Chapter 5, Section 1
advertisement

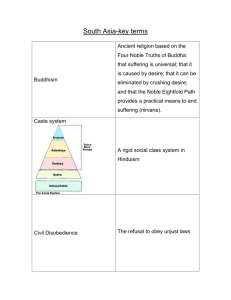
Exploring the Religions of Our World Chapter 5: Hinduism Chapter 5, Introduction a a Chapter 5, Introduction cont. The Basics • 95% of Hindus live in India • Hinduism emerged as a religion, it did not begin with a founder or particular event • Hinduism shares no doctrinal statements • Hindus hold that no one religion can possibly claim knowledge of absolute truth , which is why Hinduism is often called a lifestyle rather than a religion Periods of Hindu History Chapter 5, Introduction cont. Chapter 5, Section 1: A Brief History of Hinduism a a a Chapter 5, Section 1: A Brief History of Hinduism cont. a a You Tube Video: Hinduism National Geographic: Religions of the World: Hinduism Chapter 5, Section 1: A Brief History of Hinduism cont. Major developments of: The Indus Valley Period (3000-1500 BCE) • Emphasis on ritual purity • Focus on fertility & regeneration • The practice of meditation • Emphasis on peacefulness • Contributed the Vedas of divine knowledge Chapter 5, Section 1: A Brief History of Hinduism cont. Major developments of: The Brahminical Period (1500-300 BCE) • Ritual sacrifices by the Brahmins (priests) • Home ritual sacrifices • Gurus (teachers) train disciples in personal devotion to the gods • The gods Shiva & Vishnu gain in prominence • Rise of ascetical practices Chapter 5, Section 1: A Brief History of Hinduism cont. Major developments of: The Classical Period (300-1200 CE) • • • • Establishment of Hindu temples Growth of home-based rituals The Vedas become the authoritative scripture Emphasis shifts from the transcendent to the immanent • Emphasis on personal transformation • The concepts of karma & reincarnation emerge • The evolution of the caste system Chapter 5, Section 1: A Brief History of Hinduism cont. Jainism: • Founded by Mahavira in the sixth century BCE • Contains elements of Hinduism & Buddhism • Practice non-violence or non-injury • Vegan, commitment to not harm any living thing Chapter 5, Section 1 Review Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What was the Aryan influence on the origins of Hinduism? Who were Brahmins & what was their main function? What makes up the shruti? Describe Jainism. Why are the years 300 to 1200 CE known as the Classical Period of Hinduism? What happened when the Muslims came to India? What are some of the beliefs major Hindu figures of the nineteenth & twentieth centuries advocated? Describe one movement of Hinduism that contributed to its expansion outside of India. Chapter 5, Section 2: Sacred Stories & Scriptures *Shruti—more sacred; revealed by gods to ancient seers; don’t change; “that which is to be heard” Smriti—“that which is to be remembered”; less authoritative; passed orally; more popular Shruti Scriptures Vedas—earliest; Aryan era; hymns; fire sacrifice; 4; exclusive; priests; memory Rig Veda—oldest; most sacred; 1,000 hymns & mantras; Sanskrit; 1300 BCE Soma Veda—900 BCE; sacrificial hymns Yajur Veda—prose; priestly sacrificial instruction Atharva Veda—700 BCE; domestic hymns; healing for sacrificial mistakes Upanishads—personal action & cycle of rebirth; liberation; relationship between Brahman (Ultimate Reality) & atman (soul); “to sit down beside”; guru to student Svetaketu—father instruction; being & soul not seen, heard, thought; salt water; Chandogya Upanishad Chapter 5, Section 2: Sacred Stories & Scriptures cont. Smriti Scriptures *Mahabharata—Hindu epic; 200k verses; family war over inheritance; Krishna; avatar of Vishnu; 9 avatars & 10th end of world; supports family Bhagavad Gita—contained in; most popular; brother Arjuna; fight as warrior caste or non-violence; debate with charioteer Krishna; disinterested love in personal duties Ramayana—2nd greatest Hindu epic; Prince Rama; exiled with wife & brother; Ravana kidnaps wife; Rama rescues & becomes king Puranas—stories about 3 Hindu gods Brahma, Vishnu, & Shiva; creation; world’s history; popular with lower castes; miracles & personal devotion Knowledge of the Heart Svetaketu—12 years of studying; head knowledge but not heart; nyagrodha tree; fruit, seed, nothing; essence of all creation is nothingness & flow You Tube Video: Hinduism Hindu Scriptures Chapter 5, Section 2: Sacred Stories & Scriptures cont. Shruti Scriptures (the most sacred) 1. Rig Veda - hymns to various gods The The Holy Vedas Vedasc 2. Soma Veda - hymns chanted at sacrifices 3. Yajur Veda - instructions for priests regarding sacrifices 4. Atharva Veda - hymns, charms, spells & incantations for domestic use Chapter 5, Section 2: Sacred Stories & Scriptures cont. Shruti Scriptures – also… Concerned with