File
advertisement

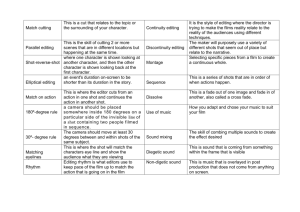
Editing Techniques Glossary Match Cut A cut between either two different objects, two different spaces, or two different compositions in which the object graphically match. Establish a strong continuity of action. Flash Cutting Editing sequences so that the shots are short and brief (less than two seconds). Subliminal Cut A cut consisting of a few frames which go by so fast that the viewer is only partly aware of them. Cross Cutting Editing that alternates shots of two or more lines of action occurring in different places Discontinuity Editing Alternative system of joining shots together using techniques unacceptable within continuity editing principles. Elliptical Editing Shot transitions that show parts of an event, causing ellipsis in plot and story duration. Jump Cut A cut that appears to be an interruption of a single shot. It occurs within a scene rather than between scenes, to condense the shot. Overlapping Editing Cuts that repeat part or all of an action, thus expanding its viewing time and plot duration. Invisible Editing Editing that is so smooth that viewers become engrossed in the movie and don’t notice the individual cuts. Line Cut Tape of the switches from one camera angle to the other that the multiple camera directors call out as the show was shot. Split Edit In a split edit, the audio and video edit do not start at the same time; either video or audio is delayed. Credits Provides attribution to the staff involved in their productions. Cutaways Interruption of a continuously-filmed action by inserting a view of something else. It is usually followed by a cutback to the first shot, but not always. Freeze Frame A single frame forming a motionless image from a film or videotape. Eyeline Match Based on the premise that the audience will want to see what the character onscreen is seeing. Flashback A scene in a film set in a time earlier than than main story. Then it can jump from one time frame to another. Graphic Match A cut in film editing between either two different objects, two different compositions in which an object in the two shots graphically match, often helping to establish a strong continuity of action and linking the two shots together. Juxtaposition The fact of two things being seen or placed close together with contrasting effect. Montage The technique of selecting, editing, and piecing together separate sections of film to form a continuous whole. Parallel Editing This involves cutting back and forth between two or more scenes in which the action is taking place simultaneously or in which one action is compared or contrasted with another. Visual Effects Various processes by which imagery is created and/or manipulated outside the context of a live action shot. Match on Action Where the editor cuts from one shot to another view that matches the first shot’s action. Shot Reverse Shot One character is shown looking (often off-screen) at another character, and then the other character is shown looking “back” at the first character. The Insert An insert is a shot of part of a scene as filmed from a different angle and/or focal length from the master shot. Continuity A system of cutting used to maintain continuous and clear narrative action by following a set of rules. 180 Degree Rule A basic film editing guideline that states that two characters (or other elements) in the same scene should always have the same left/right relationship to each other. Action Match Where the editor cuts from one shot to another view that “matches” the first shot’s action and energy. Establishing Shot A shot, normally taken from a great distance or from a “bird’s eye view,” that establishes where the action is about to occur. Non-continuity Continuity is broken and construction is more apparent. Meaning often created through juxtaposition and metaphor shot inserts. Dissolve A dissolve is a gradual transition from one image to another. The terms fade-out and fade-in are used to describe a transition to and from a blank image. Fade A visual transition between shots or scenes that appears on screen as a brief interval with no picture. The editor fades one shot to black and then fades in the next. Often used to indicate a change in time and place. Wipe Visible on screen as a bar travelling across the frame pushing one shot off and pulling the next shot into place. Superimposition Two distant images appearing simultaneously with one superimposed upon the other. Long/Short Take A long take is an uninterrupted shot in a film which lasts much longer than the conventional editing pace either of the film itself or of films in general, usually lasting several minutes. Slow/Fast Motion Slow motion is an effect in film-making whereby time appears to be slowed down, in contrast to fast motion where time is sped up. Expansion of Time When you expand time in a video, you are making the duration of the video sequence longer than real-time. Post-Production Visual Effects Visual effects (VFX) are the various processes by which imagery is created and/or manipulated outside the context of a live action shot. Visual effects using computer generated imagery has recently become accessible to the independent filmmaker with the introduction of affordable and user friendly animation. Editing The joining of one shot (strip of film) with another. The shots can picture events and objects in different places at different times. Final Cut The finished edit of a film, approved by the director and the producer. This is what the audience sees. Iris Visible on screen as a circle closing down over or opening up on a shot. Rough Cut The first version of a film after preliminary editing. Sequence Shot A long take that extends for an entire scene or sequence. It is composed of only one shot with no editing. Reaction Shot A cut to a shot of a character’s reaction to the contents of the preceding shot. Linear Edit Before digital editing video sequences were edited by inserting new frames and reconstructing the balance of the tape by adding the remainder of the frames.