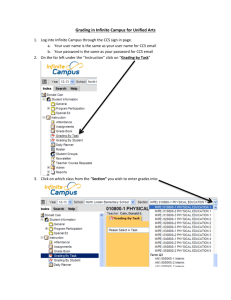
Presentation

What Do We Know About the
Compliance Costs of the Tax System?
Arindam Das-Gupta
Outline
The cost of collecting taxes
What are compliance costs (CCs)?
Why do CCs matter?
CCs: International evidence
Recent estimates for India
Determinants of CCs
How to reduce CCs?
How to estimate CCs?
The cost of collecting taxes
Include “welfare costs, opportunity costs, psychic costs, social costs and so on” (Evans and Walpole, 1997)
Costs of taxation (Yitzhaki-Slemrod).
– Excess burden of taxes
– Excess burden of tax evasion
– Tax administration costs (substitute)
– CCs and avoidance costs.
What are CCs?
Citizen’s costs of meeting tax obligations
Excludes actual taxes paid and excess burdens.
Includes avoidance (“tax planning”) and evasion costs.
Includes costs if taxpayers, non-filers, third parties (banks, tax withholders, helping others)
Components:
What are CCs? - 2
EG: Personal Income Tax Compliance Cost Components
Included in Study
Tax Compliance Costs
Category
Time spent
Taxpayers Non-filers Third Parties
Yes
Yes
Indirect estimate
Yes
Yes Direct money costs
(includes fees to tax advisors)
Bribes paid
Psychic costs
Yes
Yes
No
No
Note: Other social costs of the personal income tax
- Costs of the tax department plus part of costs of courts,
police, legislators, audit, etc.
- Excess burden of the tax and tax evasion.
Types of CCs
Mandatory versus voluntary…
...and quasi-voluntary costs
In-house versus external
Gross versus net
– Cash flow benefits
– Tax deductibility
Private versus social
– Bribes
– Tax deductibility
OVERALL versus from SPECIFIC provisions or procedures
Administration costs versus CCs
Substitutes
Other things equal, social cost considerations should dictate the choice between compliance requirements and administration responsibilities
– EG: Official versus self-assessment
Other things may not be equal…
– Documents enclosed with tax returns
– Desk versus field audits
Why look at CCs?
Three of Adam Smith’s canons of taxation relate to CCs: ‘Certainty’, ‘Convenience’, and ‘Economy’.
Policy uncertainty and complexity lead to higher CCs
Raises the effective tax rate… without any revenue benefits
Induces non-compliance and raises administration costs
CC Assessments now mandatory in some countries
International evidence: Individual income tax
Country
(percentages of tax revenue)
Year Individuals Employers Other
Private
Australia 1994-
95
Canada 1986
1984 Fed Rep of
Germany
Israel 1987
7.9
2.53
0.75
1.32
3.57 0.03
Admin Total
1.00
2.35
7.13
Netherlands 1989
New
Zealand
Norway
1992
1988
Sweden 1990-
91
1.4
8.1
2.7
0.88 0.11 0.17
1.0
1.7
0.65
9.1
4.4
1.81
United
Kingdom
U.S.A.
1986-
87
1995
2.21
9.0
1.02 0.17 1.53 4.93
International evidence: Business income taxes
Country
Australia percentages of tax revenue of relevant tax
Year Corporation tax/ Income tax
PAYE Other business taxes
1994-95 6.8
17.1 (S)
1.3
2.5 (S)
8.0
11.9 (S)
Canada
Hong Kong
Israel
Malaysia
Netherlands
1994-6
1987
1987
1994 c. 1994
New Zealand 1989-90
Norway 1987
Sweden 1993
UK 1996
USA
USA
RANGE
2000
1992
---
4.6-4.9
1.5
2.2
0.36
4.0
8.8
1.7
2.2
1.3
0.34
1.9
26.9-28.0
3.2
0.36-28.0 0.34-1.9
6.3
2.6
3.7
2.6-8.0
Estimates for India - Individual IT
Aggregate Costs of Collecting the Individual Income Tax:
Compliance and Administrative Costs
(Percentages of Individual Income Tax Collected in 2000-01)
Total Compliance Cost of Taxpayers (excluding psychic costs and litigation costs)
of which Legal Compliance Cost
Add estimated cost of representation in appeals cases
Non-filer costs (Chattopadhyay and Das-Gupta, 2002)
Cost of collecting taxes through banks
Cost of tax deduction at source
Total taxpayer and third party compliance costs
Government cost of collecting taxes – Income Tax Department
Government cost of collecting taxes – Other (ITAT, Settlement Commission, etc.)
