Introduction - UniMAP Portal
advertisement

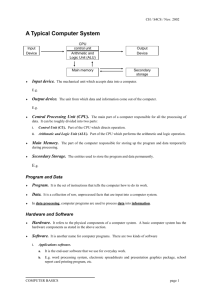
EKT 422 Computer Organization and Architecture Lecturer: En. Muhammad Imran Ahmad m.imran@unimap.edu.my Tel: 019-4267902 / 04-9798439 En. Mohd Nazrin Md Isa Text Book FPGA/UP3/Quartus II • http://users.ece.gatech.edu/~hamblen/UP3/ Books • • William Stallings, “Computer Organization and Architecture”, Seventh Edition, Prentice-Hall. (Text book) M. Morris Mano, “Computer System Architecture”, Third Edition, Prentice-Hall. VHDL • • Stephan Brown, “Fundamentals of Digital Logic Design: VHDL Design” , McGraw-Hill Education. http://www.opencores.org/browse.cgi/by_category Course synopsis This subject will focus on the computer system with various design of interface techniques, organisation an architecture. The syllabus will covered the theory of basic computer system, format of instruction set, memory organization and arithmetic logic unit as well as certain issues of designing such as bus structure, parallel processing, pipelining and memory management. The student are required to design a simple CPU during a Lab session by using Quartus II software provided by Altera. The lab session will complement the theories given in lectures. FPGA trainer board will be used as a design platform in the lab Course Outcome/Objective • Understand the theory and the architecture of a central processing unit • Ability to analyze some of design issues in term of speed, technology, cost and performance • Ability to design a simple CPU with applying the theory and knowledge in the lecture • Ability to use appropriate CAD tool to design, verify and test the CPU architecture Final Exam (50%) Coursework (50%) • • • • Lab Assessment = 10% Written Test 1 = 10% Written Test 2 = 10% Mini project + viva = 20% - Design your own CPU (individual project) - software VHDL - Target Platform: ALTERA UP3 At the end of the course you should know how to design YOUR OWN CPU inside FPGA Organization and architecture • Architecture -- refers to those attributes of a system visible to a programmer or those attributes that have a direct impact on the logical execution of a program. - instruction set, number of bits used for data representation, I/O mechanism, addressing technique. • Organization – refers to the operational unit and their interconnections that realize the architectural specification -- control signal, interface to peripherals, memory technology. Structure and function • Structure – The way in which the components relate to each other. E.g. connection between ALU and control unit, connection between Instruction register and instruction decoder. • Function – The operation of each individual component as part of structure. E.g. How the ALU, Instruction register and instruction decoder work. Function These are the basic functions that a computer can perform. - Data processing - Data storage - Data movement - Control Cont.. • Process data – data can be a variety of forms, and the range of processing requirements is broad. There are only a few fundamental methods of data processing ( refer ALU ). • Store data – computer must temporarily store at least those pieces of data that are being worked on at any given moment at least a short-term data storage function (temporary register) and also long-term data storage function (store File). • Move data – comp must be able to move data between itself and outside world. Device directly connected to computer is called peripheral. If data are moved over longer distances, the process is known data communication. • Control – Control of three function above, and given by individuals who provides the computer with instruction. Figure below depicts the four possible types of operations. Structure There are four main components in a computer structure: - Central processing unit(CPU) – controls the operation of the computer and performs its data processing functions. - Main memory – stores data - I/O – moves data between the computer and its external environment - System interconnection – some mechanism that provides for communication among CPU, main memory and I/O. Traditionally a computer consist of single CPU, but in recent years, there has been increasing use of multiple processors in single computer. The computer: Top-Level structure The central processing unit Control unit – controls the operation of the CPU and hence the computer. ALU – perform data processing function Register – provides storage internal to CPU CPU interconnection – mechanism provides communication among the control unit, ALU and register. Any Question !!!!!! OR Quiz !!! Sketch the internal connection of a Simple CPU and explain in detail how it works What are the differences between single core technology and multi core technology. Give 10 advantages of 8 bit processor and 64 bit processor.