Algebra 1 MAFS.912.F-IF.1.2
advertisement

Scaled Leadership
Standards-based Instruction – M.A.S.F
November 2015
S I L V I A A D A Y, D I S T R I C T I N S T R U C T I O N A L S U P E R V I S O R
Session Objectives
Participants will review how standards-based instruction looks
in Algebra 1, Geometry, and Algebra 2.
Participants will engage in simulations of best practices for
standards-based instruction and “look-fors” to include the
planning and its process, instructional frameworks and sample
instructional activities.
Let’s Do Some Math!
Which of the following numbers doesn't belong?
9, 16, 25, 43
Let us know what you think. And remember,
EXPLAIN YOUR REASONING!
What is Standards-based Instruction?
"Instruction involves directing students to appropriate learning
activities; guiding students to appropriate knowledge; helping
students rehearse, encode, and process information; monitoring
student performance; and providing feedback as to the
appropriateness of the student's learning activities and practice
performance.“
~Merrill, et al, 1996
Share your Thoughts!
Read each of the statements below and select which one(s) target
standard-based instruction.
Educators focus on prior teaching practices and prefer things to stay the way they are.
Instruction must remain straight to the point and narrow in understanding, unless
something forces it to change direction.
Instruction is explicitly aligned to standards to promote student achievement.
Placing emphasis on predetermined targeted goals provides guidance and support to
all stakeholders throughout the instructional process.
Standards-based Instruction
Standards-based instruction aligned to standards, includes appropriate
and meaningful activities that engage students in the learning process
and incorporates higher-order thinking skills.
It is essential to maintain alignment with the standard(s) while
planning instructional activities. Keywords identified in the
standard(s) guide educators in the instructional planning process by
bringing focus to what the student should know and be able to do.
Taking a Closer Look…
2nd Nine-Week Standards
Algebra 1
Geometry
Algebra 2
Taking a Closer Look…
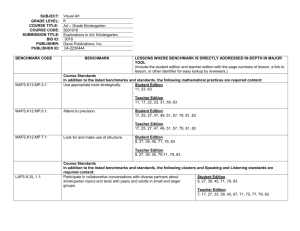
Algebra 1
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.2
Use function notation, evaluate functions for inputs in their domains, and interpret statements that use function notation in terms of a
context.
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.1
Understand that a function from one set (called the domain) to another set (called the range) assigns to each element of the domain
exactly one element of the range. If f is a function and x is an element of its domain, then f(x) denotes the output of f corresponding to
the input x. The graph of f is the graph of the equation y = f(x).
MAFS.912.F-IF.2.5
Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship it describes. For example, if the
function h(n) gives the number of person-hours it takes to assemble engines in a factory, then the positive integers would be an
appropriate domain for the function. ★
MAFS.912.F-IF.2.4
For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities,
and sketch graphs showing key features given a verbal description of the relationship. Key features include: intercepts; intervals where the
function is increasing, decreasing, positive, or negative; relative maximums and minimums; symmetries; end behavior; and periodicity. ★
MAFS.912.F-IF.3.9
Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal
descriptions). For example, given a graph of one quadratic function and an algebraic expression for another, say which has the larger
maximum.
Taking a Closer Look…
From the FSA Algebra 1 EOC Item Specifications
Algebra 1
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.2
From the FSA Algebra 1
EOC Item Specifications
Also Assesses MAFS.912.F-IF.1.1 and MAFS.912.F-IF.2.5
Pacing Guide - Topic IV
OBJECTIVES
I can:
Define relation, domain and range.
Determine the dependent variable, independent
variable, domain, and range
Explain that when ‘x’ is an element of the input of a
function f(x) represents the corresponding output.
Interpret the domain of a function within the realworld context given.
Use function notation.
Interpret statements that use function notation
within the real-world context given.
Use the definition of a function to determine if a
relationship is a function, given tables, graphs,
mapping diagrams, or sets of ordered pairs.
Evaluate functions that model a real-world context
for inputs in the domain.
Determine the feasible domain of a function that
models a real-world context.
Determine and relate the key features of a function
within a real-world context by examining the
function’s table.
Determine and relate the key features of a function
within a real-world context by examining the
function’s graph.
Use a given verbal description of the relationship
between two quantities to label key features of a
graph of a function that model the relationship.
Differentiate between different types of functions
using a variety of descriptors (e.g., graphically,
verbally, numerically, and algebraically).
