Free morphemes
advertisement

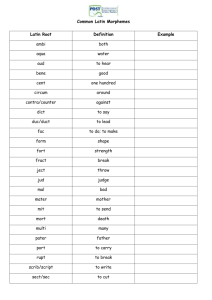
Linguistics The ninth week Chapter 3 Morphology 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Morphemes Key points 1. the definition of morphology 2. the definition of morpheme 3. the classification of morphemes Difficult points 1. Free morphemes 2. Bound morphemes Morphology Morphology is the study of the internal structure, forms and classes of words. Morphemes A morpheme is a minimal unit of meaning or grammatical function. Ex. Tourists: -tour (one minimal unit) -ist (meaning “person who does something”) -s (a third unit of grammatical function indicating plurality) Free morphemes The morphemes that can stand alone as words are called free morphemes. Root and stem A word must contain an element that can stand by itself, that is, a free morpheme, such as talk. Such an element is called a root. When they are used with bound morphemes, the basic word-form involved is technically known as the stem. Lexical and functional morphemes Lexical morphemes refer to ordinary nouns, verbs and adjectives. Functional morphemes refer to conjunctions, articles, prepositions and pronouns. Open and closed class of words lexical morphemes are called an open class of words because we can create new lexical morphemes. functional morphemes are called a closed class of words because no new fellow members can be added. Bound morphemes Bound morphemes are those that can not be used independently but have to be combined with other morphemes, either free or bound, to form a word. Occurrence position: Prefixes Suffixes infixes Function: Derivational morphemes Inflectional morphemes Eight English inflectional morphemes: (i) –‘s (possessive) (ii) –s (plural) (iii) –s (3rd person present singular) (iv) –ing (present participle) (v) –ed (past tense) (vi) –ed (past participle) (vii) –en (past participle) (viii) –est and –er (superlative and comparative degree) The chart of the different categories of morphemes Lexical morphemes (work, house, kind) Free morphemes Morphemes Functional morphemes (and, if, or, but) Derivational morphemes (-er, -ness, - ly) Bound morphemes Inflectioanal morphemes (-ed, -er, -est) Lexical morphemes Free morphemes Functional morphemes Morphemes Derivational morphemes Bound morphemes Inflectional morphemes Assignments 1. Define the following terms: (1)morphology (2) free morpheme (3) morpheme (4) stem 2. Identify the structure of the following words: wording person existentialism international statesman spokesman walkman bicyclist assignment