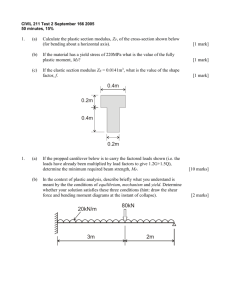
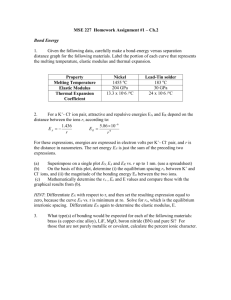
Heavy-Duty Truck Sytems Chapter 32
advertisement

Chapter 32 Vehicle Chassis Frame Objectives (1 of 2) • Describe the chassis frame of a heavy-duty truck. • Define the terms yield strength, section modulus (SM), and resist bend moment (RBM). • List the materials from which frame rails are made and describe the characteristics of each. • Explain the elements of frame construction. • Describe the different ways frame damage can occur as a result of impact and overloading. Objectives (2 of 2) • Perform some basic chassis frame alignment checks. • Describe the various categories of frame damage including diamond, twist, side-sway, sag, and bow. • Explain how the chassis frame, side rails, and cross-members can be repaired. • List some guidelines to follow when using frame repair hardware. • Outline some basic frame welding techniques. Frame C-channel Basic Frame Terms • • • • • • • Yield strength Section modulus Resist bend moment Area Applied moment Bending moment Safety factor Maximum Bending Moment Shop Talk • Two truck frames with identical RBM can perform very differently. • RBM is calculated by factoring section modulus with yield strength. – If two trucks have identical RBM but one is spec’d with a high section modulus but uses a lower yield strength material, it will be more rigid than a frame with high yield strength but low section modulus. Caution • Steel frame rails that appear to the eye similar can have drastically different yield strengths. • Always identify the frame material before attempting any repairs. Heat-treated Frame Caution Label Shop Talk • Although chassis frames are very strong, care must be taken when lifting or moving them, to avoid anything that may scratch, cut, or damage an exposed frame assembly. • Cushion all chain hoists or cable slings with a section of heavy hose. • If the frame rail is raised with a jack, place a block of wood between the jack and the frame rail. Frame Load Drilled Hole Placement Cutting and Welding Recommendations Shop Talk • The extreme front and extreme rear of a frame rail is subjected to less stress during normal operation than the sections in between. • A notable exception would be the stress to which the rear of the frame rails are subjected when a fully loaded dump box is raised on a dump truck. Caution • Previously when reassembling chassis components previously assembled with Huck fasteners, it is often unrealistic to install new Huck fasteners because of accessibility. • If you are replacing Huck fasteners with bolts, ensure that their hardness is consistent with the original fasteners. – This will usually, but not always, be equivalent to an SAE grade 8 fastener. Frame Construction • Two-element rail – Consists of the main frame rail and a single inside channel frame reinforcement • Three-element rail – Consists of the main frame rail and two frame reinforcements, a single inside channel, and a single outside channel frame reinforcement • Four-element rail – Consists of the main frame and three frame reinforcements, a single inside channel, a single outside channel, and a single inverted “L” outside frame reinforcement Fishplate and Reinforcement Guidelines Shop Talk • When any type of frame reinforcement is added, straight cut fishplates, L-sections, and C-channels should be avoided because this creates a sudden increase in section modulus. – This sudden increase in section modulus can cause frame failures immediately adjacent to the reinforced section. Caution • Additional reinforcement of the chassis frame to support additional loading or to concentrate a load, should not be made until it has been fully verified that all other vehicle components, such as the brake system, steering system, suspension system can properly and safely carry and support the increased loading. Shop Talk • Frame straightening should be performed only by a qualified frame alignment facility. – Because impact damaged frames are corrected by specialty technicians, this type of frame servicing is not covered in this book. Frame Damage • • • • Exceeding the gross vehicle weight rating Uneven load distribution Improper fifth wheel settings Using the vehicle for purposes for which it was not originally designed • The use of special equipment for which the frame was not designed • Improper modification of the frame Frame Damage Categories • • • • Diamond Twist Side-sway Sag and bow Frame Alignment • Projecting a frame diagram • Frame layout Repairs • Welding repairs Caution • A hardened steel frame weld that fails by cracking cleanly through the center of the weld profile often does so because the incorrect filler wire (electrode) has been used. • A weld that fails by cracking clean to the sides of the weld profile often does so due to crystallization caused by overheating. – Crystallization usually means that the welding procedure has been performed too rapidly. Repairs (1 of 7) Repairs (2 of 7) Repairs (3 of 7) Repairs (4 of 7) Repairs (5 of 7) Repairs (6 of 7) Repairs (7 of 7) Shop Talk • When cutting a frame, use a pencil or soapstone to make all lines, points, or other marks. • Try to avoid the use of a scriber or tool that will scratch the surface of the frame rail. • Use a machinist’s square to project all points from the webs to the upper flanges and to measure inboard from the outside face of the frame rails. Shop Talk • Cobalt high-speed drills are superior to conventional high-speed drills for drilling hardened frame rails. • Drills should be sharpened to give 150 degrees included angle with 7–15 degrees lip clearance. Drilling • A drill usually drills to a fractional oversize. The best method of drilling a frame rail is to use this method: – Drill pilot hole. – Drill to 1/8-inch under the nominal required hole size. – Taper ream to the exact nominal required hole size. Summary (1 of 6) • The chassis frame is the backbone of all heavy-duty trucks. • A truck frame is a dynamic component. – It is designed to flex when subjected to vehicle loading and road forces. – The extent to which it can flex defines the type of operation to which the truck is suited. • The frame supports the cab, hood, and powertrain components, along with the body and payload. Summary (2 of 6) • The two main components of a ladder-type frame are the two longitudinal members, which are generally referred to as rails. • Ultimate frame strength is measured for comparative purposes by resist bend moment (RBM). • RBM is factored by section modulus and yield strength. • Section modulus (SM) concerns the shape of frame beams. – High SM produces a more rigid frame. Low SM produces higher flexibility. Summary (3 of 6) • Hardened steel frame rails are formed from highstrength alloy steel, quenched and tempered (heattreated) to a minimum yield strength of 110,000 psi. • Low SM frames provide greater flexibility and therefore more ride forgiveness. High SM provides the kind of rigidity and twist-resistance required by a dump truck application. • Most frames are available with either inside or partial inside channel reinforcements or outside reinforcements. Summary (4 of 6) • Reinforcements are used to increase rigidity (section modulus) and provide a greater resist bend moment (RBM) than can be obtained by using a single mainframe rail. • Cross-members are designed to connect the frame rails. – They provide rigidity and strength, along with sufficient flexibility to withstand twisting and bending stresses encountered when operating on uneven terrain. Summary (5 of 6) • Attachments to the frame rails should be made to the frame rail web and never to the flanges, because stresses are highest in the flange areas that are subjected to tensional and compression loads. • The most common frame rail used on heavyduty trucks is the C-channel design. – Multiple frame rails can increase section modulus and RBM. Summary (6 of 6) • A bent frame can decrease the control a driver has over a vehicle during an emergency. • Frame damage can be generally categorized as diamond, twist, sidesway, sag, and bow. • Frame reinforcement can be either channel, fishplate, or L-sectioned; they should be of the same grade and thickness of steel and sudden changes in section modulus are to be avoided.