The Reformation - Fulton County Schools
advertisement

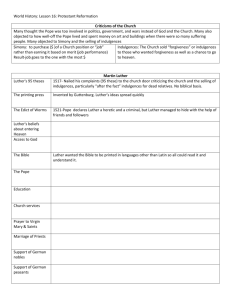
The Reformation Ch. 17 Sections 3 & 4 VI. The Reformation Causes A. 1. 2. 3. Renaissance emphasized secular beliefs (printing press spread these ideas) Northern merchants resented paying church taxes in Rome Critics claimed leaders were corrupt (Popes patronized the arts, spent extravagantly on personal pleasure, and fought wars) Reformation (cont’d) Martin Luther’s role B. 1. The 95 Thesis: Formal statements attacking the “pardon-merchants” Oct 31, 1517 Johann Tetzel; sold indulgences: a pardon 95 Thesis posted on church door; someone copied it in printer and ML became known all over Germany 2. Reformation: a movement of religious reform Reformation (cont’d) Luther’s Teachings C. 1. 2. 3. People could win salvation only by faith in God’s gift of forgiveness (catholic church taught faith and “good works”) All Church teachings should be clearly based on the bible (Pope and Church were false authorities) All people with faith were equal (people didn’t need priests to interpret the bible for them) Reformation (cont’d) Response to Luther D. 1. 2. Pope excommunicated Luther Emperor declared Luther an outlaw and ordered his books banned Luther returned to Germany and found his ideas in practice… Lutherans: separate religious group that followed Luther 3. Peasant’s Revolt Peasants demanded end to serfdom, pillaged monasteries, Luther objected VII. Protestants Form German War A. Some support Luther, some remained loyal to the pope. War erupts Protestants form: Christians who belong to nonCatholic churches Peace of Augsburg: religious settlement allowing German princes to decide religion of each province Protestants Form (cont’d) England becomes protestant B. 1. 2. 3. 4. Henry VIII wants son, divorce/annulment (set aside); Henry denied. 1529 called Reformation Parliament: ends Pope’s power in England Act of Supremacy, 1534: Henry, not pope, is head of England and church 1559: Anglican Church (Church of England) formed by Elizabeth Henry VIII timeline 1. 2. 3. 1509 Henry VIII becomes king of England; marries Catherine of Argon 1516 daughter Mary is born 1527 Henry asks the pope to end his first marriage; pope refuses 4. 5. 1529 Henry summons Reformation Parliament 1531 parliament recognizes Henry as head of Church Henry VIII timeline (cont’d) 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 1534 Act of Supremacy 1533 Henry divorces Catherine, marries Anne Boleyn; daughter Elizabeth is born 1536 Anne Boleyn is beheaded 1537 Henry marries Jane Seymour, son Edward is born, Jane dies of complications 1540-1542 Henry divorces new wife Anne of Cleves, executes his 5th wife: Catherine Howard Henry VIII timeline (cont’d) 11. 12. 1547 Henry dies; 6th wife Catherine Parr outlives him; Edward VI begins 6 yr rule; Protestants strong 1553 Mary I (bloody Mary) begins rule and restores the Catholic Church 13. 1558 Elizabeth I begins rule; restores Protestant church (Anglican Church) Protestants Form (cont’d) C. Religious Turmoil 1. Edward VI reigns; advisors run things and make England very Protestant 2. Mary I reigns; forces England to be Catholic, kills those who oppose (bloody Mary) 3. Elizabeth I reigns; returns Protestantism; sets up Anglican church (Church of England)—only legal church in England Protestants Form (cont’d) To Please Protestants: Priests allowed to marry Sermons in English (not Latin) This brought religious peace to England To Please Catholics: Kept some trappings of the Catholic service like rich robes Services revised to be more acceptable Protestants Form (cont’d) Elizabeth’s difficulties D. 1. 2. 3. Some protestants wanted more reform Some Catholics want Mary Queen of Scots to take over (she’s devout Catholic!) England needs money and wants to form colonies in America as new income—leads to conflict between monarch and Parliament VIII. Calvinism Emerges Religion based on John Calvin’s teachings Calvin tweaks Luther’s ideas A. 1. 2. Believed that men and women sinful by nature Predestination: God knows beforehand which people will be saved (remember that Luther said humans can earn salvation) Calvinism Emerges (cont’d) Calvin leads reformation in Switzerland B. 1. 2. Theocracy: gov’t controlled by religious leaders (he thought this was the perfect gov’t) Est. Geneva, Switzerland as theocracy; becomes example city; has very strict rules (ie-no bright clothes or card games) Calvinism Emerges (cont’d) Calvinism spreads C. 1. 1. John Knox takes ideas to Scotland Presbyterians: followers of Knox Becomes Scotland’s official religion Get rid of Mary Queen of Scots, lets son James rule Swiss, Dutch, and French reformers adopt Calvinist organization and today trace roots to Calvin IX. Other Protestant Reforms The Anabaptists “baptize again” A. 1. 2. 3. 4. Only baptized people who were old enough to decide for themselves to be Christian Said church and state should be separate; refused to fight wars Persecuted by both Catholics and Protestants as radicals Became Mennonites and Amish; influenced Quakers and Baptists who split from Anglican church Other Protestant Reforms (cont’d) Women’s role B. Played prominent roles (protected reformers, supported men) Splits in the Christian Church X. Catholic Reforms Catholic Reformation (counter reformation) A. Efforts to reform and renew Catholic church from within Millions remained loyal to Catholicism; reform from within Catholic Reforms (cont’d) B. Jesuits Created Followers of Ignatius of Loyola; Society of Jesus 3 main activities: Founded schools Convert non-Christians to Catholicism Stop spread of Protestantism (worked well in Southern Germany and Poland) Catholic Reforms (cont’d) Reforming Popes C. Council of Trent: most important reform Meeting of Catholic leaders to rule on doctrines criticized by the Protestant reformers Church’s interpretation of bible final; anyone with own interpretation was heretic Need faith and good works for salvation Bible and Church tradition equally powerful authorities Indulgences were valid expressions of faith; false selling of indulgences banned Next pope carried out council’s decrees and made list of dangerous books (Index of Forbidden Books) Bishops ordered to burn these books; included Protestant bibles Legacy of Reformation *Ended religious unity in Europe* Religious and Social Effects Protestant churches flourished Catholic church more unified (Council of Trent) Led to schools and colleges Political Effects Monarchs gained power Laid groundwork for Enlightenment