End of Year * Science Study Guide
advertisement

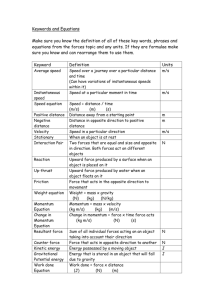
End of Year – Science Study Guide Forces and Motion Forces and Motion • Force – a push or a pull on an object • Mass – the amount of matter that makes up an object • Matter – anything that has mass and takes up space Balanced/Unbalanced Balanced Forces – forces acting on an object are equal in size and opposite in direction (cancel each other out) Examples : • Holding a book in midair (balanced because book doesn’t fall and you’re not lifting it) • Pushing against a wall (the wall doesn’t push you over and you don’t push it over) Unbalanced Forces – forces that are not equal Example: • During a tug of war competition, one team pulls the other team over the line (one team pulled with more force) Inertia – Newton’s Law of Motion An object at rest An object in motion Stays at rest Stays in motion Until another force is applied A heavier object is: more difficult to get in motion and more difficult to slow down A force must be applied to: make an object speed up or slow down An increase in speed leads to: an increase in momentum Gravity • A force that pulls objects toward each other (i.e. gravity pulls you toward Earth) • The heavier an object…. The greater its pull of gravity (the faster it will fall) • If mass increases…. The force of gravity will be greater on the object • If distance increases… the force of gravity acting on two objects is less than if they were closer together. Friction • A force that acts between surfaces that touch each other. • The smoother the surface… the less friction there will be between the objects (moves much quicker/harder to slow down) • Examples of a smooth surface: ice, tile floor • The rougher the surface… the more friction there will be between the objects (moves slower/easier to slow down) • Examples of a rough surface: road, carpet Magnetism • The force of pushing or pulling between magnetic poles. • Like poles… a repulsive force exists and magnets move away from each other • Opposite poles… an attractive force exists and the magnets move toward each other • The closer the objects… the greater the magnetic force will be (strongest at the poles of magnets) Vocabulary • Air Resistance – friction between a moving object and air particles; acts against the pull of gravity to slow a moving object (parachute) • Position – the location of an object • Motion - a change in an object’s position Speed Speed = distance/time Speed of a ball thrown in the air: • Rising – ball slows down as it rises higher and higher until it stops • Falling – ball goes from stopped position and speeds up more and more as it falls to the ground Momentum # # # # # # # # # Constant Speed # # # # # # # # # # ### Slowing Down Losing Momentum ### # # # # # # # # # # Speeding Up Gaining Momentum • Increase in Momentum = increase in speed