ch 21 The Rise of Progressivism
advertisement
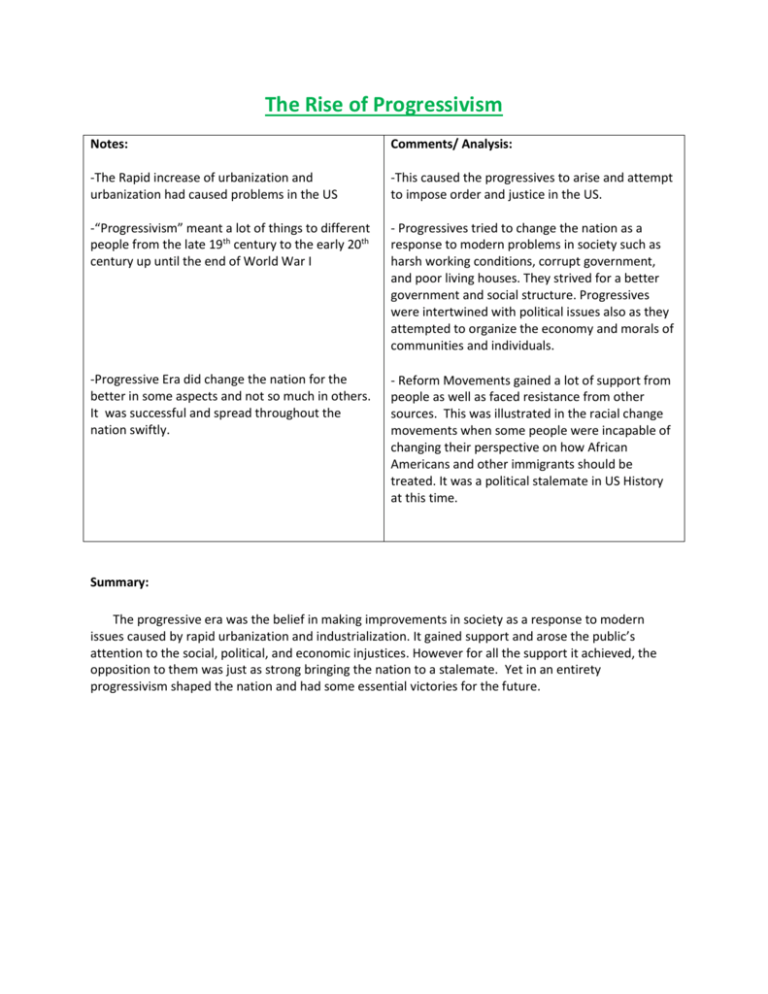
The Rise of Progressivism Notes: Comments/ Analysis: -The Rapid increase of urbanization and urbanization had caused problems in the US -This caused the progressives to arise and attempt to impose order and justice in the US. -“Progressivism” meant a lot of things to different people from the late 19th century to the early 20th century up until the end of World War I - Progressives tried to change the nation as a response to modern problems in society such as harsh working conditions, corrupt government, and poor living houses. They strived for a better government and social structure. Progressives were intertwined with political issues also as they attempted to organize the economy and morals of communities and individuals. -Progressive Era did change the nation for the better in some aspects and not so much in others. It was successful and spread throughout the nation swiftly. - Reform Movements gained a lot of support from people as well as faced resistance from other sources. This was illustrated in the racial change movements when some people were incapable of changing their perspective on how African Americans and other immigrants should be treated. It was a political stalemate in US History at this time. Summary: The progressive era was the belief in making improvements in society as a response to modern issues caused by rapid urbanization and industrialization. It gained support and arose the public’s attention to the social, political, and economic injustices. However for all the support it achieved, the opposition to them was just as strong bringing the nation to a stalemate. Yet in an entirety progressivism shaped the nation and had some essential victories for the future. Key Terms: pg 566- 589 The Progressive Impulse Belief in Progress (566) – belief tht society is capable of improving through development of growth Varieties of Progressivism “Antimonopoly” (566) – fear of concentrated power and the desire to disperse authority and wealth Other Progressivism Impulses (566) – individuals were part of a web of social relationships Faith in Knowledge (566) – social order is a result of intelligent social order and rational procedures The Muckrakers Ida Tarbell (566) – muckraker who focused on Standard Oil Trusts Lincoln Steffens (566) – influential muckraker for McCure’s magazine; portrayed machine gov and boss rule= arose feelings of want 4 public reform Muckrakers (566) – journalists who directed the public’s attention to social, political, and economic injustices The Social Gospel Progressive Sentiment (567) – outrage at social and economic injustice at societies lack of human sense of social responsibility Social Gospel (568) – early 20th century; movement within protestantism that’s goal was to redeem the nation’s cities (provided material and spiritual aid to the cities) ; dominant elementin social reform The Settlement House Movement Jane Addams and Hull House (569) – it was opened in Chicago 1889; it was the settlement house; model for 400 other institutions in the nation Settlement Houses (569) – middle class people settled in the inner cities; sought to help immigrants adapt to the language and customs of their new countries The Allure of Expertise Rise of Social Sciences (571) – use of scientific techniques to study of society and its institutions The Professions American Medical Association (572) –1901, national professional society of doctors considered professionally trained, followed strict scientific standards for admission to the practice of medicine= state and local gov passed laws requiring tht physicians be licensed National Association of Manufacturers (572) – 1895, business men created the association to support schools of business administration People were beginning to revolutionize all aspects of society starting with having qualified workers for each profession Women and the Professions Female-Dominated Professions (572) – school teachers (90%) , often 4 black women it was the only available profession/ nursing dominated by women 2 Women and Reform The “New Women” Socioeconomic Origins of New Women (573) – children were going to school at an earlier age, income producing activity was no longer at home but in factories, technology advances made housework easier and faster= women looking 4 activities outside of the house cause of growing free time “Boston Marriages” (573) – women who chose to never marry cause they felt tht it was the only way to continue their roles in the public; lived with other women instead in long term relationships The Club Women GFWC (573) – General Federation of Women’s Club; coordinated activities of local organizations; established in 1892 Women Public Space (574) – women wanted to be able to act and express themselves in public without openly challenging male dominated order Women’s Trade Union League (575) – 1903; female union workers and upper class reformers; raised $ to support