SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS
advertisement
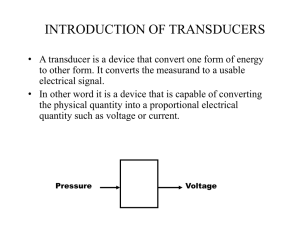
Sensors – the term sensor is used for an element which generates a signal which is proportional to the quantity being measured. Transducer – these are elements when subjected to physical change experience a related change. In measurement system a transducer in addition to sensor is used to convert signals in one form to another. A sensor/transducer is said to be analogue if it gives output which is analogue and is digital if output is in the form of signals which is digital in nature. Smart sensors – is a device which has inbuilt sensor and signal conditioning embedded in a same package. › Ability to compensate random errors › Calculation of measurement accuracy › Adjust for non-linearity and gives linear output › Self calibrate and self diagnosis Range and span o Error o Accuracy o Sensitivity o Hysteresis error o Non linearity error o Repeatability error o Range and span › Range 0 KN to 50 KN › Span is 50 KN Error Range defines the limits between which the inputs can vary. Span = max value of input – min value For a load cell Error = true value – measured value If a system gives a temperature reading of true value 25 deg Celsius and measured value is 24 deg Celsius then error is +1 deg Celsius. Accuracy Sensitivity Accuracy is the extent to which the value indicated by measurement system might be wrong. It is the summation of all possible errors, as well as accuracy to which transducer has been calculated. Accuracy is often expressed in terms of % of full range output. It is the relationship indicating how much output is there for a given input. i.e output/input. For ex a resistance thermometer has sensitivity 0.5 Ω / ºC. Other than measurement sensitivity also incorporates the external parameter. Hysteresis error Transducers can give different outputs from same value of quantity being measured whether the value has reached continuously increasing change or continuously decreasing change. Non linearity error Repeatability error Repeatability is used to describe the ability of transducer to give same output for repeated applications of the same input valve. Repeatability = (max-min values) *100 full range Transducers are elements which covert or transform one form of energy to other. Transducer is a device used to measure system parameters. Its is device that produces a measurable response to a change in physical quantity such as temperature, pressure, etc. It is used to quantify the parameters such as temp, pressure, magnetic field, voltage, flow, vibrations which are commonly called a measurands. Transducers are the physical element which is a part of sensor. A sensor is merely a sophisticated transducer, which contains signal conditioning circuits capable of amplifying and refining weak and raw signals that is available at output of transducers. Depending on type of conversion › Primary transducer › Secondary transducers Depending on output › Active transducers › Passive transducers The Mechanical device which converts physical quantity to be measured into a mechanical signal. Ex – bourdon tube The Bourdon pressure gauge uses the principle that a flattened tube tends to change to be straightened or larger circular cross-section when pressurized. Bourdon tube are instruments measuring the pressure of liquids and gases of all kinds, including steam, water and air. The tubes are C structured tubes. The angular of linear displacement is proportional to applied pressure. One end is fixed and other is free and closed. As pressure rises, the C structured tube expands which in turn moves the needle. The output of the primary transducer is again converted into a different form using a secondary transducer. Ex – bourdon tube connected to a LVDT to give a digital output LVDT is mainly used for displacement or position measurement. It consists of three coils symmetrically spaced along a insulated tube. The central coil is primary coil and other two secondary primary coils are in series whose end terminals act as outputs. A magnetic core is moved through the central tube as a result of displacement being monitored. When the core is moved or displaced right of left the number of coils in the secondary coil is exposed to primary coil changes which is due to mutual inductance. Variation of mutual inductance of each of coil, in effect, induce varied relative voltages in secondary coils. Since two windings are connected in opposition, as the core moves, the output of one decreases and another increases. The emf induced in secondary coil by a changing current i in primary coil is given by = E = M (di/dt) Depending on output › Active transducers › Passive transducers Passive equivalences are resistance, inductance, and capacitance. Transducers of this category are made up of specific materials, such as their electrical properties like resistance, inductance and capacitance vary in response to change in input measurands. Ex load cel, LVDT, capacitive transducers. Strain gauges are resistive pick type transducers. The resistance of the gauge changes in accordance with the input mesurand. The strain gauge consists of metallic filament (a resistor) of approximately 0.03 mm thickness, which is bonded or pasted directly to the strained surface by a layer of epoxy resin. When load is applied to the surface, resulting change in surface length, hence the strain. This is communicated to filament whose resistance changes linearly with measurand. The equation governing the strain and resistance is › ▲R / R = g e Wheatstone Bridge, a device for measuring electrical resistance. It can be used to convert resistance change into voltage change. R1/R2 = R3/R4 The bridge is said to be balanced. Load cell are transducers intended for measurement of high values of pressure, load and force. Resistance load cell consists of at least four strain gauges, which are adhered to cylinder. Four strain gauges are used to obtain higher sensitivity. Two of the gauges are usually subjected to tension and other two compression. When the load applied, the strain changes the electrical resistance of the gauges in proportional to the load. The principle of capacitive transducers is based on the change of distance, area and/or permittivity. Capacitive transducers are non-contact type for which accuracy and resolution are high. These are employed for the measurement of displacement, acceleration, force, level, pressure, etc.