Lecture Notes Part II
advertisement

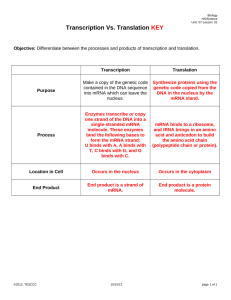
Name_______________________________________ Lecture Notes Part II: Protein Synthesis Why transcription DNA cannot leave the ____________, it is too dangerous. It must use a messenger _____________ DNA needs its message to be expressed so the cell can perform all of its jobs (the proteins go on to do the jobs) Steps of transcription Step 1: ___________________ 1. Initiation is the beginning of transcription. It occurs when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a region of a gene called the _________________ This signals the DNA to unwind so the enzyme can “read” the bases in one of the DNA strands. The enzyme is ready to make a strand of mRNA with a ______________________ sequence of bases. Step 2: _____________________ Elongation is the addition of nucleotides to the mRNA strand. Step 3: _______________________ Termination is the ending of transcription. The mRNA strand is complete, and it detaches from DNA. Processing RNA These processes (below) modify the mRNA in various ways. Such modifications allow _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Splicing removes ______________ (regions that do not code for proteins) from mRNA. Only ___________ are left. Editing changes some of the nucleotides in mRNA. This creates different forms of the protein. Polyadenylation adds a “tail” to the mRNA (consists of a string of As -adenine bases). The tail protects mRNA from ______________ that might break it down. The genetic code The set of rules by which information in DNA is turned into proteins by living cells. The genetic code is ___________________ All known living things have the same genetic code. This shows that all organisms share a common evolutionary history. The genetic code is __________________ Each codon codes for just one amino acid (or start or stop). The genetic code is ___________________. Most amino acids are encoded by more than one codon. Translation ____________________ is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology: RNA → Protein. It is the process in which the genetic code in mRNA is read to make a ___________________. Steps of translation 1. After mRNA leaves the nucleus, it moves to a _______________________, which consists of rRNA and proteins. 2. The ribosome reads the sequence of ________________ in mRNA. 3. Molecules of tRNA bring ____________________________ to the ribosome in the correct sequence 4. While bound to mRNA, tRNA gives up its amino acid. 5. _____ form between the amino acids as they are brought one by one to the ribosome, forming a polypeptide chain. 6. The chain of amino acids keeps growing until a _______________________ is reached Codons and anticodons Protein formation The polypeptide is the protein’s INITIAL structure (it’s ______________ structure) Now based on many factors (amino acids it contains, pH, temperature etc,) it will FOLD up / or combine with other polypeptides to form its FINAL structure. Protein functions Antibodies: Fighting ______________________ Contractile Proteins: Movement! Enzymes: Facilitate biochemical __________________ Hormonal Proteins: Coordinate bodily activity (blood sugar, childbirth) Structural Proteins: hair, feathers, horns, beaks, _________________, tendons Storage Proteins: Store _______________________________ Transport Proteins: Ex: hemoglobin transporting ______________________ Regulatory proteins: Decide which _______________ are turned “on” and “off”