Thunderstorms & Tornadoes
advertisement

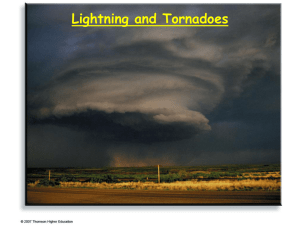
THUNDERSTORMS & TORNADOES QUESTION OF THE DAY Where would you expect to find the greatest proportion of Tstorms and why? CYCLONE Circulation around ANY lowpressure center Intensity and size do not matter Tornadoes and Hurricanes are smaller than mid-latitude cyclones and more violent THUNDERSTORMS Storm that produces lightning and thunder Characterized based upon the up/down draft of air NOT circular motion of air Forms when warm, humid air rises in an unstable environment Unequal heating of earth’s surface (Air-Mass Tstorms) Unequal heating along with frontal wedging or oorgraphic lift (Severe Tstorms) AIR-MASS THUNDERSTORMS Occur in mT air that moves Northward from Gulf. Most frequent during Spring and Summer Frequently around midafternoon Thunderstorm Project produced a model of the life cycle of a Tstorm Cumuls Stage Mature Stage Dissipating Stage CUMULUS STAGE Formation of cumulus clouds allow for moisture to be at greater heights Clouds grow vertically Cumulonimbus clouds form Dominated by updraft Downdraft forms and failing precipitation causes drag Entrainment intensifies downdraft MATURE STAGE Officially starts when precipitation leaves the cloud Updraft and downdraft exists side by side and grow the cloud Anvil top forms when cloud reaches base of the stratosphere Most active stage: Gusty winds, ligthning, hail/heavy precipitation DISSIPATING STAGE Dominated by the downdraft Cooler air aloft and falling precipitation causes cloud to evaporate SEVERE THUNDERSTORMS Characterized by heavy downpours, flash flooding, strong/gusty winds, hail, lightning, and maybe tornadoes. Must have winds over 58mph or hailstones .75 in diameter or produce a tornado SUPERCELL TSTORMS Single, powerful cell up to 65,000’ and 12-30 miles in diameter 2000-3000/year in the US Can form mesocyclones when updraft rotates THUNDER & LIGHTNING Thunder is: Expanding air Heat Lightning Lightning is created due to separation of charges in a cumulonimbus cloud Sheet Lightning Within the cloud or between clouds 80% of all lightning Cloud to Ground Lightning 20% of lightning strokes Most damaging and dangerous Flash is made up of individual strokes Leader, step leader, return stroke, and dart leader TORNADOES AKA: twisters, cyclones Violent windstorms that are a vortex Contains lower pressure inside the vortex than the surrounding areas TORNADO FORMATION Form in association with severe thunderstorms Located wherever severe weather is: cold fronts, squall lines, hurricanes, supercells Only tornado if funnel cloud touches surface F-SCALE Fujita Intensity Scale Determined based upon damage produced TORNADO FORECASTING Watches Alters public to POSSIBLITY of tornadoes over a specific area for a certain time period. 65,000sq.km for 4-6 hours Warnings Issued by local NWS ACTUAL sighted tornado in an area or indicated by radar Smaller areas and for shorter periods of time