The Cochrane Library - Centre for Clinical Brain Sciences
advertisement

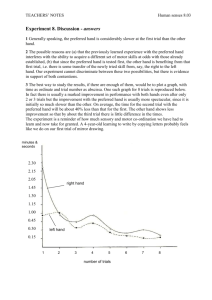
Systematic Reviews Effective Literature Searching Brenda Thomas Information Specialist Cochrane Stroke Group Stroke Review Group Comprehensive and versatile register of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and controlled clinical trials (CCTs) Prepare, keep up to date and disseminate high quality systematic reviews in all aspects of stroke healthcare Role of the Trials Search Co-ordinator (TSC)/ Information Specialist Deliver a comprehensive trials identification strategy Assess and code relevant stroke trials Develop and maintain quality and growth of the register of randomised trials and controlled clinical trials Support review authors Contribute to the review editorial process Considerable time and resources have been committed to maximising trial identification Specialised Register of Stroke Trials As many potentially relevant Randomised Controlled Trials (RCTs) and Controlled Clinical Trials (CCTs) as possible Published trials in any language from any year Unpublished trials Ongoing trials Planned trials All the available evidence The Cochrane Stroke Group Trials Register How we identified 13000 stroke trial reports Stroke Group Trials Register is one of the most advanced in the Collaboration All published trial reports included in the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials in The Cochrane Library Methods Identify sources of relevant trials Develop appropriate search strategies Screen bibliographic details for potential reports of trials Obtain full copies and apply selection criteria Arrange translation if required A systematic approach to trial identification • Electronic databases • Handsearching • Personal communication Multiple overlapping search strategies to minimise bias Supported by the considerable resources of The University of Edinburgh and NHS Scotland e-library Electronic resources Major medical bibliographic databases Eg MEDLINE and EMBASE Topic specific databases Non-English language databases International trials and research registers (ongoing trials) The Internet Regular searches of 27 bibliographic databases Approx 25,000 references screened annually Topic Specific Databases BIOSIS Previews (Biology and pharmacology) AMED (Allied and Complementary Medicine) CINAHL (Nursing and Allied Health) PsycINFO (Psychology) Digital Dissertations (Theses) MANTIS (Manual, alternative and natural therapy) International Pharmaceutical Abstracts Occupational Therapy Journal of Research Index Applied Social Sciences Index and Abstracts Clinical Trials Registers bibliographic Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library) The most comprehensive source of reports of controlled trials Chinese Clinical Trials Register The Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) Database of Randomised Controlled Trials in Hyperbaric Medicine (DORCTHIM) ongoing Stroke Trials Directory http://www.strokecenter.org/trials/ Current Controlled Trials http://www.controlled-trials.com/ GlaxoSmithKline Clinical Trials Register RehabTrials.org Electronic journals Contents pages and abstracts on-line Current awareness alerts Selected free articles or issues Full text (free or subscribed) Download pdfs Personal Communication and The Internet Trialists and colleagues Drug Companies Equipment manufacturers Websites: e.g. company press releases, research centre bulletins, research funders News alerts eg MEDSCAPE http://www.medscape.com/neurology News media (current awareness) Conference abstracts on-line Essential sources of unpublished and ongoing trials Reference lists Trial reports from publications not indexed in bibliographic databases Early trial reports References from grey literature Conference abstracts books theses Review-specific searches Electronic searches Geographic, eg Chinese Biomedical Literature Subject specific, Engineering databases Handsearching specialist journals and conference proceedings Unpublished studies Contacting pharmaceutical companies or equipment manufacturers Key advantage of searching bibliographic databases Can be searched electronically for: words in the title and abstract Standardized indexing terms or controlled vocabulary assigned to each record based on the full report. Limitations and challenges of electronic searching for published studies Selected journals and journal years indexed Conference proceedings and books in selected databases only A complex tailor-made strategy required for each database Poor indexing often limits retrieval Titles and abstracts (when available) may be insufficiently detailed for text word searching Free-text searching for full-text electronic journals! High sensitivity searches result in low precision Handsearching Advantages All reports of trials in journal Articles, editorials, letters, abstracts, news items Journals, books and conference proceedings not in electronic databases Recent issues Limitations Time consuming and expensive Large numbers of healthcare journals Access to journals Non-English language journals Subject to human error Is handsearching worthwhile? Complete retrospective search of 32 years of journal STROKE Compared with MEDLINE search of STROKE for same publication years MEDLINE search identified 44% of 803 stroke trial reports identified by handsearching. Conference abstracts and letters etc not indexed by MEDLINE Many of the trials published as conference abstracts will not come to full publication Stroke Group general strategy modified for each database STROKE specific strategy ? Highly