Fertility Rate - GeographyinActionSHSS
advertisement

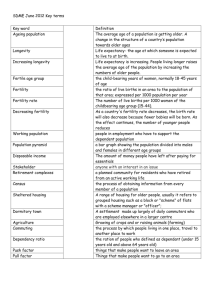
By Crystol Caesar Shaquille Elliot Definition of Fertility Rate Factors influencing Fertility Rate Video Depicting Factors Measurement of Fertility Rate(Aspects) Graph showing Total Fertility Rate Replacement Fertility Case Study Of Canada References What is Fertility Rate? The total fertility rate is referred to as the average number of children a woman is likely to have if she lives to the end of her child bearing age, based on current birth rates Status of Women Perception of children as an impediment Religion & Culture Cost of Living Advances in Technology Families being more career-minded Options given to woman- Policy General Fertility Rate (GFR) Age Specific Fertility Rate (ASFR) Total Fertility Rate (TFR) Number of live births per 1000 women age 15-49 in a given year Number of births/year Number of women ages 15 to 49 * 1000 Number of births per year per 1000 women of a specific age (group) Number of births to a woman age a *1000 Number of women age a The average number of children that would be born to a woman by the time she ended childbearing if she were to pass through all her childbearing years conforming to the age-specific fertility rates of a given year Number of women * 1000 Number of births Average number of daughters that would be born to a woman if she passed through her life-time from birth to the end of her reproductive years conforming to the agespecific fertility and mortality rates of a given year Replacement fertility is the total fertility rate at which women would have only enough children to replace themselves and their partner. Replacement Level Fertility is said to have been reached when NRR=1.0 Canada Africa Canada can be considered as an MEDC which from past studies it can be seen that countries falling in this bracket tend to have a low fertility rate. In 2002 Canada recorded a fertility rate of 1.51. It however rose to 1.59 in 2006 Reasons Gender, work and childbearing Low participation by men in household with children Work & childbearing for low fertility rate TFR fast declining as women’s employment rate was increasing (1960 to 1985) Childbearing by marital status, employment status & family structure Competition with other life goals e.g. careers Achievement of ideal family size Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health: Data Sources and Crude Indicators of Fertility Google images Case Study (Canada) : Low fertility rate in Canada – rbeaujot@uwo.ca Geography : An Integrated Approach, David Waugh