05_transistordcbias1
advertisement

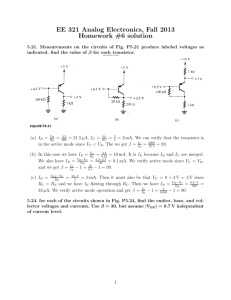
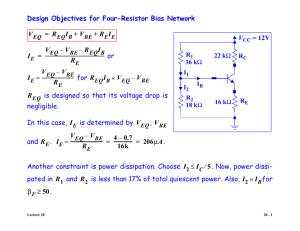
Transistor Circuit DC Bias Part 1 ENGI 242 DC Biasing Circuits • • • • • • Fixed-Bias Circuit Emitter-Stabilized Bias Circuit Collector-Emitter Loop Voltage Divider Bias Circuit DC Bias with Voltage Feedback Miscellaneous Bias Circuits February 2003 ENGI 242 2 Maximum Power Curve February 2003 ENGI 242 3 Fixed-Bias Circuit February 2003 ENGI 242 4 DC Equivalent circuit February 2003 ENGI 242 5 Base-Emitter (Input) Loop Using Kirchoff’s voltage law: – VCC + IBRB + VBE = 0 Solving for IB: February 2003 VCC - VBE IB = RB ENGI 242 6 Collector-Emitter (Output) Loop Since: IC = IB Using Kirchoff’s voltage law: VCE – VCC – IC RC Because: VCE = VC - VE Since VE = 0V, then: VC = VCE Also: VBE = VB - VE with VE = 0V, then: VB = VBE February 2003 ENGI 242 7 BJT Saturation Regions When the transistor is operating in the Saturation Region, the transistor is conducting at maximum collector current (based on the resistances in the output circuit, not the spec sheet value) such that: VCC - VCE RC where VCE = 0.2 V ICsat = February 2003 ENGI 242 8 Determining Icsat February 2003 ENGI 242 9 Determining Icsat for the fixed-bias configuration February 2003 ENGI 242 10 Load Line Analysis February 2003 ENGI 242 11 Load Line Analysis The end points of the line are : ICsat and VCEcutoff For load line analysis, use VCE = 0 for ICSAT, and IC = 0 for VCEcutoff ICsat: VCEcutoff: VCC |VCE 0V RC VCE = VCC |IC 0mA ICsat = Where IB intersects with the load line we have the Q point Q-point is the particular operating point: • Value of RB • Sets the value of IB • Where IB and Load Line intersect • Sets the values of VCE and IC. February 2003 ENGI 242 12 Circuit values effect Q-point February 2003 ENGI 242 13 Circuit values effect Q-point (continued) February 2003 ENGI 242 14 Circuit values effect Q-point (continued) February 2003 ENGI 242 15 DC Fixed Bias Circuit Example February 2003 ENGI 242 16 Load-line analysis February 2003 ENGI 242 17 Fixed-bias load line February 2003 ENGI 242 18 Movement of Q-point with increasing levels of IB February 2003 ENGI 242 19 Effect of RC on the load line and Q-point February 2003 ENGI 242 20 Effect of VCC on the load line and Q-point February 2003 ENGI 242 21 Example February 2003 ENGI 242 22 Emitter Stabilized Bias Emitter-Stabilized Bias Circuit Adding a resistor to the emitter circuit (between the emitter lead and ground) stabilizes the bias circuit February 2003 ENGI 242 24 Improved Bias Stability The addition of RE to the Emitter improves the stability of a transistor Stability refers to a bias circuit in which the currents and voltages will remain fairly constant for a wide range of temperatures and transistor forward current gain () The temperature surrounding the transistor circuit is not always constant Therefore, the transistor is not a constant value February 2003 ENGI 242 25 Base-Emitter Loop February 2003 ENGI 242 26 Equivalent Network February 2003 ENGI 242 27 Reflected Input impedance of RE February 2003 ENGI 242 28 Base-Emitter Loop Applying Kirchoffs voltage law: Since: - VCC + IB RB + VBE +IE RE = 0 IE = ( + 1) IB We can write: - VCC + IB RB + VBE + ( + 1) IB RE = 0 VCC - VBE IB = RB + (β+1)RE Grouping terms and solving for IB: Or we could solve for IE with: February 2003 RB - VCC + IE + VBE + IE RE = 0 ( + 1) ENGI 242 29 Collector-Emitter Loop February 2003 ENGI 242 30 Collector-Emitter Loop Applying Kirchoff’s voltage law: - VCC + IC RC + VCE + IE RE = 0 Assuming that IE IC and solving for VCE: IC = VCC – VCE – (RE + RC) Solve for VE: V E = IE R E Solve for VC: VC = VCC - IC RC or VC = VCE + IE RE Solve for VB: February 2003 VB = VCC - IB RB or VB = VBE + IE RE ENGI 242 31 Transistor Saturation At saturation, VCE is at a minimum We will find the value VCEsat = 0.2V For load line analysis, we use VCE = 0 To solve for ICSAT, use the output KVL equation: ICSAT = February 2003 ENGI 242 VCC - VCE RC + RE 32 Load Line Analysis The load line end points can be calculated: At cutoff: VCE VCC | IC = 0 mA At saturation: IC = February 2003 VCC | VCE = 0V RC + R E ENGI 242 33 Emitter Stabilized Bias Circuit Example February 2003 ENGI 242 34 Load Line For The Emitter-bias Configuration. February 2003 ENGI 242 35