Development
advertisement

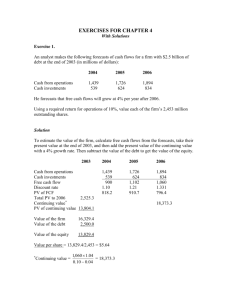
Countries according to the Human Development Index (2010) Poverty & Development Today Developing countries & development The debt crisis Current issues Developing countries & development Recognizing developing countries: geography Timeline 1500s-1945: colonization 1945-1970s: decolonization The Cold War context New countries as a “problem” The choice of words Developing countries Third World countries Less developed countries The South The global South Recognizing developing countries: $ per day 1. Geography 2. GDP per capita (PPP*): $1/day or $365/year $2/day or $730/year See the World Resources Institute search engine for basic poverty figures Proportion of population below $1/day (2008) see data for the whole world * PPP: purchasing power parity takes into account the fact that the cost of the same products varies by country. Recognizing developing countries: economic sector size Size of economic sectors in total GDP in total employment “Development”: standard definition vs. human development Peasants Dancing, 1651 Johannes Lingelbach (Dutch, 1622–1674). Oil on canvas; 26 1/2 x 29 1/2 in. (67.3 x 74.9 cm) Standard definition the Cold War & the invention of “development” copying the US/European model industrialization of agriculture from agriculture to industry to mass consumption measured by GDP growth Human development GDP growth not enough harder to measure nutrition health physical security leisure participation in community creative life Defining human development “The basic purpose of development is to enlarge people’s choices. In principle, these choices can be infinite and can change over time. People often value achievements that do not show up at all, or not immediately, in income or growth figures: greater access to knowledge, better nutrition and health services, more secure livelihoods, security against crime and physical violence, satisfying leisure hours, political and cultural freedoms and sense of participation in community activities. The objective of development is to create an enabling environment for people to enjoy long, healthy and creative lives.” Mahbub ul-Haq, quoted in United Nations Development Program. (2008). “The Human Development concept”. Retrieved 9 February 2010, from http://hdr.undp.org/en/humandev/. 2011 Human Development Report Measured by the Human Development Index (HDI). See how it’s calculated. The debt crisis Origins of the debt crisis OPEC* and oil prices “Petrodollars” in Western banks •Algeria •Angola •Ecuador •Iran* •Iraq* •Kuwait* •Libya •Nigeria •Qatar •Saudi Arabia* •United Arab Emirates •Venezuela* * Founding members Former: Gabon & Indonesia Developing countries’ need for capital Loans from Western banks Interest rates rise * Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries The International Monetary Fund (IMF) & Structural Adjustment Programs (SAPs) Lender of last resort Allowing debtor governments to pay back debts Conditionality conditions for IMF & World Bank loans “economic reforms”, “austerity measures”, “Washington consensus” Washington consensus • Privatization of stateowned enterprises • Reductions in gov. spending (health, education & social) • Elimination of subsidies (cooking oil, staple foods, fuel) • Deregulation of labour markets (less protection) • Adoption of free trade • Allow foreign investors to buy domestic companies Debtors: those who have debts Creditors: those to whom money is owed Therefore debtors are supposed to reimburse creditors SAPs’ objectives & results Impose good economic policies to restore government budget & guarantee loan repayment restore credit rating “good investment climate” “conditions for economic growth” and “give investors confidence” What they did and create reduction in wealth redistribution increase in cost of living increase in poverty, child mortality, maternal mortality political instability NB: since the late ’90s restoration of social, health & education spending Where did investments go? Same 12 developing countries 2005 to April 2011 43.3% Source: International Labour Organization. (2004). A Fair Globalization: Creating Opportunities for All. Geneva: ILO. pp. 28-29. http://www.ilo.org/public/english/wcsdg/docs/report.pdf Benefits Problems Developing countries do get investments from 12 countries, 75% of investments multinational/transnational corporations South-South competition Jobs are created Dubious labour practices Taxable income for developing countries’ governments There are more workers than are needed(!) Ability to pay back loans 56.7% Current issues More issues will be raised in the documentary Debt cancellation Jubilee 2000 (UK, US & Vatican campaigns) Impossibility of repayment generally acknowledged, but… the “odious debt” human consequences impossibility of repaying the debt which LDCs should benefit? “moral hazard” G8 summit of Gleneagles, July 2005 debt cancellation for 36 poorest countries Some strings attached Group of 8 most industrialized countries 1. Canada 2. France 3. Germany 4. Italy 5. Japan 6. Russia 7. United Kingdom 8. United States The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) Summary of successes & failures available here (red menu on the right) Officially a UN initiative But dependent on developed countries … and autonomous international organizations (IMF & World Bank) 8 goals to be achieved by 2015 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eradicate extreme poverty & hunger Requires governAchieve universal primary education ment intervention Promote gender equality & empower women with taxes, reguReduce child mortality lations & targeted policies Improve maternal health Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases Ensure environmental sustainability Develop a global partnership for development Conclusion A global capitalist system An increasingly integrated economic system… with wide disparities in wealth Numerous policies aimed at guaranteeing development & improvement in well-being… with unclear results Annex 1: International division At the time of developing of labour 1 countries’ independence N O R T H S O U T H Developed country 1 Trade Developed country 2 Trade Developed country n Manufacturing of finished goods Manufacturing of finished goods Manufacturing of finished goods Exports Exports Exports Raw material and agricultural products Raw material and agricultural products Raw material and agricultural products + some manufacturing + some manufacturing + some manufacturing Developing country 1 Developing country 2 Developing country n Annex 2: International division of labour 2 Since the 1980s N O R T H Developed country 1 R&D, manufacturing of hi-tech finished goods Exports incl. manufactured goods S O U T H Trade Investments and/or subcontractors Developed country 2 Trade R&D, manufacturing of hi-tech finished goods Exports incl. manufactured goods Investments and/or subcontractors Developed country n R&D, manufacturing of hi-tech finished goods Exports incl. manufactured goods Investments and/or subcontractors Raw material and agricultural products Raw material and agricultural products Raw material and agricultural products + growing manufacturing + services Developing country 1 + growing manufacturing + services Developing country 2 + growing manufacturing + services Developing country n Different parts of the finished good made in different developing countries