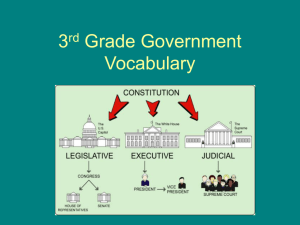
Compare and contrast the differences between the House and the
advertisement

Objective 27a Compare and contrast the differences between the House and the Senate. Including the terms and qualifications of office, election process, organization, equal vs. proportional representation, varying constituencies, and the amount of formality present in each house. The House-Terms Each member of the House serves a two-year term The Senate- Each member of the senate serves a sixyear term Qualifications for the House 1. Must be at least 25 years of age 2. Must have been a citizen of the United States for at least 7 years 3. Must be an inhabitant of the state that he or she is elected (Longstanding custom also states that he or she must live in the district they represent.) Qualifications for the Senate 1.Must be at least 30 years old 2.Must be a United States Citizen for at least 9 years 3.Must live in the state in which they are elected Election Process The House- Members of the House get elected every two years. The Senate- Members of the Senate are elected every six years The terms in the Senate are staggered every 6 years. So a third of the terms expire every two years. It is a continuous body which means all of the seats are never up for election at the same time Proportional Representation -The House represents the states proportionally, which means each state gets their number of seats by the size of their population. - This favors large states, and gives them more representation. Equal Representation -The Senate has equal representation, in which each State gets two Senators regardless of population. -This type of representation favors the smaller states. Varying Constituencies Constituencies = The people and interests that the representatives represent Senators are concerned less with small local problems, are more focused on statewide “Big Picture” Interests • The House of • Representatives focus more on small localities. They are usually focused more on the district that they are representing.. Major Differences House Larger Body (435) Short Term (Two Years) Less Prestige Lower Media Visibility Elected by districts Strict Rules/ Limited Debate Senate Smaller Body (100) Longer Term (Six Years) Two from each state More prestige Heavy Media Coverage Flexible Rules, Debate Filibuster Cloture Unlimited