Chapter 3 Study Guide - TateScience2ndSemester
advertisement

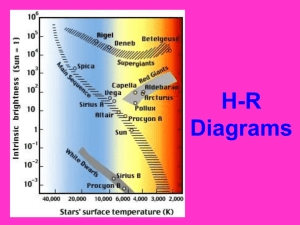
Falcon/Seahawk Section 3 1. Orbit-the path of an object as it revolves around another object in space. 2. Force-a push or pull motion 3. Gravity-a force that attracts all objects toward each other. 4. Law of Universal Gravitation-every object in the universe attracts every other object. 5. MASS of an object determines the force of gravity 6. Mass- the amount of matter in an object 7. Weight- the measure of the force of gravity on an object 8. Inertia-the tendency of an object to resist motion. 9. The more mass an object has the greater the gravity 10. Newton’s First Law of Motion-an object at rest will stay at rest & an object in motion will stay in motion with a constant speed UNLESS acted on by a force. 11.Gravity and Inertia keep objects in motion. 12. Mutual gravity caused these rocks to come together, eventually to form planets, & keeps them in close proximity to each other and not “fly” away. 13. Accretion- This 'coming together' of material is a process known as accretion. Section 4 1. Stars are classified by by a) Color, b) Temperature, c) Size, d) Composition and e) Brightness. 2. The color of a star reveals it’s Surface Temperature. 3. Cool stars are Red - 3,200 C. 4. The hottest stars are Blue – 20,000 C. 5. Large stars are Giant or Super Giant Stars. Those Earth-size are White Dwarfs, and those smaller are Neutron stars. 6. Stars are composed of 73% hydrogen, 25% helium, and 2 % other elements. 7. Spectograph- a device that breaks light into colors & produces an image of the resulting spectrum. 8. The brightness of a star depends on both its size and temperature. 9. Apparent brightness/magnitude – is the brightness of a star as seen from Earth. (the sun seems brighter b/c it’s closer) 10. Absolute brightness/Luminosity – is the brightness of a star if it were at a standard distance from Earth; it is a more accurate reading. 11. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is a chart that compares temperature and absolute brightness of stars are related. X-axis is temperature, and Y-axis is the absolute brightness. 12. H-R diagram is really a chart on which stars are graphed based on temp & absolute brightness. Astronomers use it to CLASSIFY stars & see how they change over time. 13. Main Sequence – a diagonal line, where 90% of all stars lie on the H-R diagram; the sun is one. 14. What % of stars are main sequence stars? 90% On the H-R diagram, the hot stars are located on the left side, while the cool are located on the right. 15. The bright stars are on the near the top of the HR, while the dimmer stars are at the bottom. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram The Hot are to the Top of the chart. The hot stars are to the Left side. The Cooler are to the Bottom of the chart. The cooler stars are to the Right side.