Deviance & Social Control
advertisement

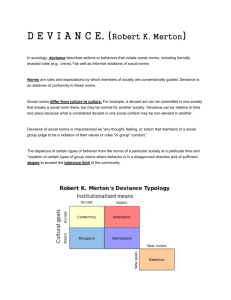
Chapter 8 Talking to oneself in public Drag racing on a public street Using illegal drugs A man wearing women’s clothing Attacking another person with a weapon Behavior that violates social norms Some norms are fairly insignificant, others are essential to a working society Violating unavoidable Deviance varies by society-divorce prohibited in Philippines, legal here, businesses on Sunday Labeling someone deviant 1.must be detected committing a deviant act, 2. be stigmatized by society. Ex. Scarlett Letter, Erving Goffman calls the “spoiled social identity”. Clarifying norms- better defines boundaries of social behavior, serve as warning of consequences Unify group-draws line between us and them Diffusing tension-minor acts of deviance allows safety valve without disrupting basic fabric of society Promoting social change-identify problem areas, when enough violate, triggers change in norm Providing jobs- police, criminologists, uniform makers Strain theory- Robert K. Merton- deviance is a natural outgrowth of the values, norms, and structure of society. Some are incompatible with reality, ex. Economic success. Not everyone has tools to achieve, poor judged Anomie is the situation that arises when the norms of society are unclear or are no longer applicable. Not enough guidelines for behavior leads to confusion, Durkheim studies Industrial Revolution Societal distance Hand Gestures Eye contact Facial expressions How to respond to culturally approved goals and legitimate ways of achieving? 5 modes of adaptation CONFORMITY- accept cultural goals and norms Always involves legitimate means INNOVATION- accept cultural goals, but reject cultural norms Want to be successful, but non-traditional means for achieving. Ex. Drug dealer. RITUALISM- reject cultural goals but accept cultural norms Abandon goals but continue to observe acceptable rules of behavior. Ex. Turn down promotion RETREATISM- reject both cultural goals and norms Make no effort to share, drop out of society. Ex. Hermits, drug addicts REBELLION- reject and replace cultural goals and norms, want to substitute new values. Ex. Members of revolutionary social movement. Last 2 bigger threats to society Competition and social inequality lead to deviance Life as struggle between those who possess power-the ruling class- and those who do not- the lower classes. People with power commit deviant acts to maintain their position. People without power commit deviant acts to obtain economic reward or because of feelings of powerlessness. Richard Quinney- the ruling classes label any behavior that threatens their power as deviant To protect power, ideologies are established (belief systems) to explain deviance as a problem of the lower classes Law enforcement is directed against these people, higher arrest and conviction rates Ex. SC and crack babies cases Control theory-deviance is a natural occurrencewhy DO people conform rather than causes of deviance COMMUNITY TIES- if weak, less conformity Travis Hirschi, people develop social bonds in 4 ways 1.form attachments with others who accept norms 2.have a strong belief in the moral codes of society 3.show commitment to traditional societal values 4.fully involved in nondeviant activities Cultural transmission theory- deviant behavior is learned through interaction with others, just as conformist behavior is learned. SOCIALIZED to deviancy Differential Association-the frequency and closeness of associations a person has with deviant and nondeviant individuals, Edwin Sutherland Techniques of neutralization-people suspend their moral beliefs to commit deviant actsdenying responsibility (accident), denying injury (no one hurt), denying the victim(had it coming), condemning the authorities(police corrupt), appealing to higher loyalties(to protect family) Labeling theory-how do individuals come to be indentified? All commit acts during life. Primary deviance is a nonconformity that goes undetected by authority. Do not view self as deviant nor does society. Secondary deviance- results in labeling and most accept as true Harold Garfinkel, degradation ceremony- a public setting, trial, individual is denounced, found guilty, and given new identity An act, labeled by authority, prohibited by law, and punishable by government Moral code v. legal violation Types of crime: Violent-rape, murder, assault, robbery Crimes against property-theft, vandalism, arson Victimless crimes-illegal drug use, helmets White-collar crime-toxic pollution, political corruption, embezzlement Organized crime- crime syndicate Police- discretion, racial profiling Courts- plea bargaining Corrections-sanctions to punish include imprisonment, parole, and probation, Serve 4 functions: 1.retribution-act of revenge for society 2.deterrence-think twice 3.rehabilitation-to prevent recidivism 4.social protection-death penalty ultimate 3rd largest category of criminals juvenile offenders Lower level of responsibility for acts Same rights?