5th Edition
PPT 8-1
Chapter 8
Site Location
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
PPT
8-2
Levy/Weitz:
Retailing Management, 5/e
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Three Levels of Analysis
PPT 8-3
Trade Area Issues
• Which Trade Areas Are Most Attractive for
Locating Retail Outlets?
• How Many Outlets to Locate in a Trade Area?
– More Stores Increases Economies of Scale and
Reduces Costs
– More Stores also Results in More Cannibalization
and Less Sales per Store
PPT 8-4
Factors Affecting Demand
for a Region or Trade Area
PPT 8-5
Factors Affecting the
Attractiveness of a Site
• How Attractive Is the Site to the Retailer’s
Target Market?
– Match Between Trade Area Demographics and
Retailer’s Target Market
– Likelihood of Customers Coming to Location
• Convenience
• Other Attractive Retailers At Location
Principle of cumulative attraction - a cluster of similar
and complementary retailing activities will have greater
drawing power.
PPT 8-6
Convenience of Going to Site
Accessibility
• Road pattern and condition
• Natural and artificial barriers
• Visibility
• Traffic flow
• Parking
• Congestion
• Ingress/egress
PPT 8-7
Location Within a Center
• In High Traffic Areas
•Near Anchor
•Center of Shopping Area
• Near Stores Selling Complementary
Merchandise
•Clustering Specialty Stores Appealing to
Teenagers
• Better locations cost more
PPT 8-8
Map of Dallas’ North Park Center
PPT 8-9
Estimating Demand for a New Location
• Definition of the Trade Area
– Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Zones
• Approaches for Estimating Demand
– Analog Approach
– Regression Approach
– Huff Gravity Model
PPT 8-10
Trade Area
Primary zone - 60 to 65 percent of its customers
Secondary zone - 20 percent of a store’s sales
Tertiary zone - customers who occasionally shop
at the store or shopping center
PPT 8-11
Factors Defining Trade Areas
•Accessibility
•Natural & Physical Barriers
•Type of Shopping Area
•Type of Store
•Competition
•Parasite Stores
PPT 8-12
Oblong Trade Area Caused by
Major Highways and Natural Boundaries
PPT 8-13
Sources of Information
• Customer Spotting
• Census Data
• Geodemographic Information
Systems
– ACORN
• Information on Competition
– Yellow Pages
PPT 8-14
Customer Spotting
Purpose: to spot, or locate, the residences of
customers for a store or shopping center.
How to obtain data:
• credit card or checks
• customer loyalty programs
• manually as part of the checkout process
• automobile license plates
PPT 8-15
Selecting a Target Market
• Home Page
Is the introductory or first material viewers see
when they access a retailer’s Internet site. It is the
equivalent to a retailer’s store-front in the physical
world.
• Virtual Store
Is the collection of all the pages of information on
the retailer’s Internet site.
• Ease of Access
PPT 8-16
Target Market
• The Limited has a welldefined target market: the
moderate-income, careeroriented woman who is
fashion conscious.
– How does this influence
location decisions?
PPT 8-17
Identifying a Target Market
• Market segment should be measurable.
• Market should be accessible.
• Market should be substantial enough to be
profitable.
PPT 8-18
Location of Store-Based Retailers
• Anchor Stores are the stores in a
shopping center that are the most
the most dominant and are
expected to draw customers to
the shopping center.
• Free-Standing Retailer generally
locates along major traffic arteries
and does not have any adjacent
retailers to share traffic with.
PPT 8-19
Retail Location Theories
• Retail Gravity Theory
Suggests that there are underlying
consistencies in shopping behavior that yield to
mathematical analysis and prediction based on
the notion or concept of gravity.
