Version Control Systems and the Subversion
advertisement

Version Control Systems and the
Subversion
Kloimstein Dominik
Overview
• Basic information about VCS/Subversion
• Standard commands of Subversion
• Branching and Merging
What is a Version Control System?
• Standard software update process
Software xyz
Version 2.0.12
• In general version 2.0.11 is deleted – use
2.0.12
What is a Version Control System?
• Same update process with arbitrary files
Textfile x
Last change:
10.10.2010
Textfile x
Last change:
10.12.2010
• Also first textfile will be overriden
What is a Version Control System?
Textfile x
Last change:
10.10.2010
Textfile x
Last change:
10.12.2010
User A
What is a Version Control System?
• Manages all versions of files or directories in
the system
• Subversion is a open source VCS
What are Revisions?
• Are like version numbers of files or directories
• Each change of a file increases the revision
number by 1
• Subversion gives the whole filesystem a number
• Such a filesystem tree is called repository
What are Revisions?
File sharing problem
File sharing problem
• Lock-modify-unlock solution
File sharing problem
• Problems are:
– Administration (enough rights to lock)
– Performance (one user must wait)
– False sense of security
• Harry works on File A
• Sally works on File B
• A and B are depend on each other
File sharing problem
• Copy-modify-merge solution
File sharing problem
• Copy-modify-merge solution
File sharing problem
• Subversion use the copy-modify-merge
method
• No waiting
• Problem of so called conflicts
– Same problem with different results
– Overlaping of changes
– Solution: Communication (direct talk or put a flag)
• Subversion can also lock files
– Necessary for sound or graphic files
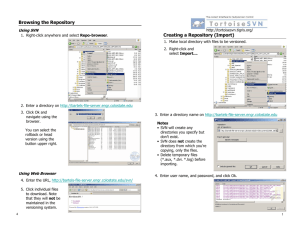
Repository
How to work with Subversion
• svn [command] [URL]
– $ svn checkout http://svn.example.com/repos/calc
• URL-forms:
– file:/// - direct local access
– http:// - access to a Apache server
– https:// - same as http with SSL encryption
– svn:// -access to a Subversion server
– svn+ssh:// - same as svn through SSH tunnel
How to work with Subversion
• file:///C:/svn/repos
• file:///svn/repos
• file:///localhost/svn/repos
• http://svn.example.com/repos
• http://svn.example.com:9834/repos
Commands
• The most often used commands are:
– svn add URL
– svn delete URL
– svn copy URL1 URL2
– svn move URL1 URL2
– svn mkdir URL
Commands
• checkout – copy files to the local working
directory
$ svn checkout http://svn.example.com/repos/calc
A calc/Makefile
A calc/integer.c
A calc/button.c
Checked out revision 1.
Commands
• commit – submit one or several files to the
server
$ svn commit button.c
Sending button.c
Transmitting file data .
Committed revision 57.
• Command commit maybe don‘t change files –
solution command update
Commands
• update – submit the whole working directory
to the server
$ svn update
Updating '.':
U button.c
Updated to revision 58.
Commands
• import – import a file or directory to the
repository
$ svn import /path/to/mytree \
http://svn.example.com/repo/some/project
Adding mytree/foo.c
Adding mytree/bar.c
Adding mytree/subdir
Adding mytree/subdir/quux.h
Committed revision 59.
Commands
• list – show files in the given directory
$ svn list http://svn.example.com/repo/some/project
bar.c
foo.c
subdir/
Commands
• status – show a overview of all changes
– ? item – This item is not under version control
– A item – Scheduled for addition to the repository
– D item – Scheduled for deleting this item in the
repository
– M item – The content in item is modified
$ svn status
? scratch.c
A stuff/loot
A stuff/loot/new.c
D stuff/old.c
M bar.c
Commands
$ svn status stuff/fish.c
D stuff/fish.c
$ svn status -v
M 44 23 sally README
44 30 sally INSTALL
M 44 20 harry bar.c
44 18 ira stuff
44 35 harry stuff/trout.c
D 44 19 ira stuff/fish.c
44 21 sally stuff/things
A 0 ? ? stuff/things/bloo.h
44 36 harry stuff/things/gloo.c
Commands
• diff – show a overview of all changes in detail
$ svn diff
Index: bar.c
===================================================================
--- bar.c (revision 3)
+++ bar.c (working copy)
+#include <sys/types.h>
+#include <sys/stat.h>
+#include <unistd.h>
+
+#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
- printf("Sixty-four slices of American Cheese...\n");
+ printf("Sixty-five slices of American Cheese...\n");
return 0;
}
Index: README
...
Commands
• log – show a time based overview of all
changes in detail
$ svn log
-----------------------------------------------------------------------r3 | sally | 2008-05-15 23:09:28 -0500 (Thu, 15 May 2008) | 1 line
Added include lines and corrected # of cheese slices.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------r2 | harry | 2008-05-14 18:43:15 -0500 (Wed, 14 May 2008) | 1 line
Added main() methods.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------r1 | sally | 2008-05-10 19:50:31 -0500 (Sat, 10 May 2008) | 1 line
Initial import
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Commands
$ svn log -r 8 -v
-----------------------------------------------------------------------r8 | sally | 2008-05-21 13:19:25 -0500 (Wed, 21 May 2008) | 1 line
Changed paths:
M /trunk/code/foo.c
M /trunk/code/bar.h
A /trunk/code/doc/README
Frozzled the sub-space winch.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Commands
• cat – return the content of a file
$ cat sandwich.txt
Top piece of bread
Salami
Mortadella
Prosciutto
Commands
• revert – delete changes and start from the beginning
$ cat sandwich.txt
Top piece of bread
Salami
Mortadella
Prosciutto
Now change Salami to Salad.
$ cat sandwich.txt
Top piece of bread
Salad
Mortadella
Prosciutto
$ svn revert sandwich.txt
Reverted 'sandwich.txt‘
$ cat sandwich.txt
Top piece of bread
Salami
Mortadella
Prosciutto
Commands
$ svn cat -r 2 sandwich.txt
Top piece of bread
Salad
Mortadella
Prosciutto
Branching and Merging
• Trunc – is the main directory
• Branch – is a copy of a file or directory of the
trunc section with small differences
• Tag – is a kind of „snapshot“ of a revision
• Merge – is the combining of two branches (or
to combine the branch back with the trunc)
Branching and Merging
Branching and Merging
• Tag – example
$ svn copy http://svn.example.com/repos/calc/trunk \
http://svn.example.com/repos/calc/tags/release-1.0 \
Committed revision 902.
Branching and Merging
• Merge – example
$ svn merge --reintegrate ^/calc/branches/my-calc-branch
--- Merging differences between repository URLs into '.':
U button.c
U integer.c
U Makefile
--- Recording mergeinfo for merge between repository URLs into '.':
U.
$ svn commit -m "Merge my-calc-branch back into trunk!"
Sending .
Sending button.c
Sending integer.c
Sending Makefile
Transmitting file data ..
Committed revision 391.
Branching and Merging
# Which changes have already been merged from trunk to branch?
$ svn mergeinfo ^/calc/trunk
r341
r342
r343
…
r388
r389
r390
# Which changes are still eligible to merge from trunk to branch?
$ svn mergeinfo ^/calc/trunk --show-revs eligible
r391
r392
r393
r394
r395
$