What are 2 motions of the Earth?
advertisement

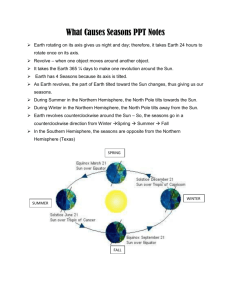
Aim: What is evidence of the 2 motions of the Earth? Do Now: What are 2 motions of the Earth? Homework: Study for Midterm January 28, 2008 What are the two motions of the earth? How long does it take the earth to rotate? Rotation & Revolution 24 hours (one day) to rotate (spin) once on its axis How long does 365 ¼ Days (one year) to complete one revolution it take the earth to revolve around the sun around the sun? What does the earth’s rotation cause? Day & Night As the earth rotates (counter-clockwise), part of it faces the sun and the rest of it faces away from the sun and is in darkness. Why does the length of the day change throughout the year? Due to the tilt of the earth’s axis (23.5° angle) Example: When the North Pole is tilted toward the sun, the Northern Hemisphere has longer days and shorter nights = SUMMER Where does the north pole of the earth always point? Towards Polaris (A.K.A. The North Star) Where does the sun and moon appear to rise and set? •The sun, moon, & stars all appear to rise in the East and set in the West •Due to the counter-clockwise rotation of the Earth How does the rotation of the earth affect the motion of the winds & ocean currents? Northern Hemisphere: Southern Hemisphere: The Earth rotates Counterclockwise The Earth rotates Clockwise. Causing: winds and ocean currents to be deflected to the Right. Causing: winds and ocean currents to be deflected to the Left. What is the deflection (of winds & water) at Earth’s surface called? Observe an animation of the Coriolis effect over Earth's surface. The Coriolis Effect. Yahoo! Video Detail for coriolis.avi What evidence 1) Coriolis Effect shows that the 2) Satellite Pictures earth rotates? 3) Pictures from the earth of the night sky would show arcs of light, or star trails, from the motions of the earth. What evidence 1) Constellations (patterns shows that the of stars) appear to move earth revolves Observing the Sky: Motion of the Sun and Stars - The Night Sky around the 2) The Sun appears to be larger sun? during the winter months and smaller as summer approaches. • Perihelion – earth closest to the sun •Aphelion – earth furthest away from the sun LET’S REVIEW… • Why do we have day and night on earth? • If the earth’s axis was not tilted every where on earth would have how many hours of daylight and darkness? • Why does the sun appear to rise in the east and set in the west? • What would happen if the earth did not rotate? Summary… • What is the Coriolis Effect? • How do we know that the Earth rotates? • Which motion of the earth causes day and night? • How do we know the earth revolves around the sun? Aim: Why do we have seasons? Do Now: How does the rotation of the earth affect winds in the Northern Hemisphere? Homework: Big 8 Review Book pgs 57-64 & Review Sheet (Study for next Friday’s Midterm) 2/2 What causes summer? The hemisphere that is tilted toward the sun gets: 1. more hours of sunlight & 2. more direct sun The combination of more direct sunlight & longer days causes the Earth’s surface and atmosphere to receive more heat from the sun. Summer and winter are not affected by the Earth’s distance from the sun. Which day of the year gives us the most sunlight? Summer: a) Begins in the Northern Hemisphere on June 21 b) Called the Summer Solstice “Sun Stop” c) The most sunlight is received on this day d) Length of daylight varies depending on your distance from the equator Which day of the Winter: year is the a) Begins in the Northern shortest? Hemisphere on Dec 21st b) Called the Winter Solstice c) The day of the year when the Northern Hemisphere gets the least amount of sunlight What is an a) 2 days of the year the sun shines directly overhead on equinox? the equator: Spring equinox is March, 21st & Fall equinox is September, 23rd b) During this time all places on earth have 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness. If it is summer in the northern hemisphere, what season is it in the southern hemisphere? The Northern and Southern hemispheres have opposite seasons. Earth: What causes the Seasons? SUMMARY • During the year when is the earth closer to the sun? • Why do we have seasons on earth? • If the North Pole is having summer, what season is the South Pole having? Aim: How can we explain time zones on Earth? Do Now: What causes the seasons on earth? Homework: Handout (17-4) What are the time zones? The earth is divided into 24 time zones (called standard time) WHY 24? USA has 4 time zones: 1. EASTERN STANDARD TIME 2. CENTRAL STANDARD TIME 3. MOUNTAIN STANDARD TIME 4. PACIFIC STANDARD TIME As you move west the time in each zone is one hour earlier than in the previous zone. What is the international date line? The boundary formed where the 1st and 24th time zones meet What happens when you cross the International Date Line? How could you travel back in time? Pacific 7 pm Mountain Central 8 pm 9 pm Eastern 10 pm Practice Problem You board a 6 PM flight from New York’s JFK Airport headed to Los Angeles’ LAX in California. The expected flight time is 5 hours. Predict the time your plane will land and explain why you chose that time. Why are some time zones crooked? Time Zones NASA Math News Summary • Why do we have 24 time zones? • What happens when you cross the International Date Line? • How could you travel back in time? • Why are some time zones crooked? • In your own words, explain what time zones are.