PPT 8-20
Typical Size & Trading Area of Shopping Centers
LO 2
Type of Shopping
Center
Neighborhood
Gross Leasable
Square Feet
30,000 to 150,000
Primary Trade Area
3 Miles
PPT 8-21
Typical Size & Trading Area of Shopping Centers
LO 2
Type of Shopping
Center
Community
Gross Leasable
Square Feet
100,000 to 350,000
Primary Trade Area
3-6 Miles
PPT 8-22
Typical Size & Trading Area of Shopping Centers
LO 2
Type of Shopping
Center
Regional
Gross Leasable
Square Feet
400,000 to 800,000
Primary Trade Area
5-15 Miles
PPT 8-23
Typical Size & Trading Area of Shopping Centers
LO 2
Type of Shopping
Center
Super-Regional
Gross Leasable
Square Feet
800,000
Primary Trade Area
5-25 Miles
PPT 8-24
ID and Geographic Segments
• www.claritas.com
– http://cluster1.claritas.com/claritas/Default.jsp
– Free stuff
• Similar people share similar traits
– Tend to live together
PPT 8-25
Geographic Information Systems
• Geographic Information System (GIS) - a
computerized system that combines physical
geography with cultural geography.
• Thematic maps are generated
• Color coded
• Culture – a set of shared values and behaviors
held in common by an identifiable group of people.
• Culture can create barriers.
PPT 8-26
GIS Components
Cultural Geography
Physical Geography
Latitude/Longitude
Land/Water
Terrain
Rainfall/Snow
Temperature
Data
Inputs
GIS
(Data Aggregation and
Analysis via Computer)
Output
Maps and Other
Displays of Information
PPT 8-27
Demographics
Manmade Structures
Consumption Patterns
Work Patterns
Leisure Behavior
Deviant Behavior
Uses of GIS
• Market selection.
• Site analysis.
• Trade area definition.
• New store cannibalization.
• Advertising management.
• Merchandise management.
• Evaluation of store managers.
PPT 8-28
Process for Selecting a Retail Location
LO 3: Exhibit 7.5
Identify the most attractive
markets in which to operate
Identify the most attractive
sites that are available
within each market
Select the best site(s)
available
PPT 8-29
Customer Spotting Map for a Supermarket
LO 5: Exhibit 7.8
City Limits
Store
2 miles from
store
PPT 8-30
4 miles from
store
3 miles from
store
1 mile from
store
Store Density and Site Availability Map
LO 5: Exhibit 7.11
PPT 8-31
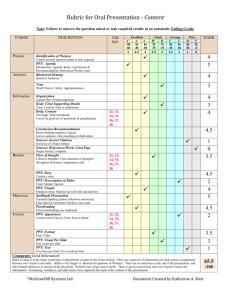
Checklist for Site Evaluations
•Local Demographics
•Population and/or household base
•Population growth potential
•Lifestyles of consumers
•Income potential
•Age makeup
•Population of nearby special markets, that is,
daytime workers, students, and tourists, if
applicable
•Occupation mix
PPT 8-32
Checklist for Site Evaluations
•Traffic Flow and Accessibility
•Number and type of vehicles passing location
•Access of vehicles to location
•Number and type of pedestrians passing location
•Availability of mass transit, if applicable
•Accessibility of major highway artery
•Quality of access streets
•Level of street congestion
•Presence of physical barriers that affect trade area
shape
PPT 8-33
Checklist for Site Evaluations
•Cost Factors
•Terms of lease/rent agreement
•Basic rent payments
•Length of lease
•Local taxes
•Operations and maintenance cost
•Restrictive clauses in lease
•Membership in local merchants association required
•Voluntary regulations by local merchants
PPT 8-34
Nature of Site
• Store Compatibility Exists when two similar
retail businesses locate next to or nearby each
other and they realize a sales volume greater
than what they would have achieved if they
were located apart from each other.
PPT 8-35
Debate Points:
• The most important factor in determining where a
retailer is located is the place of residence of
consumers in the area.
• 4 Super Walmarts operate in Hatco, TX, with a
trade area of 125,000 people. 1 Super Target
store is also located there. Should a 5th Super
Walmart be added?
PPT 8-36