Slide
advertisement

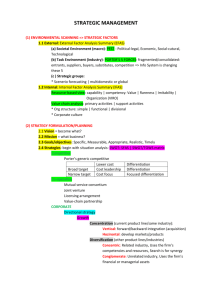
Principles of Management 2.0 Mason Carpenter, Talya Bauer, Berrin Erdogan, and Jeremy Short ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 1 Chapter 5 Strategic Management Learning Objectives © Jupiterimages Corporation See how strategy fits in the planning-organizing-leadingcontrolling (P-O-L-C) framework Better understand how strategies emerge Understand strategy as tradeoffs, discipline, and focus Conduct internal analysis to develop strategy Conduct external analysis to develop strategy Formulate organizational and personal strategy with the strategy diamond ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 2 Understand How Strategy Fits in the P-O-L-C Framework ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 3 Definition: Strategy Strategy is the pattern of decisions in a company that determines and reveals its objectives, purposes, or goals, produces the principal policies and plans for achieving those goals, and defines the range of business the company is to pursue, the kind of economic and human organization it is or intends to be, and the nature of the economic and noneconomic contribution it intends to make to its shareholders, employees, customers, and communities. Kenneth Andrews, The Concept of Corporate Strategy 4 The Strategist’s Challenge 5 Strategic Management Process The process by which a firm manages the formulation and implementation of its strategy • The coordinated means by which an organization achieves its goals and objectives ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 6 Strategic Management Process Strategy Formulation Strategy Implementation • The set of processes involved in creating or determining the strategies of the organization • The methods by which strategies are operationalized or executed within the organization ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 7 Strategizing in P-O-L-C ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 8 Corporate and Business Strategy ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 9 The strategy Hierarchy • Corporate strategy refers to the overarching strategy of the diversified firm. Such a corporate strategy answers the questions of "in which businesses should we compete?" and "how does being in these business create synergy and/or add to the competitive advantage of the corporation as a whole?" • Business strategy refers to the aggregated strategies of single business firm or a strategic business unit (SBU) in a diversified corporation. According to Michael Porter, a firm must formulate a business strategy that incorporates either cost leadership, differentiation or focus in order to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage and long-term success in its chosen arenas or industries. • Functional strategies include marketing strategies, new product development strategies, human resource strategies, financial strategies, legal strategies, supply-chain strategies, and information technology management strategies. The emphasis is on short and medium term plans and is limited to the domain of each department’s functional responsibility. http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Business_Strategy/Approaches_to_Strategic_Management 10 Diversification • Related Diversification • Unrelated Diversification Synergy Corporate Strategy Focus: McDonald Diversify Yum! Brands ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 11 (Link) 12 Asking/Answering 4 Basic Questions Before or After SWOT Analysis An assessment of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats What can we do? What do we want to do? What might we do? What do others expect us to do? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 13 ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 14 15 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SWOT_analysis SWOT Analysis • Strengths • Weaknesses • Opportunities • Threats Suggest strategies that should be tested against • • • • • • • • • • • Vision Goals Company Values Financial Status Cash Position ROI Position Societal Demands Competition Core Competencies People Skills Overall Resources Comparative and Competiveness Study Know the enemy and know yourself; in a hundred battles you will never be in peril. Internal Analysis Tools External Analysis Tools Value chain PESTEL VRIO Industry analysis http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PEST_analysis ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 19 PESTEL Analysis Political, Economic, Social (Demographic), Technological, Environmental, and Legal (Ethical) http://www.strategicmanagementinsight.com/tools/pest-pestel-analysis.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PEST_analysis ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 20 Discussion • What is the difference between strategy formulation and strategy implementation? • What is the difference between business strategy and corporate strategy? • What are some of the forms of diversification and what do they mean? • What do you learn from a SWOT analysis? • In SWOT analysis, what are some of the tools you might use to understand the internal environment (identify strengths and weaknesses)? • In SWOT analysis, what are some of the tools you might use to understand the external environment (identify opportunities and threats)? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 21 Various Factors Can Undermine a Strategy The plan is poorly constructed Competitors undermine the advantages envisioned by the plan The plan was good, but poorly executed ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 22 Intended, Deliberate, Realized, and Emergent Strategies 10%~30% The primary determinant of realized strategy is emergent strategy The decisions that emerge from the complex processes in which individual managers interpret the intended strategy and adapt to changing external circumstances. ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 23 Pivoting ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 24 Discussion • What is an intended strategy? • What is a realized strategy? • Why is it important to understand the difference between intended and realized strategies? • Why is there not a perfect match-up between realized and intended strategies? • What might interfere with the realization of an intended strategy? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 25 What is Strategic Focus? Strategic focus is seen when an organization is very clear about its mission and vision, and has a coherent, well-articulated strategy for achieving those. strategy as discipline strategy as trade-offs ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 26 Porter’s Generic Strategies Differentiation Focus ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 27 Focus: Gain Relative Superiority • By discovering the enemy's dispositions and remaining invisible ourselves, we can keep our forces concentrated, • while the enemy's must be divided. (The Art of War: Chapter 6) • Divide and conquer (各個擊破) • 我專而敵分 Differentiation or Price Leadership Strategy? Southwest Airlines has combined cost cutting measures with differentiation, proving that it is possible to succeed using combination strategies © Jupiterimages Corporation ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 29 Discussion • What is strategic focus and why is it important? • What are Porter’s three generic strategies? • Can a firm simultaneously pursue a lowcost and a differentiation strategy? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 30 Developing Strategy Through Internal Analysis The primary purpose for internal analysis is to understand the unique •resources, •capabilities, and •core competencies of organizations that may enable them to outperform their competitors overtime. ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 31 Measuring Value with Core Competencies Product’s performance characteristics Value Attributes for which customers are willing to pay ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 32 Resources and Capabilities ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 33 Resources and Capabilities Capabilities ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 34 The Value Chain Vertical Integration Or Outsourcing ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 35 Adding Value Within a Value Chain ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 36 VRIO Analysis Value Rarity Inimitability Organization ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 37 VRIO • Value: "Is the firm able to exploit an opportunity or neutralize an external threat with the resource/capability?" • Rarity: "Is control of the resource/capability in the hands of a relative few?" • Imitability: "Is it difficult to imitate, and will there be significant cost disadvantage to a firm trying to obtain, develop, or duplicate the resource/capability?" • Organization: "Is the firm organized, ready, and able to exploit the resource/capability?" ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 38 (defensive strategy) ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/competitive-parity.html 39 Valuable? Rare? Costly to imitate? Exploited by the organization? Competitive disadvantage No Yes Yes Yes Yes Competitive implication No Competitive parity Yes No Temporary competitive advantage Yes No Unexploited competitive advantage Yes Sustained competitive advantage Yes Yes Yes http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VRIO ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 40 Discussion • What is the objective of internal analysis? • What is the difference between a resource and a capability? • What is the difference between a tangible and an intangible resource or capability? • What is a core competency? • What framework helps you identify those resources, capabilities, or core competencies that provide competitive advantage? • Why might competitive advantage for a firm be fleeting? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 41 DEVELOPING STRATEGY THROUGH EXTERNAL ANALYSIS An external analysis tells the strategist •Begin with the general what is environment outside the organization. ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 42 Six General Environment Segments PESTLE Analysis legal political environmental technical economic social ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 43 AN ORGANIZATION’S MICROENVIRONMENT Industry • A group of firms producing products that are close substitutes • Upstream Markets: industries that provide the raw material or inputs for the focal industry • Downstream Markets: industries (sometimes consumer segments) that consume the industry outputs Industry Microenvironment • Consists of stakeholder groups that a firm has regular dealings with. • The way these relationships develop can affect the costs, quality, and overall success of a business. ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 44 Porter’s Competitive Analysis Source: http://bcs.wiley.com/he-bcs/Books?action=resource&bcsId=4903&itemId=0470343818&resourceId=16146 Porter’s Five Forces ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 46 ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 47 Porter’s Attractiveness and Profitability Analysis Likely to Profit Is the industry difficult to enter? Is there limited rivalry? Are buyers relatively weak? Are suppliers relatively weak? Are there few substitutes? Challenges to Profit Is the industry easy to enter? Is there a high degree of rivalry between firms within the industry? Are buyers strong? Are suppliers strong? Is it easy to switch to alternatives? When the answer is YES ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 48 Discussion • What are the six dimensions of the environment that are of broad concern when you conduct a PESTLE analysis? • Which of the PESTLE dimensions do you believe to be most important, and why? • What are the key dimensions of a firm’s microenvironment? • What are the five forces referred to in the Porter framework? • Is there a dimension of industry structure that Porter’s model appears to omit? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 49 The Strategy Diamond ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 50 Planning and Your Personal Growth and Development Strategy ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 51 Personal Arenas and Differentiators Personal Vehicles • What type of work do I want to do? • What leisure activities do I like? • Where do I want to live? • What capabilities (differentiators) do I need to participate in these arenas? • What organizations value these capabilities (differentiators) • What capabilities (differentiators) do I want to have and excel in? • What do I need to accomplish on my own? • What do I want to accomplish on my own? • What do I need to accomplish with the help of others? • Who are they? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 52 Personal Staging and Pacing • What sequence of events does my strategy require? • What are the financial requirements and consequences of each event? • What is my deadline for the first event? • Is the deadline flexible? Can I manage the pacing of the achievement of each event? • How will timing affect achievement of my personal growth and development strategy • Do some events provide an opportunity to reconsider or adjust my strategy? Personal Economic Logic • How does achievement of my strategy help me pay the bills? • What dimensions of my strategy, like arenas or differentiators, is the economic logic of my strategy most dependent on? • How sustainable is the economic logic of my strategy? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 53 Discussion • What are the five facets of the Hambrick & Fredrickson strategy diamond? • What is the relationship between arenas and differentiators if the strategy yields a positive economic logic? • If a firm is performing poorly financially, what might this say about the differentiators, arenas, or both? • Why is it important to consider vehicles as part of an organization’s strategy? • What is the difference between staging and pacing in terms of the strategy diamond? • What are some ways that you might apply staging and pacing to an organization’s strategy? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 54