PCMH 2014 (PCDC - Maia Bhirud)
advertisement

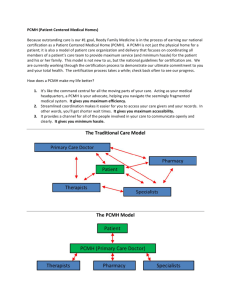
Regional Care Collaborative March 26, 2015 Slide 1 2011/2014 Crosswalk (Standards 1-6) Maia Bhirud Slide 2 Standard 1 Crosswalk PCMH 1: Enhance Access PCMH 1: Enhance Access and Continuity and Continuity 2011 2011 Access during office hours A.A. Access during office B. hours After-hours access B. After-hours access Electronic access C.C. Electronic access Continuity D.D. Continuity E.E. Medical home Medical home responsibilities responsibilities Culturally and linguistically F.F. Culturally and appropriate services linguistically services G. appropriate The Practice Team G. The Practice Team Slide 3 PCMH 1: PatientCentered Access 2014 A. Patient-centered appointment access B. 24/7 Access to clinical advice C. Electronic access 2014 Standard 1: Must Pass PCMH 1A: Patient-Centered Appointment Access The practice has a written process and defined standards for providing access to appointments and regularly assesses its performance on: 1. Providing same-day appointments for routine and urgent care (critical factor) 2. Providing routine and urgent-care appointments outside of regular business hours 3. Providing alternative types of clinical encounters 4. Availability of appointments 5. Monitoring no-show rates 6. Acting on identified opportunities to improve access Slide 4 • Standard 1B: 24/7 Access – Basically the same as 2011. Telephone access during and after hours has been combined into one factor • Standard 1C: Electronic Access – Also basically the same as 2011 – MU reports but MU stage 2 Slide 5 Standard 2 PCMH 1: Enhance Access PCMH 1: Enhance and Continuity Access 2011 and Continuity D. Continuity 2011 Medical Home D.E. Continuity Responsibilities E. Medical Home F. Responsibilities Culturally and linguistically F. Culturally andServices Appropriate linguistically G. The Practice Team Appropriate Services G. The Practice Team Slide 6 PCMH 2: Team-Based Care 2014 A. Continuity B. Medical Home Responsibilities C. Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services D. The Practice Team • Standard 2A: Continuity – Mapped to 2011 1D Continuity – Factor 3: process to orient pts to staff and they really are looking for a process – Factor 4: transition plan for pts transitioning from pediatric to adult care (formerly 5B) • Documentation: written transition plan • Standard 2B: Medical Home Responsibilities – Same idea with added criteria to add into your brochure or website • Standard 2C: Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services – Unchanged Slide 7 2014 Standard 2: Must Pass PCMH 2D: The Practice Team (10 factors) The practice uses a team to provide a range of patient care services by: 1. Defining roles for clinical and nonclinical team members. 2. Identifying the team structure and the staff who lead and sustain team based care. 3. Holding scheduled patient care team meetings or a structured communication process focused on individual patient care (critical factor). 4. Using standing orders for services. Slide 8 2014 Standard 2: Must Pass 5. Training and assigning members of the care team to coordinate care for individual patients. 6. Training and assigning members of the care team to support patients/ families/caregivers in self-management, self-efficacy and behavior change. 7. Training and assigning members of the care team to manage the patient population. 8. Holding schedule team meetings to address practice functioning. 9. Involving care team staff in the practice’s performance evaluation and quality improvement activities. 10. Involving patients/families/caregivers in quality improvement activities or on the practice’s advisory council. Slide 9 Standard 3 Crosswalk PMCH 2: 2: Identify andand Manage PMCH Identify Manage PatientPatient Populations Populations 2011 2011 Patient Information A.A. Patient Information B.B. Clinical Data Clinical Data C.C. Comprehensive Comprehensive Health Health Assessment Assessment D. Use of Data for D. Population Use of Data for Population Management Management Slide 10 PCMH 3: Population Health Management 2014 A. Patient Information B. Clinical Data C. Comprehensive Health Assessment D. Use of Data for Population Management E. Implement Evidence-Based Decision Support • • • • • • 3A: Patient Information (2011 2A) 3B: Clinical Data (2011 2B) (remember now aligned with MU Stage 2) 3C: Comprehensive Health Assessment (2011 2C) Review of completeness Report clearly showing how many patients had incomplete or complete assessments for all factors • Or Review of patient records (using record review workbook) Slide 11 2014 Standard 3: Must Pass PCMH 3D: Use Data for Population Management At least annually the practice proactively identifies populations of patients and reminds them, or their families/caregivers, of needed care based on patient information, clinical data, health assessments and evidence based guidelines including: 1. At least two different preventive care services 2. At least two different immunizations 3. At least three different chronic or acute care services 4. Patients not recently seen by the practice 5. Medication monitoring or alert Slide 12 • 3E: Implement Evidence Based Decision Support – Different from proactive pop mngt activities that are reminding pts to come in to receive specific services - Point of care reminders related to your clinical decision support. – Pick conditions and show templates of the tools or electronic system organizer Slide 13 Standard 4 PCMH 3: Plan and Manage 2011 A. Implement Evidence-Based Guidelines B. Identify High-Risk Patients C. Care Management (Must Pass) D. Medication Management E. Use Electronic Prescribing PCMH 4: Provide Self-Care Support and Community Resources A. Support Self-Care Process (Must Pass) B. Provide Referrals to Community Resources PCMH 4: