EST REVIEW What is a Plant and Seedless Plants
advertisement

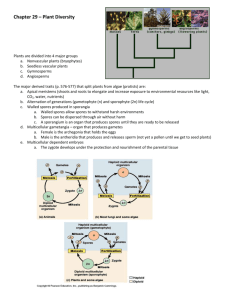
1) Green substance, or chemical, that captures solar energy. chlorophyll 2) Plants without different types of tissue for carrying water and nutrients. nonvascular 3) Stage during which plants produce spores. sporophyte 4) Chemical reaction that produces sugar from CO2, H20, and light energy. photosynthesis 5) Cells with a nucleus and other organelles. eukaryotic 6) Earlier, unicellular ancestor of plants. green algae 7) Capable of producing its own food (through photosynthesis). autotrophic 8) Non-flowering plants that hold their seeds in a cone, rather than in a fruit. gymnosperm 9) Organelle that stores water within a cell. vacuole 10) Outer cell layer that allows certain things in or out. cell membrane 11) Rigid structure that surrounds a plant cell. cell wall 12) Organelle that contains chlorophyll. chloroplast 13) Stage during which a plant produces its sex cells, called gametes. gametophyte 14) An organism consisting of more than one cell. multicellular 15) Plants with specialized tissue which transports substances, similar to the way our veins transport blood. vascular 16) Flowering plants that become pollinated before producing seeds and fruit. angiosperm 17) Waxy outer coating of a leaf, which helps it retain its moisture. cuticle 18) Mini-organ that carries out a specific function within a cell. organelle 19) Ability of a membrane to allow certain substances in and out. semi-permeable 20) A woody carbohydrate (sugar) which makes the cell wall. cellulose Eukaryotic cells have nucleus and other organelles Multicellular made of multiple cells Autotrophic make their own food using chlorophyll (through photosynthesis) Terrestrial almost all live on land Cell wall made of a carbohydrate called cellulose (a type of sugar) Energy storage stored as sugars (short term) and starch (longer term) Remember, a lot of these organelles are hard to see under a light microscope because they are clear. Leaf cells under a regular light microscope (400x) A single plant cell under the high magnification of an electron microscope What is this? What is this? cell membrane cell wall cytoplasm vacuole nucleus DNA chloroplasts Each group define one term: A. organelles Mini “organs” within the cell B. cell wall Rigid outer structure of the cell; made of cellulose C. cell membrane Flexible layer within the cell wall; allows materials in and out (semi-permeable) D. cytoplasm Liquid gel within the membrane E. vacuole Water storage F. nucleus Holds the DNA G. chloroplasts Green organelles that perform photosynthesis Draw what you see! Different types of Green Algae • Single-celled or colonial • Actually considered protists, not plants • Evolved around 425 million years ago Modern Gymnosperm Primitive Plant (kelp) • Photosynthesis (with chlorophyll) • Cell wall made of cellulose • Both store energy as sugar and starch • Cell wall • Eukaryotic • Multicellular • Waxy cuticle • Autotrophic Plants Vascular Seeds Angiosperm Nonvascular Seedless Gymnosperm Ferns Reproduce with spores • Sexual reproduction • Flowering • Sexual reproduction • Seeds in fruit • Coniferous • Seeds in cone Present Algae Moss, liverwort, hornwort, etc. • Reproduce with spores • Obtains food and water through diffusion only Past 10 min. 1) What is the overall purpose of photosynthesis? 2) How do nonvascular plants transport water? 3) What is one way plants keep from drying out? Mosses What do all these plants have in common? Liverwort Hornwort Transportation of nutrients and water via cell-by-cell contact Equilibrium So moss just absorbs water through diffusion. But how do other plants get water out to the tips of the branches? Water molecules enter through the roots and travel out through veins of the leaf Then, water diffuses from cell to cell until every cell has the water it needs to carry out… PHOTOSYNTHESIS Can you see the vascular tissue? Ferns Fiddleheads sori (hold the spores) Seedless vascular Nonvascular Mosses, liverworts, and hornworts First plants to adapt to life on land (very simple) No vascular tissue Sperm has flagella and swim to fertilize egg Absorb nutrients and water through a rhizoid (tiny root hairs) Sexual reproduction (with spores) Ferns and horsetails First plants to have vascular tissue (Xylem and Phloem) Vascular tissue Sperm with flagella Rhizome (thick underground stem, or root) Sexual reproduction (with spores) Formed vast forests 300 MYA. Those remains are now coal Rhizoids “root-like” Rhizome Thick, underground stem, which roots grow from. Rhizomes store energy for the next growing season. Fern rhizome ginger root Plants with rhizomes are hard to get rid of because even when the stems and roots die off, it can still shoot out more roots the next year. Rhizoid Rhizome • Horizontal underground • Tiny “root-like” Absorb stem water and hairs nutrients; • Found in ferns and other • Found in Undervascular plants nonvascular ground plants (moss) • Stores energy for the winter Sporophyte Produces spores which grow into a male or female gametophyte. contains spores Gametophyte Produces gametes (sperm and egg) Draw what you see in the space provided in Part IV: sporophytes gametophytes Describe what each part does. Ferns fiddleheads or leaves with spores Moss with sporophytes Spores inside the capsule of the sporophyte Sori on underside of fern frond Operculum lid of the spore capsule Peristomal teeth hold the lid in place Thousands of spores inside each sporangium Spores inside the capsule of the sporophyte Peristomal teeth hold the lid in place Operculum lid of the spore capsule