughput • Total throughput increases with the increase of disks 4MB Sequence 200 Total Bandwidth (MB/s) Total Bandwidth (MB/s) 4KB Sequence 150 100 50 0 Read 1disk 2disks 4disks 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 Write 8disks 12disks Read 1disk 2disks 4disks Duplex throughput of one root: 540MB/s Total throughput of our prototype: 2160MB/s Write 8disks 12disks School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Switching Time 12 Latency (s) 10 8 6 Mount delay Expose delay 4 Recognize delay 2 0 1 2 3 4 8 Number of Switched Disks 16 School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Whole System’s Power Consumption Power Consumption (W) 250 200 222.5 193.5 166.8 150 100 83.5 50 28.9 0 Spinning DD860/ES30 Powered off Pergamum UStore 22.1 School of EECS, Peking University CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK Microsoft Research Asia School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Conclusion • Cheap – Low capital expense – Low operational expense • Incrementally deployable – No need to over-provision too much • Good Performance – Reasonable throughput – Relatively low access latency • Reliable and Available School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Future Work Provide data redundancy in UStore, leveraging low coupling of disks and servers School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Thank You! Questions? School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Failure Rate • MTTF of servers is 3.4 months • MTTF of disks is 10-50 years School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Prototype’s interconnect topology School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Power Management • A lot of mechanisms proposed for power saving in storage system – managing data redundancy and placement • Provide disk control interface that allows upper layer services to control the state of the disks that belong to them (spin-down/spinup). • Spin down disks after a configured interval School of EECS, Peking University Microsoft Research Asia Power Consumption 8 Hub 1W 6 1W 4 2 0 Spin Down SATA Disk Idle Read/Write USB Bridge&Disk Power Consumption (W) Power Consumption (W) Disk 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 1 2 3 4 Number of Connected Disks