the cycle of rebirth The The Upanishads Upanishads The mystical relationship between Brahman (Ultimate Reality of all living things) & atman (soul) Often shared in a dialogue between guru & student Chapter 5, Section 2 Review Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. What are shruti scriptures? What are smriti scriptures? What is the dilemma of Arjuna in the Bhagavad Gita? What are the Puranas? Chapter 5, Section 3: Beliefs & Practices No absolute beliefs & practices but some that most hold: Beliefs—deities, cycle of rebirth, sacredness of life Practices—communal life, caste system, stages of life Deities 330 million = so many that they cannot be counted All images of Brahman = Absolute Reality, all pervading life force of the universe, material & immaterial, one essence Human attributes but not Brahman which is transcendent Even 5 senses fall short! Primary forms = life cycle—Brahma (Create), Vishnu (Preserve), Shiva (Destroy) Avatars—incarnation of a deity, form of Brahman along with primary forms Krishna & Rama are avatars of Vishnu Gautama the Buddha also of Vishnu—founder of Buddhism Chapter 5, Section 3: Beliefs & Practices cont. Female Goddesses Female forms of Brahman Parvati—Shiva; love, fertility, devotion, divine power & strength or standing alone Devi = Great Goddess, Durga = Warrior, Kali = justice deliverer Saraswati—Brahma; learning, literature, & music Lakshmi—Vishnu; prosperity, good fortune, & beauty Atman Individuals essential nature, real self, & innermost soul Identical to Brahman; goal is union with Brahman = union with atman Moksha = liberation from the endless cycle of rebirth Hidden & elusive so physical & mental discipline Body, mind, emotions not included since are maya = illusions & passing Chapter 5, Section 3: Beliefs & Practices cont. Cycle of Rebirth Life is cyclical not linear; nature exemplifies Karma determines cycle; moral law of cause & effect; consequences Samsara = cycle of birth, life, death, rebirth (reincarnation or transmigration) Eternal atman lives on in another body determined by karma Determined not by judge but by nature; seed Moksha = liberation from samsara by removing karmic residue due to rebirth Yoga = 3 disciplines or practices for doing so; training of entire person; body, mind, spirit; goal is to make an identity between Brahman & atman Karma yoga (Path of Action)—selfless service to others; purge motives; even desire for liberation; action Jnana yoga (Path of Knowledge)—learning, thinking, & viewing self in 3rd person; meditation Bhakti yoga (Path of Devotion)—pure, long devotion to Brahman; most Hindus; stresses immanence over transcendence Chapter 5, Section 3: Beliefs & Practices cont. The Sacredness of Life Brahman is in all things so all things are sacred Ahimsa = desire to not harm any form of life; basis of non-violence, vegetarianism, & cows being sacred Satyagraha = application by Mohandas Gandhi to British attacks in liberating Caste System Diverse beliefs but more uniform actions 4 stages & 4 pursuits of life in context of 3-4-5 castes; high to low Tolerant of individual beliefs but not of straying from castes Aryans introduced 3, 4th added later, 5th so low not even part of Related to karma & samsara—caste depends on actions of previous life Brahmins—priests; highest; pure, wise, learned families Kshatriyas—warriors; protect & rule Vaishya—farmers & merchants; provide Shudra—servants; lowest; serve other castes; no scripture study Chapter 5, Section 3: Beliefs & Practices cont. Caste System cont. Asprishya—“untouchables”; defiled families; degrading work; garbage men; vile actions in previous life; Gandhi sought to raise; discrimination illegal now Caste system still has a strong hold today; bound by birth until death to caste & duties of caste (clothing, habits, religious practices) How one lives differs but not reasons for living Dharma—social & caste duties Artha—material/political wealth Kama—artictic, recreational, sensual Moksha—liberation from cycle The Stages of Life Ashramas; 4; general patterns of life; Hindu males traditionally; women called to be daughters, wives, & mothers under the protection & support of a man; 1st 3 castes; most only 2; must fulfill 1 & 2 if going to pursue 3 & 4 Bhahmancarin—learn Hindu traditions from a guru Grihastha—householder, marry, family, contribute to society Vanaprastha—”forest dweller”, slowly move away from life as a hermit Sannyasin—spiritual pilgrim, renounce all, pursue moksha You Tube Video: Hinduism Crash Course: Hinduism Chapter 5, Section 3: Beliefs & Practices cont. Most Hindus hold these beliefs in common, though they are not “doctrines”: The caste system Millions