L.16.13 Human Reproductive System
advertisement

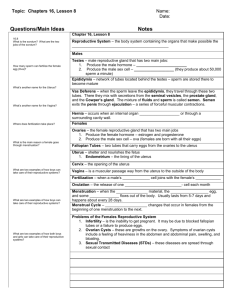
Human Reproductive System SC.912.L.16.13 Describe the basic anatomy and physiology of the human reproductive system. Describe the process of human development from fertilization to birth and major changes that occur in each trimester of pregnancy. What do I need to know? how the following structures function in the female reproductive system: ovaries, oviduct (fallopian tube), uterus, cervix, and vagina. how the following structures function in the male reproductive system: testes, scrotum, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle, prostate gland, urethra, and penis. summarize the major changes that occur during each trimester of human development Female Reproductive System OVARIES 1. The ovaries produce the female gonads, or eggs. 2. Ovaries also produce estrogen which maintains secondary sexual characteristics. Female Reproductive System FALLOPIAN TUBES 1. The fallopian tubes (also known as the oviducts) allow passage of the egg from the ovary to the uterus. 2. This is where fertilization occurs. Female Reproductive System UTERUS 1. The uterus is a hollow, pear-shaped organ where implantation of the blastocyst and fetal development takes place. 2. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to the fallopian tubes. Female Reproductive System CERVIX 1. The cervix is the lower, narrow portion of the uterus where it joins with the top end of the vagina. 2. The cervix has an opening to allow sperm and menstrual fluid to move through. Female Reproductive System VAGINA 1. The vagina is a hollow muscular organ that joins the cervix to the outside of the body. 2. The vaginal walls are lined in a mucus membrane for protection and to keep it moist. 3. Receives sperm Male Reproductive System TESTES 1. The testes produce the male gametes, or sperm. 2. Testes also produce testosterone which maintains secondary sexual characteristics. Male Reproductive System SCROTUM 1. The scrotum is a pouch-like structure that hangs behind the penis. 2. It holds and protects the testes. 3. It also contains numerous nerves and blood vessels. Male Reproductive System EPYDIDYMIS 1. The epididymis is a whitish mass of tightly coiled tubes cupped against the testicles. 2. It acts as a maturation and storage place for sperm before they pass into the vas deferens. Male Reproductive System VAS DEFERENS 1. The vas deferens, also known as the sperm duct, is a thin tube that starts from the epididymis to the urethra. 2. Allows sperm to travel out of the testicles. Male Reproductive System SEMINAL VESICLES 1. Seminal vesicles are sac-like structures attached to the vas deferens at one side of the bladder. 2. They produce a sticky, yellowish fluid that provides sperm cells with energy. Male Reproductive System PROSTATE GLAND 1. The prostate gland surrounds the ejaculatory ducts at the base of the urethra, just below the bladder. 2. Adds alkaline fluid to help in the production of semen. Male Reproductive System URETHRA 1. The urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of fluids from the body. 2. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine. Male Reproductive System PENIS 1. The penis is the male sex organ. 2. It releases the sperm from the body. What are the major milestones of the first trimester? 1. All organ systems begin to form (cell differentiation) 2. Nervous system begins forming (Neurulation) 3. Heart begins beating 4. Embryo begins to move 5. Ears, eyelids, and teeth buds are formed What are the major milestones of the second trimester? 1. Mostly growth 2. Fetal skeleton forms 3. Mother can feel the fetus moves 4. Fetus can now hear. 5. Hair forms on the body What are the major milestones of the third trimester? 1. Fetus turn into a head-down position. 2. Fat is deposited beneath the skin 3. A greasy substance forms on the fetus skin. 4. Lungs mature 5. Fetus can see light and react to sounds. Show What You Know A fertilized egg undergoes several stages before it is successfully implanted. The diagram below shows these stages as the fertilized egg travels through the female human reproductive system. In which of the following structures of the female human reproductive system is the blastocyst implanted during normal human development? A. ovary B. uterus C. vagina D. amniotic sac Show What You Know Which of the following correctly compares the functions of the vas deferens and the fallopian tubes? A. Sperm leaves the body through the vas deferens, and eggs leave the body through the fallopian tubes. B. Sperm travels through the vas deferens, and eggs travel through the fallopian tubes. C. The vas deferens produces sperm, and the fallopian tubes produce eggs. D. The vas deferens stores sperm and the fallopian tubes store eggs. Show What You Know Which of the following structures in the human female reproductive system is correctly matched with its function? A. ovary – site where fertilization takes place B. uterus – serves as storage for immature eggs C. oviduct – serves as the location for blastocyst implantation D. cervix – separates the bottom part of the uterus from the vagina and provides support for the developing fetus during the pregnancy Show What You Know Which of the following describes part of a baby's development in the second trimester of pregnancy? A. The fetus turns into a head-down position in the uterus. B. The fetus develops fat under the skin and practices breathing movements. C. The fetus is in the embryonic stage, and the amniotic sac forms. D. The fetus grows soft hair called lanugo over its skin and can swallow and hiccup. Show What You Know Which of the following pairs of male and female reproductive structures are most alike in their function? A. testes and ovaries B. prostate gland and vagina C. vas deferens and uterus D. seminal vesicle and oviduct