Care Management and Support 2014 A. Identify Patients for Care Management B. Care Planning and SelfCare Support C. Medication Management D. Use Electronic Prescribing E. Support Self-Care and Shared Decision Making Slide 14 • 4A: Care Management and Support (2011 3A) – New from 2011 is designation of specifically high cost/utilization population as well as a population specifically made vulnerable by a social determinant of health (such as exposure to crime, access to education, housing status, etc. – Documentation: process and criteria for identifying populations; percentage of the total patient population to benefit from care management based on the number/type of conditions selected for factors 1-5 Slide 15 Standard 4: Must Pass PCMH 4B: Care Planning and Self-Care Support The care team and patient/family/caregiver collaborate (at relevant visits) to develop and update an individual care plan that includes the following features for at least 75% of the patients identified in Element A: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Incorporates patient preferences and functional/lifestyle goals. Identifies treatment goals. Assesses and addresses potential barriers to meeting goals. Includes a self-management plan. Is provided in writing to the patient/family/caregiver. Slide 16 • 4C: Medication Management (2011 3D) – Just like 3D although now aligned w Meaningful Use Stage 2 • 4D: Use Electronic Prescribing (2011 3E) – Just like 3E in 2011 • 4E: Support Self-Care and Shared Decision Making – Adapted from 2011 4A and 4B, emphasis on providing educational resources to patients for their use in self management, including referrals to available community resources. Slide 17 Standard 5 PCMH 5: Track and Coordinate Care PCMH 5: Care Coordination and Care Transitions 2011 A. Test Tracking and FollowUp B. Referral Tracking and Follow-Up (Must-Pass) C. Coordination with Facilities and Care Transitions 2014 A. Test Tracking and FollowUp B. Referral Tracking and Follow-Up (Must-Pass) C. Coordinate Care Transitions Slide 18 • 5A: Test Tracking and Follow Up – Very closely aligned with 5A from 2011. Larger thresholds for the percent of lab and radiology orders that are electronically recorded in the pt record. Slide 19 Standard 5: Must Pass PCMH 5B: Referral Tracking and Follow-Up The practice: 1. Considers available performance information on consultants/specialists when making referral recommendations. 2. Maintains formal and informal agreements with a subset of specialists based on established criteria. 3. Maintains agreements with behavioral healthcare providers. 4. Integrates behavioral healthcare providers within the practice site. 5. Gives the consultant or specialists pertinent demographic and clinical data, including test results and the current care plan. Slide 20 Standard 5: Must Pass PCMH 5B: (continued) The practice: 6. Gives the consultant or specialist pertinent demographic and clinical data, including test results and the current care plan. 7. Has the capacity for electronic exchange of key clinical information and provides an electronic summary of care record to another provider for more than 50% of referrals.+ 8. Tracks referrals until the consultant or specialist’s report is available, flagging and following up on overdue reports. (critical factor) 9. Documents co-management arrangements in the patient’s medical record. 10. Asks patients/families about self-referrals and requesting reports from clinicians. Slide 21 • 5C: Coordinate Care Transitions – very similar to 2011 Slide 22 Standard 6 PCMH 6: Measure and Improve Performance 2011 A. Measure Performance B. Measure Patient/Family Experience C. Implement Continuous Quality Improvement (Must Pass) D. Demonstrate Continuous Quality Improvement E. Report Performance F. Report Data Externally PCMH 6: Performance Measurement and Quality Improvement A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Slide 23 2014 Measure Clinical Quality Performance Measure Resource Use and Care Coordination Measure Patient/Family Experience Implement Continuous Quality Improvement (Must Pass) Demonstrate Continuous Quality Improvement Report Performance Use Certified EHR Technology • 6A: Measure Clinical Quality Performance – Like Population management, separated measurement of immunization measures from other preventative care measures • 6B: Measure resource use and care coordination – Added two measures related to care coordination. Examples include: biopsy follow up, patient follow up after ER visit (see pg. 82 in standards for more examples) • 6C: Measure Patient/Family Experience – Exactly aligned 2011 standards for measuring patient experience(2011 6B) Slide 24 Standard 6: Must Pass PCMH 6D: Implement Continuous Quality Improvement The practice uses an ongoing quality improvement process to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Set goals and analyze at least three clinical quality measures from Element A. Act to improve at least three clinical quality measures from Element A. Set goals and analyze at least one measure from Element B. Act to improve at least one measure from Element B. Set goals and analyze at least one patient experience measure from Element C. Act to improve at least one patient experience measure from Element C. Set goals and address at least one identified disparity in care/service for identified vulnerable populations. Slide 25 • 6E: Demonstrate Continuous Quality Improvement – Closely aligned with 2011 6D…credit for achieving improvement on measures from elements A through C • 6F: Report Performance – Report performance data internally and publicly by individual clinician and at the practice-level • 6G: Use Certified EHR Technology – Not scored so no impact on points but they want you to report whether or not you use an EHR to perform a number of capabilities Slide 26