Compare and contrast properties of two functions
using a variety of function representations (e.g.,
algebraic, graphic, numeric in tables, or verbal
descriptions).
Algebra 1
Topic IV
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.2
Also Assesses
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.1 and MAFS.912.F-IF.2.5
The points on the graph show the population data, in
millions, of the State of Florida for each decade from
1900 to 2000. The data are modeled by the function
𝑃 𝑥 = 506975(1.43)𝑥 , shown on the graph. What is
the domain of the graph of P(x) that is shown?
A. x ≥ 0
B. 1900 ≤ x ≤ 2000
C. All whole numbers
D. 0 ≤ x ≤ 10
From the FSA Algebra 1
EOC Item Specifications
Algebra 1
MAFS.912.F-IF.2.4
Pacing Guide - Topic IV
From the FSA Algebra 1
EOC Item Specifications
Also Assesses MAFS.912.F-IF.3.9
OBJECTIVES
I can:
Define relation, domain and range.
Determine the dependent variable, independent
variable, domain, and range
Explain that when ‘x’ is an element of the input of a
function f(x) represents the corresponding output.
Interpret the domain of a function within the realworld context given.
Use function notation.
Interpret statements that use function notation
within the real-world context given.
Use the definition of a function to determine if a
relationship is a function, given tables, graphs,
mapping diagrams, or sets of ordered pairs.
Evaluate functions that model a real-world context
for inputs in the domain.
Determine the feasible domain of a function that
models a real-world context.
Determine and relate the key features of a function
within a real-world context by examining the
function’s table.
Determine and relate the key features of a function
within a real-world context by examining the
function’s graph.
Use a given verbal description of the relationship
between two quantities to label key features of a
graph of a function that model the relationship.
Differentiate between different types of functions
using a variety of descriptors (e.g., graphically,
verbally, numerically, and algebraically).
Compare and contrast properties of two functions
using a variety of function representations (e.g.,
algebraic, graphic, numeric in tables, or verbal
descriptions).
I need to look for…
“Look-fors…”
Multiple Representations
Algebraic
Verbal/Narrative
Verbal explanation of processes and/or results
Explanation of choice in process
Making predictions
Interpreting meaning
Real World Context
Modeling
Tabular
Graphical
“Look-fors…”
Key Words
Explain
Justify
Interpret
Construct
Prove
Write
(e.g. write the equations
that models…)
Graph
Evaluate
Calculate
Predict
Compare
Create
Identify
Choose
Solve
Estimate
Model
Classify
(e.g. choose the best
explanation to why…)
Algebra 1
Textbook Resources
Algebra 1
Standard
Prior Knowledge
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.1
Topic IV
Academic Support
Resources
MAFS.8.F.1.1
MAFS.8.F.1.2
MAFS.8.F.1.3
Prior Knowledge
Checking for Readiness
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.2
(assessment items from
various sources)
MAFS.6.EE.1.2c
Sample Remediation Items
MAFS.912.F-IF.2.5
Checking for Readiness
1. Which relation is not a function?
A. {(1, −5), (2, −4), (1, −4)}
B. {(1, −5), (2, −4), (3, −3)}
C. {(1, −5), (2, −4), (3, 2)}
D. {(1, −5), (2, −4), (3, −4)}
2. Does the table represent a function? If so, state the domain and
range. If not, state why.
𝒙
𝒇(𝒙)
-5
0
-4
2
0
10
3
16
3. Determine whether the following situations represent functions.
Explain your reasoning. If the situation represents a function,
give the domain and range.
a) Each U.S. coin is mapped to its monetary value.
b) A $1, $5, $10, $20, $50, or $100 bill is mapped to all the
sets of coins that are the same total value as the bill.
4. https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/HSF/IF/A/1/tasks/624
Sample Remediation Items
1. Model the rule 𝑓(𝑥) = −2𝑥 + 1 with a table and a graph.
2. The production cost for 𝑔 graphing calculators is 𝐶(𝑔) = 3.7𝑔.
Evaluate the function at 𝑔 = 12. What does the value of the
function at 𝑔 = 12 represent?
3. Shari is printing a report. There are 120 sheets of paper in the
printer, and the number of sheets 𝑝 left after 𝑡 minutes of
printing is given by the function 𝑝(𝑡) = −6𝑡 + 100. a. How
long would it take the printer to use all 100 sheets of paper?
Explain how you found your answer.
1. The function 𝑘(𝑛) gives the number of person-hours it takes to
assemble 𝑛 engines in a factory. What is a reasonable domain
for 𝑘(𝑛)? Explain.