Total direct cost of collecting personal income taxes
Total cost less bribes (transfer between individuals)
49.01
46.61
0.25
3.40
1.15
5.68
59.49
2.40
0.09
61.98
59.58
Estimates for India - Individual IT - 2
Legal compliance costs as a percentage of gross income
8
6
4
2
0
16
14
12
10
Rs 50,000 or less
Rs 50-100 thousand
Rs 100-200 thousand
Rs 200-300 thousand
Rs 300-400 thousand
Rs 4,00,000 and above
Non-Salaried Salaried
Estimates for India - Corporation IT
Summary of Findings on the Income Tax Compliance Cost of Indian Companies (2000-01)
Compliance Cost Measure
Legal compliance costs - LCC
Sample Averages
Highly variable. 4.12% of profit before tax, 30.41% of tax paid
Projection for All
Companies
4.33% to 13.18% of tax paid
Size Distribution
Opportunity cost of delayed refunds
(ODR)
Cash flow benefits from advance tax and TDS (C)
Regressive for all measures --
46% of taxes. 2.11% of tax paid
Over 50% of LCC --
Net compliance costs = LCC – C - cash flow benefits – tax deduction of compliance expenditure
"Social" compliance costs = LCC + social ODR
"Social" operating costs = "Social" compliance costs + admin costs
15% of legal compliance costs. Negative for most large firms.
--
--
Minus 0.72% to plus
0.62% of tax paid
5.61% to 14.46% of tax paid
5.92% to 14.77% of tax paid
Features of individual CCs in India
Time costs : Non-salaried: 88 hours; Salaried: 28 hours; plus
3-4 hours helping others.
– Approx. 11 hours (USA); 27 hours (NZ)
– “Conservatively” valued in cost estimates
Monetary costs : Even if time compliance costs are excluded monetary compliance costs are large compared to other studies
– Median % of tax paid: 52% (non-sal); 1.6% (salaried)
Advisor’s are used more to deal with tax uncertainty and administrative procedures rather than tax planning.
Incidence of bribe payment and bribe quantum are high, especially so for non-salary earners.
– Refunds, clearances and permissions
Harassment of assessees is widespread.
– Delayed refunds, PAN cards
Features of company CCs in India
62% benefit from compliance requirements: income statements & balance sheets are better prepared.
50% find audit requirements helpful in detecting dishonesty.
Scrutiny assessment and accounting requirements are major cost items.
70%, especially small companies use external assistance.
External costs: 39%.
Voluntary costs: 19% to 43% of gross CCs
Typical company has 12 to 14 open assessment years.
– 10 to 11 assessment years locked in disputes.
– Each extra disputed year raises legal compliance costs by 5.7%
CCs and indicators of company size
Book Value of Assets (Log Scale)
Tax Paid Index (Log Scale)
“Hot spots”
Legal requirements
– Audit requirements
– Tax deduction at source
– International tax provisions
– Loss carry forward and set off
– Valuation of perquisites to employees
– Others:export concession claims; non-resident withholding; inconsistencies with Companies
Act, depreciation provisions, free trade zone reporting; Minimum
Alternate Tax
Administrative procedures
– Refunds
– Scrutiny assessment procedures
– Accounting for TDS
– Appeals and litigation
– Completion and filing corporation tax return
– Obtaining IT clearances and approvals
How to reduce CCs? Framework
Overall CCs only show if broad tax reform is needed
CCAs of specific administration procedures or legal provisions can suggest specific reforms
MECF framework
MECF
M arg inal
NET excess m arg burden inal
revenue
CCs
M arg inal
M govt .
arg inal exp .
exp .
benefit
•
Applied in Poapongsakorn et. al. to taxpayer surveys
How to reduce CCs of the individual IT?
Tax policy process reform to reduce instability and uncertainty
Tax structure simplification
– More presumptions?
Simpler administrative procedures
– Improved taxpayer services
Institutional reform of tax administration
If this does not reduce compliance costs…abolish Individual IT?
Reducing corporation tax CCs
Net private CCs can be reduced, on average, to zero, if refunds delays and associated corruption are tackled
– Strengthen penalties for IT officials
– Institutional reform as for Individual IT
Reduce complexity and ambiguity of tax law.
Reform procedures for international transactions
Streamline clearances and permissions.
Streamline dispute resolution
Alleged bribe taking by appellate authorities to give favourable judgments?
How to estimate CCs and their impact?
Questionnaires/interviews needed
Questionnaires cannot be long
So clarity about objective crucial
– Overall CCs - interesting but not so useful?
– Impact of recent reform?
– Tax reform or administrative reform?
– Specific provisions and procedures?
CCAs for specific items most promising
How to estimate CCs and their impact? -2
Taxpayer (individual, or business) sample
– Random sample of taxpayers
– Use (short!) questionnaires for taxpayers
– PRETEST PRETEST PRETEST 2-3 versions for clarity and length…and focus groups
– 3 questionnaires:
• Canvassed/mailed with no evasion or bribe questions
• Anonymous mailing for non-compliance and bribes with a few extra questions to match samples
• Canvassed “bridge” questionnaires
Canvassed/mailed questionnaires from a sample of third parties
Tax practitioners sample on costs and activities
Data from tax administration on enforcement, detected non-compliance and disputes if needed