strikes, marched on picket lines, bailed striking women out of jail and held public meeting on behalf of the women workers Women Suffrage Women Suffrage Movement (575) – lrgest single reform movement in the progressive era= women deserved the same rights as men including the right to vote, challenged the women’s sphere in which the omens 1st and main priority was as mothers and wives NAWSA (576) – National American Women Suffrage Association; 1893, leaders of the Women Suffrage Movement; gained support and made it possible for the movement to gain support Conservative Arguments (576) – support for the suffrage movement also came from people (middle class part); thought tht if blacks and immigrants got access to franchise then it would make it a matter of justice for edu, well born women to vote 19th Amendment (576) – 1920; guaranteed political rights of women throughout the nation Equal Rights Amendment (576) – some women felt tht 19th amendment wasn’t enough and tht there should be one tht provided clear legal protection tht would prohibit discrimination based on gender The Assault on the Parties Reforming Government (577) – attempt to reform political institutions because they were seen as outdated, corrupt, and insufficient; 1st step to gov reform was to eliminate political party dominance Early Attacks Attacking Party Rule (577) – 1890s people felt tht party power had to prevented by placing power in the hands of nonpartisan and nonelective officials & increasing g the power of the people Municipal Reform Middle-Class Progressives (578) – saw politics as a demeaning activity snd avoided it, but now aristocrats were taking an interest in the gov New Forms of Governance Commission Plan (579) – when the mayor and council of cities were replaced by an elected nonpartisan commission City-Manager Plan (579) –form of municipal reform; elected officials hired an outside expert (professional businessman) to take charge of the gov in order to avoid corruption Statehouse Progressivism Initiative and Referendum (580) – 1890s; initiative: allowed reformers to circulate state legislatures by submitting new legislation directly to voters & refer: method in which legislature could return to electorate w/ approval Direct Primary and Recall (580) – efforts to limit the power of party and improve quality of elected officials Robert La Follette (580) – state level reformer, elected governor in 1900= passed laws to regulate the workplaces/ railroads/ utilities= spread public awareness of progressive goals Parties and Interest Groups Decline of Party Influence (581) – decline in voters 81% in 1800s to 59% 1912= other powers like professional/ trade associations gained the lost power Sources of Progressive Reform Labor, the Machine, and Reform Triangle Shirtwaist Fire (582) –1911= fire caught in a factory in NY, 146 (mainly women) workers died= state commission looked at workplaces because so many deaths were caused by the locked doors by the management Western Progressives Sources of W Progressivism (583) – Federal gov main source (not state/local gov) = political parties had power in the W African Americans and Reform W.E.B. Du Bois (583) – chief spokesman for African Americans race relationships with Washington= goal to eliminate the prejudice and injustices NAACP Founded (583) – (National Association for the Advancement f Colored People) 1905, Du Bois and his supporters met in Niagara Falls and launched the Niagara Movement=movement for equal rights using lawsuits in fed courts NAACP’s Strategy (584) – wanted full equality for exceptional blacks= hoped by creating an elite group capable of leadership, they could fight for the entire race in the future Crusade for Social Order and Reform The Temperance Crusade WCTU (585) – (Women’s Christian Temperance Union) 1879, led by Frances Willard= publicized the evils of alcohol by connecting it to family violence, unemployment, drunkenness, poverty, and disease 18th Amendment (585) – 1920, regulated the consumption of alcohol Immigration (586) – felt that to improve society, immigrants had to conform to American culture Eugenics (586) – science of altering reproduction of animals and plants to create new hybrids/breeds Eugenics Movement (586) – applied to humans= spread belief tht human inequalities were genetic and tht immigrants were contributing to the unfit population Challenging the Capitalist Order The Dream of Socialism Election of 1900(587) – few voters/ supporters Eugene Debs (587) – candidate, only durable leader, strong loyalty in urbanization immigrants, protestant farmers “Wobblies” (588) – aka as a racial labor union Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) , led by William Haywood, wanted to abolish wage slave system= favored strikes Decentralization and Regulation Problems of Corporate Centralization (588) – considered inefficient; thought it was a threat to freedom and of individuals to control their own destinies “Good Trusts”/ “Bad Trusts” Faulty trusts were being given out






