THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE MASS
MEDIA IN THE UNITED STATES
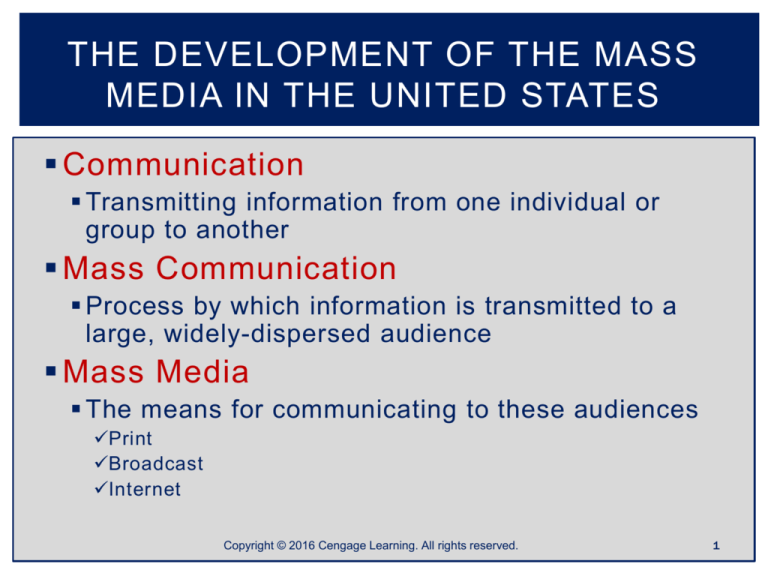
Communication
Transmitting information from one individual or
group to another
Mass Communication
Process by which information is transmitted to a
large, widely-dispersed audience
Mass Media
The means for communicating to these audiences
Print
Broadcast
Internet
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
1
THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE MASS
MEDIA IN THE UNITED STATES
Prominent mass media for political
content . . .
Newspapers
Magazines
Radio
Television
The Internet
Other media for political content . . .
Music
Movies
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
2
THE GROWTH OF BROADCAST
MEDIA SINCE 1920
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
3
THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE MASS
MEDIA IN THE UNITED STATES
Newspapers
First newspapers: financed by political parties
1830s: Independent ownership
1880s: Most large cities had many newspapers
1960s: Radio and television competition
Today: Circulation down but readership up (online)
Institute paywalls
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
4
THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE MASS
MEDIA IN THE UNITED STATES
Magazines
Can wield political power
Attentive policy elites
Two-step flow of communication
Circulation has declined
Time magazine biggest in U.S.
Political magazines
The National Review
The Weekly Standard
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
5
THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE MASS
MEDIA IN THE UNITED STATES
Radio
1920s: Continuous broadcasting began
NBC first radio network
Edward R. Murrow
Today: Nearly 15,000 licensed stations
Nine out of ten Americans listen to radio every week
Audience of talk radio more Republican
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
6
THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE MASS
MEDIA IN THE UNITED STATES
Television
1940s: 23 stations in U.S.
1951: first coast-to-coast broadcast
Harry Truman’s address at Japanese peace treaty conference
Kefauver’s coverage of organized crime investigation
2012: 1,300 commercial stations in U.S.
97% of households have television
Three large networks with large audiences
Millions of viewers moving to cable networks
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
7
WATCHING THE PRESIDENT
ON TELEVISION
This close-up of
John Kennedy
during a debate
with Richard Nixon
in the 1960
campaign showed
Kennedy to good
advantage. In
contrast, close-ups
of Nixon made him
look as though he
needed a shave.
MPI/Stringer/Archive Photos/Getty Images
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
8
Many people learn about
politics by watching
comedians like Jon Stewart,
the host of The Daily Show.
Almost 30 percent of adults
surveyed said that they
learned about the 2008
political campaign from
comedy shows like The
Daily Show, The Colbert
Report, or Saturday Night
Live.
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
AP Images/Jason DeCrow
LAUGH AND LEARN
9
THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE MASS
MEDIA IN THE UNITED STATES
Internet
1969: Began with ARPANET
Initially used for e-mail
1991: World Wide Web
Created by European physicists
Fifty websites in 1993
860 million websites today
Development of wireless technology
Smartphones and tablets
Blogs
?
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
Critical
Thinking
Question
10
PRIVATE OWNERSHIP
OF THE MEDIA
U.S. takes private ownership for granted
Chinese government employs Internet police
Some Western democracies’ print media privately
owned, broadcast media not
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
11
PRIVATE OWNERSHIP
OF THE MEDIA
The Consequences of Private Ownership
Private ownership results in . . .
