Direct and online marketing
advertisement

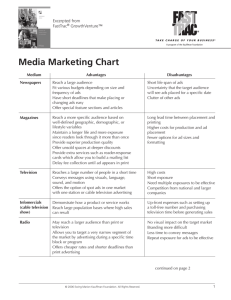
Ch. 17 DIRECT AND ONLINE MARKETING Building Direct Customer Relationships Allison Reilly Jordan Zook Billy Scheid OBJECTIVES 1. Define direct marketing and discuss its benefits to customers and companies 2. Identify and discuss the major forms of direct marketing 3. Explain how companies have responded to the internet and other powerful new technologies with online marketing strategies 4. Discuss how companies go about conducting marketing to profitably deliver more value to customers 5. Overview the public policy and ethical issues presented by direct marketing DIRECT MARKETING • Connecting directly with carefully targeted segments or individual consumers, often on a one-to-one, interactive basis • Direct marketers seek a direct, immediate, and measurable consumer response as well as brand and relationship building BENEFITS TO BUYERS • Convenient, easy, and private • Customers don’t have to trek through stores and wait in lines to purchase a product BENEFITS TO SELLERS • Powerful tool for building customer relationships • Provides a one-to-one nature of direct marketing • Companies can communicate by phone or online to personalize a customers product and experience • Offers a low-cost, efficient, speedy alternative for reaching their markets CUSTOMER DATABASES • An organized collection of comprehensive data about individual customers or prospects, including geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavior data • Useful in creating different versions of catalogs and emails tailored to the individuals needs • Helps locate good potential customers and generate sales leads • Important tool for building stronger long-term customer relationships • Walmart captures data from more than 1 million customer transactions every HOUR, resulting in a database with more than 2.5 petabytes of data….or 1,200 billion pages of standard print text. FORMS OF DIRECT MARKETING • • • • Direct Mail Catalog Telemarketing Direct-Response Television • Kiosk DIRECT MAIL • Marketing that occurs by sending an offer, announcement, reminder, or other item directly to a person at a particular address • The largest direct marketing medium • Permits high target-market selectivity, can be personalized, is flexible and allows the easy measurement of results • To reduce loosing money from spam, marketers use a permission-based program CATALOG • Direct marketing through print, video or digital catalogs that are mailed to select customers, made available in stores, or presented online • Catalogs are becoming more and more digital • 70 percent of online purchases are driven by catalogs TELEMARKETING DIRECTRESPONSE TELEVISION • Using the telephone to sell directly to customers • Last year, telemarking accounted for nearly 14.9 percent of all direct-marketing • The Do-Not-Call legislation has hurt telemarketing so some marketers develop an “opt-in” option and give customers special offers • Direct marketing via television, including direct-response television advertising (or infomercials) and interactive television advertising • Direct-response advertsing : 60-120 seconds • Infomercials: Full 30 minutes • Recently appearing on mobile, online, and social media platforms KIOSKS • Old-fashioned vending machines but so much more • Located in stores, airports, hotels, college campus’, malls, and more ONLINE MARKETING • Efforts to market products and services and build customer relationships over the internet • The fastest growing form of direct marketing MARKETING AND THE INTERNET • The internet has fundamentally changed customers’ notions of convenience, speed, price, product information and service • Click-only companies: Operate online only and have no actual walk-in store (Amazon, Netflix, Facebook, twitter) • Click-and-mortar companies: Companies that have added online marketing to their operations ONLINE MARKETING DOMAINS BUSINESS-TOCONSUMER BUSINESS-TOBUSINESS CONSUMER-TOCONSUMER CONSUMERTO-BUSINESS • Businesses selling goods and services online to final consumers • Businesses using online marketing to reach new business customer s, serve current customers more effectively, and obtain buying efficiencies and better prices (Ex. Sysco) • Online exchanges of goods and information between final consumers (Ex. Craigslist, eBay) • Online exchanges in which consumers search out sellers, learn about their offers, initiate purchases, and sometimes even drive transaction terms (Ex. Priceline.com, Complaints.com) EXAMPLES OF ONLINE MARKETING : • • • • • Web sites Ads and Promos Social Networks E-mail Mobile marketing SETTING UP AN ONLINE MARKETING PRESENCE Creating Web Sites: • Corporate (or brand) Web site : A Web site designed to build customers feedback, and supplement other sales channels rather than sell the company’s products directly (Wonka.com) • Marketing Web site : A Web site that interacts with consumers to move them closer to a direct purchase or other marketing outcome (Samsung.com) PLACING ADS AND PROMOTIONS ONLINE • As consumers spend more and more time on the internet, companies are shifting more of their marketing dollars to online advertising • Online Advertising : advertising that appears while consumers are browsing the internet, including display ads, search related ads, online classifieds, and other forms • The largest form of advertising is search-related ads which accounted for 46.5 percent of all online advertising (Ex. Ads alongside Google) • Viral Marketing : The internet version of word-of-mouth marketing: a Website, video, e-mail message, or other marketing event that is so infectious that customers will seek it out or pass it along to friends CREATING OR PARTICIPATING IN ONLINE SOCIAL NETWORKS • Online Social Networks : Online communities where people congregate, socialize, and exchange views and information • They can participate in existing communities or they can create their own (joining is easier) • Dunkin’ Donuts, Harley – Davidson to Nissan and Victoria’s Secret have created YouTube channels • Marketers need to be wary of intruding on these networks and must learn to become a valued part of their online experience SENDING E-MAIL MOBILE MARKETING • Sending highly targeted, highly personalized, relationship building marketing message via E-mail • To address the concern of Spam, marketers now practice “permissionbased e-mail marketing” • Marketing to on-the-go consumers through mobile phones, smartphones, tablets, other mobile communication devices • Involves placing search ads, display ads, or videos on relevant mobile Internet sites and online communities such as Facebook or YouTube • May also involve texting promos to consumers PUBLIC POLICY ISSUES IN DIRECT MARKETING • Marketers must be aware of Irritation, Unfairness, Deception, and Fraud. • The FBI’s internet Crime Complaint Center provides consumers with a convenient way to alert authorities to suspected violations • One example of fraud is phishing : a type of identity theft that uses deceptive e-mails and fraudulent online sites to fool users into divulging their personal data • Another consumer concern is online security • Another marketers concern is access by vulnerable or unauthorized groups (Minors getting access to adult-oriented material) • Some critics worry that marketers may know too much about consumers lives and use that for an unfair advantage • The direct marketing industry is addressing public policy issues THE END