Chapter 3 - Biology12-Lum
advertisement

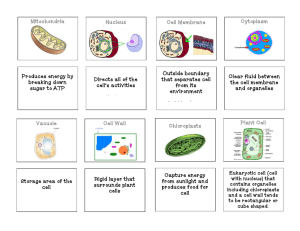
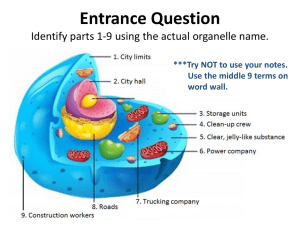
Chapter 3 Why are cells small • Surface area to volume ratio • The larger the cell the smaller the ratio • The smaller the cell the larger the ratio 10 units 1 unit 10 units Volume = 1000 units3 Surface Area =600 Ratio 3:5 units2 Volume = 1 units3 Surface Area = 6 units2 Ratio 6:1 • This means that a small cell can get more food for its size than a larger cell • A small cell can get rid of its waste more easily than a larger cell The parts of a Cell • The parts of a cell are called Organelles • The first organelle is the cell membrane or the plasma membrane Work Sheet • Use your book to answer the worksheet. • Label the Animal cell Work Sheet Answers 1. Nucleolus 2. Nucleus 3. Ribosome 4. Vesicle 5. Rough Endoplasmic reticulum 6. Golgi apparatus (Golgi body) 7. Cytoskeleton 8. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum 9. Mitochondrion 10.Vacuole 11.Cytoplasm 12.Lysosome 13.Centriole Label Pictures Ribosomes • This is where proteins are made ( Amino acids are put together to make proteins) • Ribosomes made of 2 sub-units, composed of rRNA and protein • Found on the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum When free ribosomes are in groups they are called polyribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum • Also called the ER • It is attached and is continuous with the nuclear envelope • Rough ER has ribosomes all over it • Proteins are made then go into the ER to be transported • Smooth ER does not have any ribosomes • Makes phospholipids used in the cell membrane and makes steroids Golgi Apparatus • Packaging and distributes materials to the rest of the cell • Import and Export Centre • Export – Modifies Proteins for export out of the cell – Forms secretory vesicles – Exocytosis of • Proteins • Lipids • Waste products Lysosome • Lyse to break up or to break apart • Some body • Lysosome is an organelle the breaks up things. It can break up and digest food. Or it can break up parts of the cell • Lysosomes use digestive enzymes to break up things • They are made by the Golgi Body Chloroplasts • These are responsible for photosynthesis in plants (makes food) Mitochondria • In both plants and animals • Does Cell Respiration (Turns food into energy) Cytoskeleton • Made of Microtubules and Microfilaments • The are Filamentous Protein structures that help the cell: – Keep its shape – Keep organelles where they are, or – Help the organelles move Vacuole • • • • Occur in both plant and animal cells Very large central vacuole in plant cells Stores water-soluble compounds Helps maintain cells shape – When a plant does not have water the leaves droop Cytoplasm • The liquid that all the organelles float in Cell Wall • Cell Wall is only in Plant cells • It provides structural support • It is made of Cellulose and cannot be digested by humans Cell Wall Located outside of the cell membrane On a test • You will be asked to identify organelles from a TEM (Transmission Electron Micrograph) picture. Review • Mr. Lum is going to tape the name of a cell organelle onto your back • You will walk around the class asking people questions • The questions can only be a “yes” or a “no” question • You can only ask one question to one person