of gods & goddesses The sacredness of life The cycle of rebirth The four stages of life Chapter 5, Section 3: Beliefs & Practices cont. Brahman = one Ultimate Reality or Absolute Reality which: Cannot be grasped by the five senses Is manifested in gods & goddesses Is transcendent Includes everything material and immaterial Has no attributes Is the “lifeForce” of the universe Chapter 5, Section 3: Beliefs & Practices cont. 3 primary forms of Brahman 1. Brahma is the Creator god 2. Vishnu is the Preserving god 3. Shiva is the Destroying god An avatar is the incarnation of personification of a god or goddess e.g. Krishna & Ganesh Chapter 5, Section 3: Beliefs & Practices cont. Atman: • Is the “real self” (mind, body, & emotions are “maya” or illusions) • Hindus strive for release from maya in order to achieve union with Brahman/atman • Moksha (liberation) is achieved through rigorous physical & mental discipline Chapter 5, Section 3: Beliefs & Practices cont. Samsara - the cycle of rebirth Rebirth Breaking the cycle: Knowledge Birth Karma Death Good deeds Devotion Chapter 5, Section 3: Beliefs & Practices cont. Moksha The major pursuits of life: Pursuit of liberation from the cycle of rebirth through actions, thoughts, & devotions Artha Dharma One’s duties in life, especially as dictated by caste Pursuit of both material & political wealth Kama Pursuit of artistic, recreational, & sensual pleasure Chapter 5, Section 3 Review Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is meant by Brahman? How is Brahman linked to atman? What are the three primary forms of Brahman? Describe the Hindu cycle of rebirth related to the three paths of liberation. Name & describe the four stages of life for Hindu castes; also define “untouchables”. Name & describe the four stages of life for Hindu males. What are the four life goals for a Hindu male in the first three castes? Chapter 5, Section 4: Sacred Times n a a n a Chapter 5, Section 4: Sacred Times cont. a n a a n a You Tube Video: Hinduism a Chapter 5, Section 4: Sacred Times cont. Sikhism • A blending of Hinduism and Islam • Is monotheistic • Beliefs: karma, samsara, moksha, equality • Rejects: caste system, idol worship • Signs of devotion: unshorn hair, comb, short pants, steel bracelet, short sword • Many have a desire to found and establish their own homeland Chapter 5, Section 4 Review Questions 1. 2. 3. How do Hindus compensate for the different number of days between solar & lunar calendars? What do the festivals of Diwali & Holi celebrate? How are they celebrated? Name & explain at least two of the sixteen stages of the Hindu life cycle. Chapter 5, Section 5: Sacred Places & Spaces n a a n a a n a Chapter 5, Section 5: Sacred Places & Spaces cont. a n a a n a a n a You Tube Video: Hinduism a Chapter 5, Section 5: Sacred Places & Spaces cont. Temples Home shrines many images of gods/goddesses many images of gods/goddesses Ganges River symbol of life w/o end ritual bathing Puja honoring the gods Chapter 5, Section 5 Review Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. Why is everything sacred to Hindu’s? Describe a home puja and its purpose? How does a temple puja differ from a home puja? Why is the Ganges River the most sacred place for Hindus? Chapter 5, Section 6: Hindusim Through a Catholic Lens n n a a n a a a Chapter 5, Section 6: Hinduism through a Catholic Lens cont. n a n a a n n a a a a You Tube Video: Hinduism a Chapter 5, Section 6: Hinduism through a Catholic Lens cont. Similarities: • Toleration of religious diversity • Pursuing social issues • Honoring Jesus and his teachings • The tradition of depicting and venerating religious images Chapter 5, Section 6: Hinduism through a Catholic Lens cont. Differences: • Karma • Reincarnation • The caste system • Jesus as the one and only incarnation of God Chapter 5, Section 6 Review Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. In dialoguing about human dignity, what topic in particular do Hindus have in mind? Name at least three views of Jesus that can be found among Hindus. Name similar views Catholics and Hindus have about Jesus. List three functions of religious imagery. Chapter 5: Conclusion n a Chapter 5: Hinduism Vocabulary Brahmins Shruti Gurus Bhakti Sanskrit Karma Caste system Mantra Hare Krishnas Avatar Brahman Transcendent Atman Maya Samsara Yoga Satyagraha Puja Iconoclasm Devas Chapter 4 Islam – Vocabulary Definitions a–a Chapter 5 Review Questions (Extra Credit) Section 1: 1. a Chapter 5 Review Questions cont. (Extra Credit) a Section 2: 13. a Section 3: 17. a 11. Chapter 5 Review Questions cont. (Extra Credit) Section 4: 21. a Section 5: 23. a Section 6: 26. a