November 27th - Pleasantville Middle School
advertisement

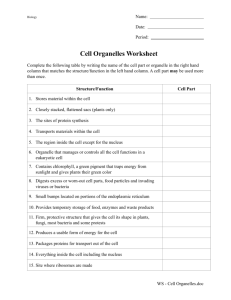
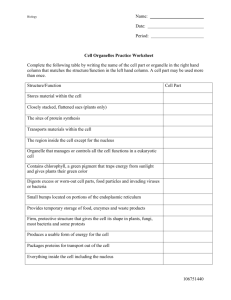
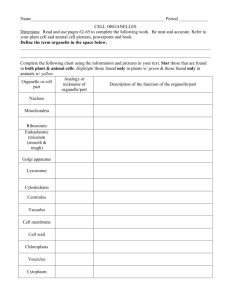
November 27th Quick Write: 1. What are all living things made of? 2. What is the basic unit in all living things? 3. Is it true that all living cells come from pre-existing cells? SWBAT: • Describe the cell theory. • Explain how each scientist helped to develop the cell theory? Homework: • Read pgs. 69-71, Section Review 3-11, pg 71 answer questions 1-3 In Conclusion . . . 1. What did Robert Hooke discover? 2. What did Robert Brown observe in each cell? 3. What did Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden conclude about all living things? Together they all helped to create what theory? The History of the Cell • Brief_History_of_the_Cell_.mov The Cell The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. The structures that make up a cell are called organelles. 1665 - Robert Hooke looked at cork - he saw "little rooms" that he called cells. At the same time: Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a simple microscope to see moving objects that he called "animalcules." He was actually looking at bacteria. • Matthius Schleiden – Botanist who studied the parts of plant cells. Determined that all plants are made of cells • Theodore Schwann: – Zoologist who studied animals. Determined that all animals are made of cells • Rudolf Virchow: – All living cells come from other living cells. Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of cells. 2. Cells arise from pre-existing cells. 3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. November 30th Quick Write: 1. Write down your acronym for the cell theory. 2. Identify the image to the right. 3. What function does it perform? 4. Name the life process that occurs within this organelle. Homework: • read your notes and highlight key words • prepare for a possible quiz soon SWBAT: • Describe the cell theory. • Identify the function of each organelle. • Identify each organelle. December 1st Quick Write: 1. Identify the image to the right. 2. What function does it perform? 3. Name the organelle and its functions from yesterday’s Quick Write. 4. Draw a quick sketch of a plant cell versus an animal cell. Homework: SWBAT: • Read pgs 71-81 • Describe the function of • Define each highlighted vocabulary word each organelle. and sketch an image representing the structure due Monday, December 4th • Identify each organelle. • Complete the Organelle Class work Packet nucleus mitochondrion nucleolus chromosome ribosome vacuole nuclear membrane endoplasmic reticulum cell membrane cytoplasm lysosome Closure 1. Which organelle is grainlike in appearance (little dots) and is typically found on the endoplasmic reticulum? 2. Which organelle is tubular and found near the nucleus? 3. Which 2 organelles are found within the nucleus? 4. Which organelle is made of cellulose? The Cell Structures of the Eukaryotic Cell a. Cell Wall b. Cell membrane c. Cytoskeleton d. Nucleus Go to Section: Cell wall • Composed of cellulose, a strong stiff carbohydrate made of long chains of glucose. – Cellulose is found in the stringy part of the celery. • Only found in plant cells and bacteria • Allows water, oxygen, carbon dioxide and other dissolved materials to pass through to the cell membrane. Cell membrane • Composition: lipids, proteins, cholesterol glycoproteins – Fluid mosaic model – Phospholipid: hydrophilic: (polar) – Fatty acids: hydrophobic: (nonpolar) • Function: barrier, selectively permeable, cell recognition/signaling • Nucleus: contains: – – – – – – Nucleus chromosomes made of DNA, DNA contain genes, genes contain sequences of nucleotides Nucleotide sequences code for amino acids amino acids sequences create a polypeptide Controls activities of the cell and determines the protein to be synthesized • Nucleolus: – – – – Inside the nucleus Parts of the ribosome are synthesized here Are tangles of chromatin and unfinished ribosomes RNA synthesis Name ___________________ Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell Structures and Organelles Section 7-2 Animal Cells Go to Section: Plant Cells Section 7-2 Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell membrane Ribosomes Cell wall Animal Cells Plant Cells Cell membrane Ribosomes Nucleus Lysosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Centrioles Many small vacuoleGolgi apparatus Mitochondria Cytoskeleton Go to Section: Cell Wall Chloroplasts 1 large vacuole Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Mitochondria Cytoskeleton Animal Cell Section 7-2 Go to Section: Plant Cell Section 7-2 Go to Section: B. Organelles in the Cytoplasm Rough Endoplasmic reticulum Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi Apparatus Ribosomes Lysosomes Vacuoles Chloroplasts Mitochondria Centioles Ribosomes Site of protein synthesis Lysosomes digestion of food particles, or old organelles 06_14LysosomeFormation_A.html Vacuoles: 1. storage of water, salts, and minerals 2. Fresh water protista: contractile vacuoles to pump excess water out: ex: amoeba, and paramecium Plant Cell Animal Cell Endomembrane systems • Rough endoplasmic reticulum: 06_16EndomembraneSystem_A.html – site of protein synthesis • Smooth endoplasmic reticulum – – – – Synthesizes steroid hormones/fats Connects the RER to Golgi Appart. Detoxifies the cells Carbohydrate metabolism • Golgi apparatus: – Near the nucleus – Flattened stacks of membranes – Modify, store, and package substances produced by the RER – Secretes these substances out of the cell Mitochondria • Site of Cellular respiration/ATP production • Outer double membrane • Cristae: series of inner membrane folded, increases surface area for ATP production • Enzymes are embedded in the cristae to assist in cellular respiration • Have DNA • Can self-replicate Chloroplasts • Site of Photosynthesis • Production of plant’s mass (glucose) • Double membrane • Stroma: fluid interior • Granum: stacks of thylakoids containing chlorophyl • Chlorophyll: pigment absorbing light energy to stimulate photosynthesis Centriole• • • • • Only animals have centrioles and centrosomes Found near the nucleus and required for cellular division Centrosome: consists of 2 centrioles at right angles Centrioles and spindle fibers have same structure 9 triplets of microtubules in a circle 06_14LysosomeFormation_A.html 06_16EndomembraneSystem_A.html 06_24CiliaFlagella_A.html Video Clip Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What is the most outer layer of the animal cell? What can easily diffuse through this structure? What is the meaning of the word organelle? What does the nucleus function as? What organelle produces protein? What organelle turns oxygen and glucose to ATP/energy? What organelle packages proteins with lipids and carbohydrates and places them into vesicles to be shipped out of the cell? What organelle contains enzymes to digest particles and old organelles?