13.2 Severe Weather
advertisement

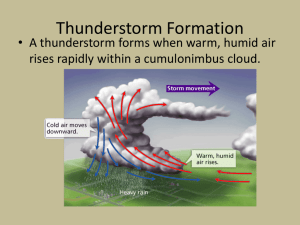
Overview All t’storms are not created equal Severe thunderstorms produce the most violent weather conditions on Earth Supercells – characterized by intense, rotating updrafts; can last several hours and have updrafts up to 240 km/h. In the U.S., less than 10% of storms are severe Lightning Lightning is electricity caused by the rapid rush of air in a cumulonimbus cloud Lightning forms when and advancing stepped leader unites with an upward moving return stroke A bolt heats the air around it to 30,000 degrees Celsius, producing thunder 7500 forest fires, 300 injuries, 93 human deaths each year Damaging Wind Downbursts are violent downdrafts concentrated in a certain area; could be more than 160 km/h Hail Causes $1 billion in damage in the U.S. each year Largest recorded hailstone weighed 1.67 punds First, water droplets collide with ice pellets and they freeze instantly forming larger pellets Updrafts and downdrafts cause more collisions Floods The leading cause of weather related deaths More rain falls in an area than the ground can absorb More rain falls in an area than rivers and streams can transport away from that area Tornadoes A tornado is a whirling, violent column of air in contact with the ground Tornadoes are associated with supercell thunderstorms and begin as a funnel cloud Wind shear allows the formation of a tornado Classified using the Fujita intensity scale (F0 – F5) Most form in spring during the late afternoon 80 deaths and 1500 injuries occur in the U.S. each year