Factorising Expressions
advertisement

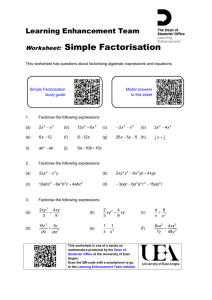
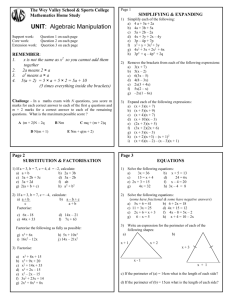
Match the expressions Some of the expressions below are the same. Match up the ones that are equal then write the others in a way similar to the others. 4(y – 2) 4y – 2y² 3(y + 4) 10 – 5y y(y + 2) 4y – 8 2y² - 4y 2y(y – 2) y(4 – 2y) y² + 2y Answers 4(y – 2) 4y – 2y² 3(y + 4) 10 – 5y y(y + 2) 4y – 8 5(2 – y) 2y² - 4y 2y(y – 2) y² + 2y y(4 – 2y) 3y + 12 Factorising Expressions Learning outcomes All – To be able to factorise simple expressions with common integer factors Most – To be able to factorise an expression into one pair of brackets Some – To be able to factorise quadratic expressions An example To factorise an expression we write it using brackets and take out all the common 1. Find the highest common factors. What is the factor of the numbers largest factor Examples of 12 and 16? 2. Look for any common unknown factors 4 1. 12a - 16 3. Write the common factors 4x3xa 4x4 Common factors? Now add any unknowns So outside the brackets 4. Write what is left inside the brackets (Rembering the operation +/-) 12a – 16 = 4 ( 3a – 4 ) Example 2 Remember to follow each step. What is the largest factor of 15 and 10? 5 Examples 2. 15ab2 + 10b 5x3xaxbxb Common factors? Now add any unknowns So 5x2xb 1. Find the highest common factor of the numbers 2. Look for any common unknown factors 3. Write the common factors outside the brackets 4. Write what is left inside the brackets (Rembering the operation +/-) 15ab2 + 10b = 5b ( 3ab + 2 ) Questions Factorise the following expressions 1. 3x – 9 2. 10 + 4b 3. 12c – 18c2 4. 20xy + 16x2 5. 5 – 35x Task 2 Intermediate GCSE book Page 228 Ex 19.6 Start with Q2 Factorising Quadratics Aim – For students to be able to factorise simple quadratics where the coefficient of x2=1 Level – GCSE grade B Recap Simplify the expression (x + a)(x + b) (x + a)(x + b) F – First O – Outside I – Inside L – Last Note – use FOIL x × x = x2 x × b = bx a × x = ax a × b = ab x2 + bx + ax + ab = x2 + (a + b)x + ab So … (x + a)(x + b) = x2 + (a + b)x + ab This is useful when factorising quadratics because… The coefficient of x is ‘a + b’ The numberical part is ‘a × b’ Example – Factorise x2 + 7x + 12 You are looking for two numbers a and b s.t. a + b = 7 and ab = 12 1 + 6 = 7 but 1 × 6 = 6 – No good 3 + 4 = 7 and 3 × 4 = 12 – Great! Let a = 3 and b = 4 So x2 + 7x + 12 = (x + 3)(x + 4) More difficult! Example Factorise x2 – 4x – 5 You are looking for two numbers a and b s.t. a + b = -4 and ab = -5 Note – If their product is negative one must be 2 + -6 = -4 but 2 × -6 = -12 – No good negative 1 + -5 = -4 and 1 × -5 = -5 – Great! Let a = 1 and b = -5 Therefore x2 – 4x – 5 = (x + 1)(x – 5) Task Factorise each of the following expressions 1. x2 + 4x + 3 2. x2 + 8x + 15 3. x2 + 9x + 20 4. x2 – 3x – 4 5. x2 – 7x – 30 6. x2 + 4x – 12 7. x2 – 5x + 6 Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. x2 + 4x + 3 = (x + 1)(x + 3) x2 + 8x + 15 = (x + 3)(x + 5) x2 + 9x + 20 = (x + 4)(x + 5) x2 – 3x – 4 = (x – 4)(x + 1) x2 – 7x – 30 = (x – 10)(x + 3) x2 + 4x – 12 = (x – 2)(x + 6) x2 – 5x + 6 = (x – 2)(x – 3)