More political freedom
Dependence on advertising revenues
Must appeal to audience
Newsworthiness
Market-driven journalism
Hook-and-hold approach of local television news
Major broadcasters part of huge conglomerates
Infotainment
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
12
DUCKING THE CENSORS
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
13
GETTING THE NEWS:
CONSIDER THE SOURCE
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
14
PRIVATE OWNERSHIP
OF THE MEDIA
The Concentration of Private Ownership
Trend toward concentrated ownership
NBC-Comcast merger
Increases risk of a few owners controlling news flow
Gannett chain owns over 80 daily newspapers
Suggested that newspapers operate as nonprofits
No major paper has done
Concentration of ownership not a problem in
television industry
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
15
GOVERNMENT REGULATION
OF THE MEDIA
Technical and Ownership Regulations
Federal Radio Act of 1927
Federal Communications Act of 1934
Created Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
FCC regulates interstate and international communications
FCC sets social, economic, and technical goals for industry
?
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
Critical
Thinking
Question
16
GOVERNMENT REGULATION
OF THE MEDIA
Technical and Ownership Regulations
Telecommunications Act of 1996
Relaxed ownership rules
Allowed phone companies to compete and sell TV services
FCC regulates Internet
No jurisdiction to regulate content
Emerging technologies, ownership issues, cross -platform content
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
17
GOVERNMENT REGULATION
OF THE MEDIA
Regulation of Content
First Amendment protects freedom of speech
U.S. has freest news media in world
FCC regulates content
Fairness Doctrine (repealed in 1987)
Equal Opportunities Rule
Reasonable Access Rule
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
18
FUNCTIONS OF THE MASS MEDIA
FOR THE POLITICAL SYSTEM
Four functions
Reporting the news
Interpreting the news
Setting the agenda for government action
Socializing citizens about politics
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
19
As press
conferences have
become more
formal and scripted,
they have also
become less
frequent. When
journalists and the
president had more
of a collegial
relationship, press
conferences were
common. With the
exception of Bill
Clinton, modern
presidents are
clustered at the
bottom of the
graph.
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
20
FUNCTIONS OF THE MASS MEDIA
FOR THE POLITICAL SYSTEM
Reporting the News
5,000 journalists in congressional press corps
Special access to president began in 1902
Theodore Roosevelt
Mediated through Office of Press Secretary
White House and Congressional news
News releases
Congressional reports
Social networking
C-SPAN coverage
News leaks
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
21
FUNCTIONS OF THE MASS MEDIA
FOR THE POLITICAL SYSTEM
Interpreting and Presenting the News
Gatekeepers
Horse race journalism
Media events
Where the Public Gets Its News
Until early 1960s: newspapers
Television dominant since 1960s
Radio
Internet
Social networks
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
22
FUNCTIONS OF THE MASS MEDIA
FOR THE POLITICAL SYSTEM
Media Influence on Knowledge and
Opinions
Television hypothesis
Soft news
Can improve levels of political knowledge
Can lead people to be more cynical about politics
Nine out of ten Americans believe media strongly
influence public opinion
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
23
FUNCTIONS OF THE MASS MEDIA
FOR THE POLITICAL SYSTEM
Setting the Political Agenda
Media’s greatest influence is on political agenda
Issues not on agenda will not get political attention
Media can force government to address issues
Some issues receive too much coverage
Crime
Politicians eager to influence media coverage
Media influences public opinion by defining “the news”
Going public
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
24
FUNCTIONS OF THE MASS MEDIA
FOR THE POLITICAL SYSTEM
Socializing the Citizenry
Young people acquire political values through
entertainment media
Criminal justice system portrayed differently on TV today
TV reinforces the hegemony of existing culture and order
Media plays contradictory roles
Promote popular support of government
Erode public confidence
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
25
Jason Reed/Reuters
OBAMA GOES ALL IN
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
26
EVALUATING THE MEDIA
IN GOVERNMENT
Is Reporting Biased?
News filtered through ideological bias of owners,
editors, and reporters
Citizens skeptical of news
News reports criticized for liberal bias
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
27
EVALUATING THE MEDIA
IN GOVERNMENT
Is Reporting Biased?
Newspapers tend to favor Republican candidates
Congressional incumbents receive more coverage
Bias depends on political party in power
Citizens act as editors to judge information
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
28
This graph
shows that
the public
increasingly
sees the
news media
as
inaccurate
and biased,
especially in
the past few
years.
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
29
EVALUATING THE MEDIA
IN GOVERNMENT
Contributions to Democracy
U.S. political communication goes from government
to citizens by going through media
Watchdog journalism
Media reports citizens’ reactions to political events
Media suggests courses of government action
Majoritarian model of democracy
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
30
EVALUATING THE MEDIA
IN GOVERNMENT
Effects on Freedom, Order and Equality
Media plays role in advancing equality
Civil Rights movement
Offers disadvantaged groups opportunity to state their case
Journalists resist government infringement on
freedom of press to promote order
Sensational journalism
Weakens public trust
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
31
SOCIAL MEDIA AND CONGRESS
Click picture to view video
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
32
VIDEO DISCUSSION QUESTIONS
1. What is your major source of political
information? Do you follow any political
figures on social networking sites?
2. Why do members of Congress use social
media to communicate with voters instead of
relying on traditional media?
3. Is the traditional press conference still
effective? What are its advantages and
disadvantages?
Copyright © 2016 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
33