2. A farmer market sells two brands of cheese by the pound.
Brand A costs $4.19 per pound, and brand B costs $4.79 per
pound. Brand A can be purchased in any amount, whereas
brand B comes in prepackaged containers of either 0.5 pound
or 1 pound. Write a function rule that represents the revenue
earned for each of the brands and determine a reasonable
domain for each. Explain your answers.
https://www.illustrativemathematics.
org/contentstandards/HSF/IF/A/1/tasks/589
https://www.illustrativemathematics.
org/contentstandards/HSF/IF/A/1/tasks/598
https://www.illustrativemathematics.
org/contentstandards/HSF/IF/A/1/tasks/630
https://www.illustrativemathematics.
org/contentstandards/HSF/IF/A/1/tasks/635
https://learnzillion.com/search?utf8=
%E2%9C%93&query=8.F.A.1&pag
e=1&sort=Relevance&models%5B
%5D=LessonSet
https://learnzillion.com/resources/46
527
https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/HSF/IF/A/2/tasks/599
https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/HSF/IF/A/2/tasks/625
https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/HSF/IF/A/2/tasks/626
https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/HSF/IF/A/2/tasks/634
https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/HSF/IF/A/2/tasks/664
https://learnzillion.com/resources/46528
https://www.illustrativemathematics.
org/content-standards/tasks/631
https://www.illustrativemathematics.
org/content-standards/tasks/387
https://learnzillion.com/search?utf8=
%E2%9C%93&query=8.F.B.5&pag
e=1&sort=Relevance&models%5B
%5D=LessonSet
https://learnzillion.com/resources/46
531
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.1
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.2
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.2
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.2
MAFS.912.F-IF.2.5
MAFS.912.F-IF.2.5
Algebra 1
Topic IV
Getting Started
Misconceptions
Moving Forward
Examples of Student
Work at this Level
Almost There
Got It
Questions Eliciting
Thinking
Instructional
Implications
NOT Available for Algebra 2
Algebra 1
Topic IV
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.2
MAFS.912.F-IF.2.5
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.1
MFAS Formative Assessments
What about these examples?
Share your Thoughts!
"Education for the future has left the harbor and is already on the
open seas. Some educators are still clinging to the belief that the
ship hasn't left and are invested in business as usual. Some
educators are enjoying the freedom of the open seas ... excited
about the foreign ports and places they will visit.“
~Renata and Geoffrey Caine
Algebra 1
Topic IV
GIZMO CORRELATION
GIZMO TITLE
Function Machines 1 (Functions and Tables)
Function Machines 2 (Functions, Tables, and Graphs)
Function Machines 3 (Functions and Problem Solving)
Linear Functions
Introduction to Functions
Points, Lines, and Equations
STUDENT’S e-RESOURCES
KHAN ACADEMY
Functions
Khan Academy
Evaluating functions
Learn how to find the value of a function for a given input value.
Functions and equations
Understand the subtle differences and similarities between functions and equations. In this exercise, we will see how an equation can be turned into
a function.
Interpreting function
notation
Solve some word problems by interpreting expressions of modeling functions.
Introduction to the domain and
range of a function
Learn what the domain and the range of a function are. Practice finding the domain and the range of a function given its graph.
Determining the domain of a
function
Determine the domains of functions according to various considerations.
Recognizing functions
Recognizing functions.
Interpreting features of graphs
Interpret the graphs of functions in terms of the contexts that are modeled by the functions.
Average rate of change
Learn what's the average rate of change of a function and how to find it over given intervals.
Supplemental Resources
Teacher Directed Supplemental Instruction
2015-2016 MDCPS 1200310 Algebra 1 MAFS Full Year: Teacher Directed
2015-2016 MDCPS 1206310 Geometry MAFS Full Year: Teacher Directed
2015-2016 MDCPS 1200330 Algebra 2 MAFS Full Year: Teacher Directed
Teacher Directed Academic Support Courses
Algebra 1 MAFS Academic Support
Geometry MAFS Academic Support
Algebra 2 MAFS Academic Support
Virtual Tutor Courses
VT-FL-EOC-Algebra 1 - MAFS
VT-FL-EOC-Algebra 1- NGSSS
VT-FL-EOC-Algebra 2 - MAFS
VT-FL-EOC-Geometry - MAFS
VT-FL-PERT-Math
NEW!