sensitive TRIALS strategy Screened for stroke trials Review-specific intervention-based strategy STROKE specific strategy ? ? ? Screened for additional relevant trials Highly sensitive Cochrane TRIALS strategy Review specific INTERVENTION-based strategy New developments that make life easier Increasing availability of electronic journals 77% of relevant MEDLINE trial reports in 2006 Free open access journals and conference proceedings More detailed reporting of study methods Increasing numbers of ongoing trial registers Including drug company (eg GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Roche) International trial registration WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform Multiple Registers (ISRCTN, NCT, ANZCTR) Universal Trial Reference Number Easier to track trial reports and link to studies Looking for Research Studies? How to search like a professional! Increasing numbers of resources available Need a focused approach using high quality information resources Increased use of electronic sources Efficient search strategies Where do we start? Search question? Purpose of search? How much information do we need? Where do we look? How much time do we have? How much money do we have (if any!)? Sources of Bias Publication bias “Level of publication” bias Cited work is more likely to be positive Electronic database bias? abstracts and letters may more often report negative results Reference/citation bias negative results are often not published Need to search multiple databases Language bias Aim to minimize bias Bibliographic Databases MEDLINE Major general medical database Indexes articles from >5000 journals (2100 not EMBASE) 37 languages >16 million citations from 1950 All articles indexed using Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) to describe each article Available on Ovid SP through University or NHS e-Library Bibliographic Databases EMBASE Major general medical database Indexes articles from 4800 journals (1700 not MEDLINE) 30 languages >11 million citations from 1974 All articles indexed using Emtree Headings to describe each article (Different from MeSH) Pharmacological studies indexed in greater depth than MEDLINE Available on Ovid SP through University or NHS e-Library Both databases required for a comprehensive search MEDLINE Record searchable fields Authors Title Journal title MeSH Subject Headings Abstract Publication Type Language MEDLINE Developing a Search Strategy Use a combination of MeSH terms and free text for: Disease under investigation Intervention Study design (methodological filters) Use “Publication Type” field to focus the type of research (eg randomised controlled trial) Apply other logical limiters (eg age group, human, time period) Ask your local medical librarian for help! Stem Cell Transplantation for ischemic stroke MEDLINE (Ovid) 1. cerebrovascular disorders/ or basal ganglia cerebrovascular disease/ or exp brain ischemia/ or carotid artery diseases/ or carotid artery thrombosis/ or intracranial arterial diseases/ or cerebral arterial diseases/ or exp "intracranial embolism and thrombosis"/ or exp stroke/ 2. (isch?emi$ adj6 (stroke$ or apoplex$ or cerebral vasc$ or cerebrovasc$ or cva or attack$)).tw. 3. ((brain or cerebr$ or cerebell$ or vertebrobasil$ or hemispher$ or intracran$ or intracerebral or infratentorial or supratentorial or middle cerebr$ or mca$ or anterior circulation) adj5 (isch?emi$ or infarct$ or thrombo$ or emboli$ or occlus$ or hypoxi$)).tw. 4. 1 or 2 or 3 5. cell transplantation/ or stem cell transplantation/ or cord blood stem cell transplantation/ or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation/ or mesenchymal stem cell transplantation/ or peripheral blood stem cell transplantation/ 6. stem cells/ or adult stem cells/ or embryonic stem cells/ or fetal stem cells/ or fibroblasts/ or hematopoietic stem cells/ or myeloid progenitor cells/ or erythroid progenitor cells/ or mesenchymal stem cells/ or multipotent stem cells/ or exp myoblasts/ or pluripotent stem cells/ or totipotent stem cells/ or tumor stem cells/ 7. exp cells/tr 8. ((stem or progenitor or embryo$ or fetal or foetal or umbilical or bone marrow or cord blood) adj5 (cell or cells)).tw. 9. (cell adj5 (transplant$ or graft$)).tw. 10. (fibroblast$ or myoblast$).tw. 11. cell transplantation.jn. 12. 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 13. 4 and 12 14. limit 13 to humans Search results Review retrieved citations Modify search strategy New text word terms Synonyms, related terms, variant spellings Check MeSH headings Check that search strategy identified known references Gradually build a comprehensive strategy Features of reference management software Personal reference database organise references create bibliographies Imports references from various databases Automatic formatting of papers and bibliographies Reference Manager, EndNote Locally installed or networked EUCS provides half-day courses on Reference Manager and EndNote in almost every month of the year Conclusions Be systematic but realistic! Clearly define search question Identify relevant available sources Prepare search strategy(ies) Conduct and modify search Consider reference management software Translation? Correctly document and report the search methods Essential Reading Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Chapter 6 Searching for studies •Main sources of potential studies •Planning the search process •Designing and carrying out the search strategies •Managing references •Correctly documenting and reporting the search process http://www.cochrane.org/resources/handbook/