Magnetically responsive photonic films with high tunability and stability
advertisement
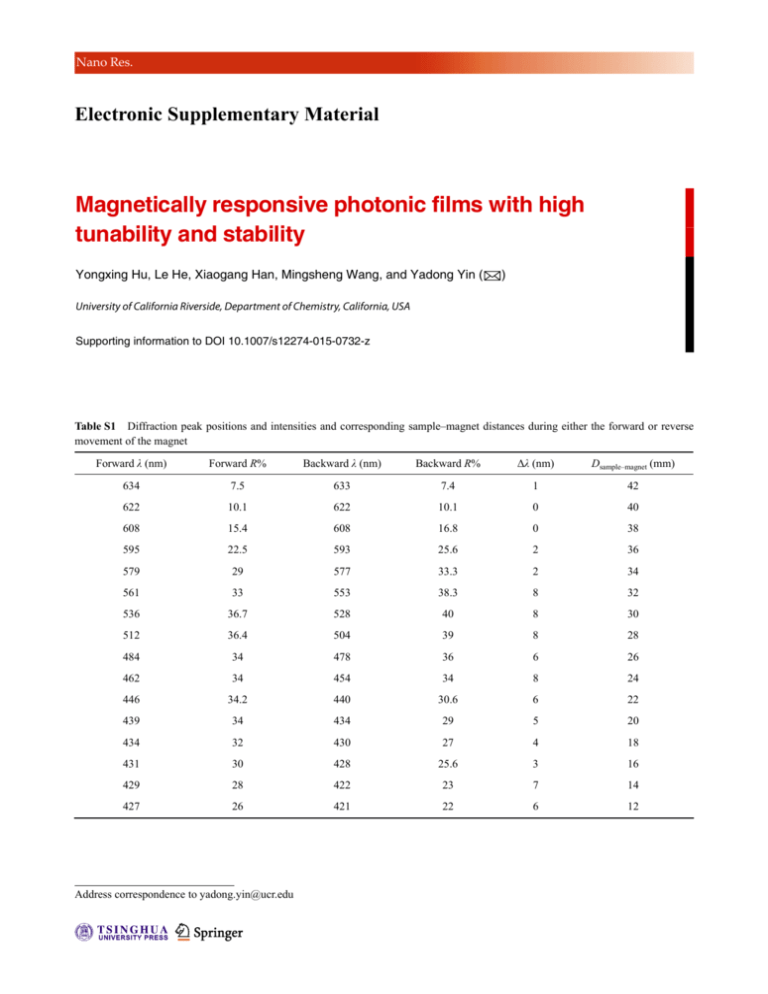
Nano Res. Electronic Supplementary Material Magnetically responsive photonic films with high tunability and stability Yongxing Hu, Le He, Xiaogang Han, Mingsheng Wang, and Yadong Yin () University of California Riverside, Department of Chemistry, California, USA Supporting information to DOI 10.1007/s12274-015-0732-z Table S1 Diffraction peak positions and intensities and corresponding sample–magnet distances during either the forward or reverse movement of the magnet Forward λ (nm) Forward R% Backward λ (nm) Backward R% Δλ (nm) Dsample–magnet (mm) 634 7.5 633 7.4 1 42 622 10.1 622 10.1 0 40 608 15.4 608 16.8 0 38 595 22.5 593 25.6 2 36 579 29 577 33.3 2 34 561 33 553 38.3 8 32 536 36.7 528 40 8 30 512 36.4 504 39 8 28 484 34 478 36 6 26 462 34 454 34 8 24 446 34.2 440 30.6 6 22 439 34 434 29 5 20 434 32 430 27 4 18 431 30 428 25.6 3 16 429 28 422 23 7 14 427 26 421 22 6 12 Address correspondence to yadong.yin@ucr.edu Nano Res. Figure S1 Plots of reflectance intensity (■) and peak position (●) versus time for the magnetic photonic structure in water in an external magnetic field of 360 G with a gradient of 115 G/cm. Figure S2 The corresponding parameters of the cubic magnet: (a) the magnetic field strength (H) as a function of the sample–magnet distance; (b) the gradient of magnetic field strength (H) as a function of the sample–magnet distance. | www.editorialmanager.com/nare/default.asp