Assessment Resources
Hand Held Scientific Calculators
TI-30Xa
fx – 260 Solar
Updated October 2, 2015
fx-82 Solar
Sharp EL-510R
Sharp EL-510RN
Please note as it relates to the following statement extracted from attachment number 3 page 1 last paragraph in the
WB 18469.
“Schools may use calculators not on this list if district Mathematics specialists determine they meet the specifications on
the following page. FDOE will not review or approve additional models not listed above.”
The mathematics department will NOT recommend/approve any calculator that is not already included on the FDOE
approved list as we do not have the man power required to vet calculators for FSA compliance.
Briefing ID #: 18469
Topic Assessments
Pacing
Traditional
Block
Date(s)
14
7
Topic IV Assessment Window
11/02/15 – 11/20/15
11/02/15 – 11/20/15
11/13/15 – 11/20/15
• Data from Topic Assessments should be used to make informed decisions regarding remediation and
enrichment.
• Topic Assessments are housed in Gateway 2 Data (G2D), and can be accessed at
ttps://tg.dadeschools.net through Google Chrome.
o First time G2D users, enter your employee number as your username and enter MiamiDade2015*
as your password; please note that the password is case sensitive.
o From main menu options, select Assessment.
o Click on the expand button of the District Assessment tile.
o Select the applicable Grade(s) and Mathematics for the subject. For high school, in addition to the
subject, select the course(s). Click on Search.
o For further instructions, you may click on Help and select Thinkgate TV; Thinkgate 101 provides
overview of the key capabilities of and how to use the features available through the platform.
• Problems accessing G2D should be directed to http://oada.dadeschools.net/G2D/G2D.html
Briefing ID #: 18469
FSA Mid-Year Assessments
November 16 - December 18
Algebra 1
Assessment Format
Computer Base Test
Multiple Choice
Assessment Platform
Thinkgate
NEW!
Geometry
Algebra 2
Statistics &
The Number System
Congruence, Similarity, Right
Triangles, & Trigonometry
Statistics, Probability, &
The Number System
MAFS.912.S-ID.1.1
MAFS.912.S-ID.1.2
MAFS.912.S-ID.1.3
MAFS.912.S-ID.2.5
MAFS.912.N-RN.1.1
MAFS.912.N-RN.1.2
MAFS.912.N-RN.2.3
MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1
MAFS.912.G-CO.1.2
MAFS.912.G-CO.1.3
MAFS.912.G-CO.1.4
MAFS.912.G-CO.1.5
MAFS.912.G-CO.2.6
MAFS.912.G-CO.2.7
MAFS.912.G-CO.2.8
MAFS.912.G-CO.3.9
MAFS.912.G-CO.3.10
MAFS.912.G-CO.4.12
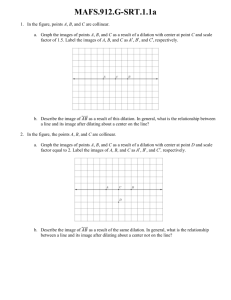
MAFS.912.G-SRT.1.1a
MAFS.912.G-SRT.1.1b
MAFS.912.N-CN.1.1
MAFS.912.N-CN.1.2
MAFS.912.N-RN.1.1
MAFS.912.N-RN.1.2
MAFS.912.S-IC.1.1
MAFS.912.S-IC.1.2
MAFS.912.S-IC.2.3
MAFS.912.S-IC.2.4
MAFS.912.S-IC.2.5
MAFS.912.S-IC.2.6
MAFS.912.S-ID.1.4
MAFS.912.S-CP.1.1
MAFS.912.S-CP.1.2
MAFS.912.S-CP.1.3
MAFS.912.S-CP.1.4
MAFS.912.S-CP.1.5
MAFS.912.S-CP.2.6
MAFS.912.S-CP.2.7
Algebra & Modeling
MAFS.912.A-SSE.1.1a
MAFS.912.A-CED.1.1
MAFS.912.A-CED.1.3
MAFS.912.A-CED.1.4
MAFS.912.A-REI.1.1
MAFS.912.A-REI.2.3
Functions & Modeling
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.1
MAFS.912.F-IF.1.2
Circles, Geometric
Measurement, & Geometric
Properties with Equations
MAFS.912.G-GPE.2.7
Functions & Modeling
MAFS.912.F-IF.2.4
MAFS.912.F-IF.2.5
MAFS.912.F-IF.3.9
Math in the News!
Briefing ID #: 18403
Thank You!